Fall Semester 2007 Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

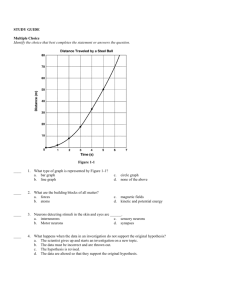
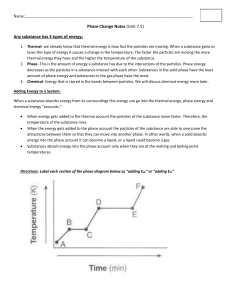
Fall Semester 2014 Advanced Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Ways to Study: Do NOT wait until the last minute to start studying. It is hard for even the best student to cram 7 chapters of information in one night! Study in chunks: 20-50 minute time periods followed by a brief break (5-10 minutes) Read the section reviews at the end of each chapter to review key concepts. Look over old quizzes, tests, labs, notes, and study guides. Quiz yourself using the practice questions at the end of each chapter. Make flash cards of definitions you are having trouble remembering. Unit One: Chemistry Matter Know basic properties used to identify matter What is density? How is it calculated? What does it have to do with floating? Compare and contrast physical and chemical properties of matter Define physical and chemical change What evidence can you have that a chemical change occurred (there are 5 common ways)? Compare and contrast exothermic and endothermic reactions Solids, Liquids, Gases When given a picture of the particles of a solid, liquid, and gas, be able to identify each one based on particle arrangement. How do the particles in solids, liquids, and gases move? How they are spaced? Which have a definite volume/shape? Describe the different gas laws (Boyle, Charles, Gay-Lussac). Changes in Phase Know the phase changes discussed in class: freezing, melting, evaporation, condensation, sublimation What happens to energy of the particles during each phase change? Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Be able to define and give key characteristics of elements, compounds, and mixtures Elements are composed of extremely small particles called ______________? What is the difference between a compound and a mixture? Be able to identify compounds and mixtures when shown a diagram of the two based upon how atoms are bonded together. Compare and contrast the components and properties of acids and bases. Describe solutions in terms of solute/solvent, conductivity, and concentration. Demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve. 1. Which substance is the most soluble at 25 degrees C? 2. Which two substances intersect at 67 degrees? 3. There is 120 grams of Potassium nitrate in water at 75 degrees. Is the solution saturated, supersaturated Elements and the Periodic Table Know how the definitions and how to find neutrons, atomic mass, atomic number, protons, and electrons. Know how to use the periodic table: o Where do you find elements with similar properties? o Where are the metals located on the table? o Where are the metalloids located on the table? Who created the first periodic table? How was the first periodic table of elements arranged? How is it currently organized? Be able to draw and read Bohr and Lewis Dot Models/Structures Know characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Chemical Bonds Compare and contrast Ionic and covalent bonds. Know how to name ionic and covalent bonds What is a cation/anion? What does a subscript stand for? A superscript? Know how to find oxidation numbers. What is a coefficient? How do you use them? Draw a Bohr model and Lewis dot structure for Neon. What is an isotope? Magnesium-23 Magnesium-25 -10 # of protons -12 # of protons 6 # of neutrons # of neutrons # of electrons # of electrons 6 Roman Numerals 1. What does a roman numeral represent in a compound? 2. Write the chemical formula for each of the following: Iron (III) oxide lead (IV) phosphide Copper (II) chloride Balance the equations below: 1) ____ N2 + ____ H2 → ____ NH3 2) ____ NaCl + ____ F2 → ____ NaF + ____ Cl2 3) ____ H2 + ____ O2 → ____ H2O 4) ____ P + ____O2 → ____P2O5 5) ____ Ag2O → ____ Ag + ____O2 6) ____ K + ____ MgBr → ____ KBr + ____ Mg Radiation: 1. Explain the difference between alpha, beta and gamma particles (include size, level of danger, what they can penetrate) 2. Explain half-life and radioactive decay 3. Be able to use the half-life equation. Unit 2: Energy and Heat Nuclear Energy: 1. Define Nuclear energy2. Know the difference between fission and fusion 3. Know pros and cons to using nuclear energy as an alternate energy source. Energy Energy is the ability to do ___________ or to produce change. What is kinetic energy? When is kinetic energy the greatest? What is potential energy? When is potential energy the greatest? Describe elastic PE. Give 3 examples of each of the forms of energy o Chemical Ex: battery, food, fire Thermal Ex: ___________________ o Nuclear Ex: _______________ Electromagnetic Ex: _____________ o Electrical Ex: ______________ Mechanical: Energy Conversions Change from one form of energy to another is called _________. Describe energy conversions between the 6 forms of energy Describe the law of conservation of energy Thermal Energy and Heat Temperature is the measure of the _________ ___________ energy of each particle within an object. Describe the temp of an object during a change in state. In what direction does heat move? Compare and contrast conductors/insulators Explain the difference between temperature, heat, and thermal energy o Temperature is the ___________ kinetic energy, while thermal energy is the __________ kinetic energy. List the 3 temperature scales. List the lowest temperature on each scale. What is the freezing/boiling point of water using the SI scale? How is heat transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation? Give an example for each. What is specific heat? If 200. grams of water is to be heated from 24.0°C to 100.0°C to make a cup of tea, how much heat must be added? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/kg∙°C The specific heat of wood is 1420 J/kg∙°C. How much heat is needed to convert 550. g of wood at 15.0°C to 10.0°C? What is the total amount of heat needed to change 2.25 kg of silver at 0.0°C to 200.0°C? The specific heat of silver is 240 J/kg∙°C