File - 12 Ancient History
advertisement
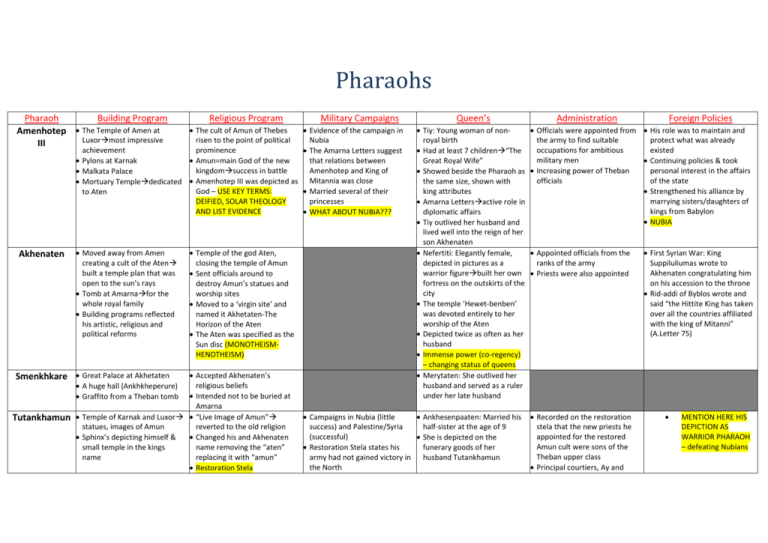
Pharaohs Pharaoh Building Program Amenhotep The Temple of Amen at Luxormost impressive III Religious Program The cult of Amun of Thebes risen to the point of political achievement prominence Pylons at Karnak Amun=main God of the new kingdomsuccess in battle Malkata Palace Mortuary Templededicated Amenhotep III was depicted as God – USE KEY TERMS: to Aten DEIFIED, SOLAR THEOLOGY AND LIST EVIDENCE Akhenaten Moved away from Amen creating a cult of the Aten built a temple plan that was open to the sun’s rays Tomb at Amarnafor the whole royal family Building programs reflected his artistic, religious and political reforms Smenkhkare Great Palace at Akhetaten Accepted Akhenaten’s religious beliefs Intended not to be buried at Amarna Temple of Karnak and Luxor “Live Image of Amun” statues, images of Amun reverted to the old religion Sphinx’s depicting himself & Changed his and Akhenaten small temple in the kings name removing the “aten” name replacing it with “amun” Restoration Stela A huge hall (Ankhkheperure) Graffito from a Theban tomb Tutankhamun Temple of the god Aten, closing the temple of Amun Sent officials around to destroy Amun’s statues and worship sites Moved to a ‘virgin site’ and named it Akhetaten-The Horizon of the Aten The Aten was specified as the Sun disc (MONOTHEISMHENOTHEISM) Military Campaigns Evidence of the campaign in Nubia The Amarna Letters suggest that relations between Amenhotep and King of Mitannia was close Married several of their princesses WHAT ABOUT NUBIA??? Queen’s Tiy: Young woman of nonroyal birth Had at least 7 children“The Great Royal Wife” Showed beside the Pharaoh as the same size, shown with king attributes Amarna Lettersactive role in diplomatic affairs Tiy outlived her husband and lived well into the reign of her son Akhenaten Nefertiti: Elegantly female, depicted in pictures as a warrior figurebuilt her own fortress on the outskirts of the city The temple ‘Hewet-benben’ was devoted entirely to her worship of the Aten Depicted twice as often as her husband Immense power (co-regency) – changing status of queens Merytaten: She outlived her husband and served as a ruler under her late husband Campaigns in Nubia (little Ankhesenpaaten: Married his success) and Palestine/Syria half-sister at the age of 9 (successful) She is depicted on the Restoration Stela states his funerary goods of her army had not gained victory in husband Tutankhamun the North Administration Foreign Policies Officials were appointed from His role was to maintain and the army to find suitable protect what was already occupations for ambitious existed military men Continuing policies & took Increasing power of Theban personal interest in the affairs officials of the state Strengthened his alliance by marrying sisters/daughters of kings from Babylon NUBIA Appointed officials from the ranks of the army Priests were also appointed Recorded on the restoration stela that the new priests he appointed for the restored Amun cult were sons of the Theban upper class Principal courtiers, Ay and First Syrian War: King Suppiluliumas wrote to Akhenaten congratulating him on his accession to the throne Rid-addi of Byblos wrote and said “the Hittite King has taken over all the countries affiliated with the king of Mitanni” (A.Letter 75) MENTION HERE HIS DEPICTION AS WARRIOR PHARAOH – defeating Nubians Ay Horemheb Ramesses I Seti I Tomb in the Western Valley of Followed the policy of Ankhesenamun the Kings Tutankhamunworship of Amun Mortuary Temple Rock-cut shrine Pylons at Karnak Attack on Atenism Syrian Campaign Mutnodjmet: Link back to the Horemheb’s religious policy Confrontation with the Hitties female royal blood line Commenced the Hypostyle was strictly orthodox Amun Possible peace treaty during Hall at Karnak cult was fully restored his reign Rock Temple at Gebel Repairing the temple of Amun depicting his battles Hypostyle hall at Karnak StelaSignifying his authority Temple built at Abydos Dedicated his buildings to Osiris, Isis and Ptah Ramesses II Built a new capital in Delta Close link to the Amen referring to him as his ‘father’ Honours other God’s not just Amen Elevates himself to the same level as the gods in his Abydos templeestablishment of a new dynasty Pharaohs regarded equal to all gods He claimed divine descent Additions to the Amun Temple from Amun His temple at Abu-Simbel was Several Temples in Nubia His work/inscriptions is mostly dedicated to Re-Horakhy and the adjacent temple built for self-praise Nefertari (wife) was dedicated The Mortuary temple was located at the western bank at to Hathor Foreign gods were recognised Thebes seen on the temples Horemhebacquired position of pharaoh after Tut’s death Left no heirs so the throne fell to Horemheb Overseer of building works in the Palace of Eternity Corruption among officials, The Edict of Horemheb: major reforms were Desired to remedy various undertaken by Horemheb excesses committed by servants of the state New judges and officials strict regulation of conduct Harsh punishments for those “The Edict of Horemheb” found guilty of corruption Led to an expedition to Palestine further evoked by Seti Active Military Program; Tuya: Political role writing to Warned officials against the Hittie KingPeace treaty interfering with the kings First Campaign: Palestine with Egype building projects, temples and acquired control, capturing estates. towns Had a sacred wedding Punishment for these offences Second Campaign: Launched a included the cutting off of campaign against Libyans noses and ears, lashes and Third Campaign: Attack on bodily wounds. The victims’ Kadeshconquer some families were also punished territory Fourth Campaign: Hitties Great Slaughter claiming northern Syria Fifth Campaign: Nubia Egypt had control and it was exploited for mining and trade First Syrian campaign Nefertari: played important religious and diplomatic roles Second (important)The in her husband’s reign. Hittites Depicted officiating jointly Third Battle of Kadesh, with him in religious violating the treaty set by his ceremonies on the walls of a father shrine at Gebel el Silsila. Ramesses II led the armyhe fell into an ambush set by the Exchanged greetings with Hittite queenpeace treaty Hittite kingnew treaty In his second campaign to Syria, he used his same strategy securing coastal towns before venturing inland Fights with Hittites in hand-tohand combat Hittite records mention a treaty at this time Peace was achieved with the Hittites after 200 years of fighting – THROUGH TREATY Ramesses II married a Hittite princess Moved the ancient Egyptian capital from southern Egypt to the Delta Shrine dedicated to Amun PER-RAMESSES (RAMESSEUM)












