Intro to Gases Notesheet
advertisement

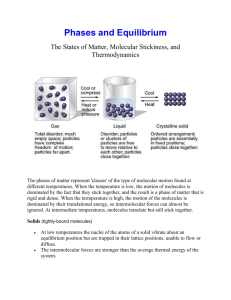
Ch. 11: Gases Name_______________________ Hr___ Introduction In this chapter we will focus on a study of gases. Using prior knowledge, draw a molecular view of a solid, a liquid, and a gas. Explain the amount of movement of the molecules at each state of matter on the lines below the boxes. Solid _________________ Liquid _________________ Gas __________________ Air is a mixture of gases. Approximately 78% of the air is composed of nitrogen gas. The next most abundant gas in the air is oxygen at about 21%. The remaining 1% of gases in the air include water vapor, argon, carbon dioxide, helium and hydrogen. Draw a molecular view of air. Be specific and label with key. How would your molecular view look if it was air on top of a very high mountain? In this chapter we will discuss relationships among the characteristics of gases such as pressure, volume, temperature and amount (number of moles) of a gas. Section 11.1 (Read pp. 341-344) ___________________ of air molecules generate pressure. Pressure depends on ___________ and _______. --Ballet dancer: flat feet vs. on toes OR tennis shoes vs. high heels A device that measures atmospheric pressure is a ___________________, invented by an Italian scientist named ________________________. *Draw a picture of this instrument. Give an example of a time when you experienced a change in atmospheric pressure: _______________________________________________________________________ **********At sea level, the average atmospheric pressure = __________mmHg*********** When a meteorologist says that there is a “low” approaching, it means the atmospheric pressure will ___________________________, often in conjunction with a _____________. A device called a _______________________ can be used to measure the pressure of an _________________ gas sample. Because instruments used for measuring pressure often contain mercury, the most common unit of measurement is ________________. Four other units of pressure are: _______________________________________________________________________. List 4 conversion factors (think factor-label method) that can be used to convert from one unit of pressure to another. (Use the "Units of Pressure" chart on pg. 344 or another resource) Using the factor-label method, solve the following problems: 1. Convert 785mmHg to atm. 2. Convert 0.975atm to torr.