STAAR Study Guide Scientific Process
advertisement
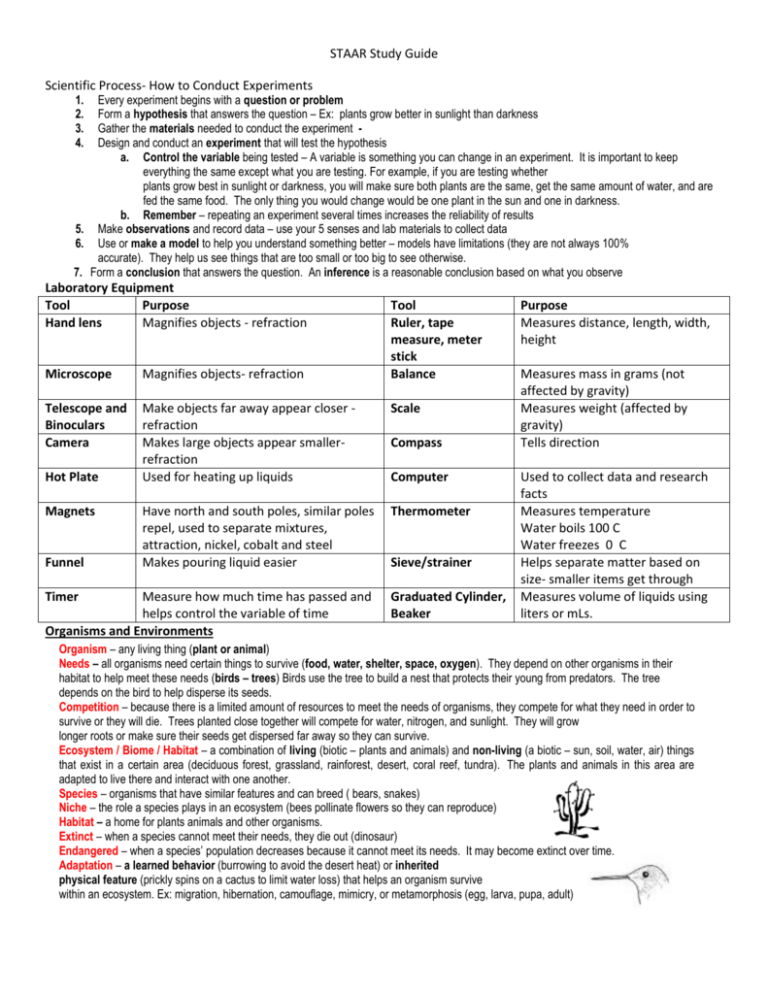
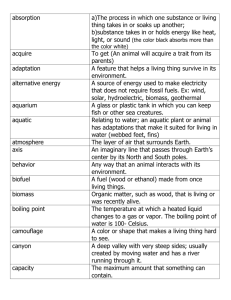
STAAR Study Guide Scientific Process- How to Conduct Experiments 1. 2. 3. 4. Every experiment begins with a question or problem Form a hypothesis that answers the question – Ex: plants grow better in sunlight than darkness Gather the materials needed to conduct the experiment Design and conduct an experiment that will test the hypothesis a. Control the variable being tested – A variable is something you can change in an experiment. It is important to keep everything the same except what you are testing. For example, if you are testing whether plants grow best in sunlight or darkness, you will make sure both plants are the same, get the same amount of water, and are fed the same food. The only thing you would change would be one plant in the sun and one in darkness. b. Remember – repeating an experiment several times increases the reliability of results 5. Make observations and record data – use your 5 senses and lab materials to collect data 6. Use or make a model to help you understand something better – models have limitations (they are not always 100% accurate). They help us see things that are too small or too big to see otherwise. 7. Form a conclusion that answers the question. An inference is a reasonable conclusion based on what you observe Laboratory Equipment Tool Purpose Hand lens Magnifies objects - refraction Tool Ruler, tape measure, meter stick Balance Microscope Magnifies objects- refraction Telescope and Binoculars Camera Make objects far away appear closer refraction Makes large objects appear smallerrefraction Used for heating up liquids Scale Have north and south poles, similar poles repel, used to separate mixtures, attraction, nickel, cobalt and steel Makes pouring liquid easier Thermometer Hot Plate Magnets Funnel Timer Measure how much time has passed and helps control the variable of time Organisms and Environments Compass Computer Sieve/strainer Graduated Cylinder, Beaker Purpose Measures distance, length, width, height Measures mass in grams (not affected by gravity) Measures weight (affected by gravity) Tells direction Used to collect data and research facts Measures temperature Water boils 100 C Water freezes 0 C Helps separate matter based on size- smaller items get through Measures volume of liquids using liters or mLs. Organism – any living thing (plant or animal) Needs – all organisms need certain things to survive (food, water, shelter, space, oxygen). They depend on other organisms in their habitat to help meet these needs (birds – trees) Birds use the tree to build a nest that protects their young from predators. The tree depends on the bird to help disperse its seeds. Competition – because there is a limited amount of resources to meet the needs of organisms, they compete for what they need in order to survive or they will die. Trees planted close together will compete for water, nitrogen, and sunlight. They will grow longer roots or make sure their seeds get dispersed far away so they can survive. Ecosystem / Biome / Habitat – a combination of living (biotic – plants and animals) and non-living (a biotic – sun, soil, water, air) things that exist in a certain area (deciduous forest, grassland, rainforest, desert, coral reef, tundra). The plants and animals in this area are adapted to live there and interact with one another. Species – organisms that have similar features and can breed ( bears, snakes) Niche – the role a species plays in an ecosystem (bees pollinate flowers so they can reproduce) Habitat – a home for plants animals and other organisms. Extinct – when a species cannot meet their needs, they die out (dinosaur) Endangered – when a species’ population decreases because it cannot meet its needs. It may become extinct over time. Adaptation – a learned behavior (burrowing to avoid the desert heat) or inherited physical feature (prickly spins on a cactus to limit water loss) that helps an organism survive within an ecosystem. Ex: migration, hibernation, camouflage, mimicry, or metamorphosis (egg, larva, pupa, adult) Purpose of Adaptation Getting food Protection Reproduction Water conservation Getting oxygen Examples • Eagles have sharp beaks that they use to tear apart small animals. • Female mosquitoes use their straw-like mouthparts to suck blood. • Rosebuds have thorns that help protect them from plant-eating animals. • When skunks are threatened, they can spray a bad-smelling liquid onto their enemies. • The seeds of coconut palm trees float on water and can be carried from one island to another by the ocean • The shells around bird eggs help protect their young until they are ready to hatch. • Lizards have scaly skin that prevents water loss. • Some plants have small leaves to prevent water loss. • Fish have gills that they use to take oxygen from the water in which they live. • A dolphin breathes air through a single nostril on top of its head when it comes to the ocean’s surface. Traits and Behaviors Traits – physical characteristics of an organism (color, height) Inherited Traits – characteristics passed down from parents to offspring (a flower’s petal color, eye color) can be dominant or recessive. The dominant trait usually shows up unless two recessive genes are passed to the offspring. Learned Traits – skills an organism can learn to do (seal balancing a ball on his nose) Roles of Organisms Predator – hunts other organisms for food (lion, shark) usually a carnivore Prey – organism that is hunted for food (zebra, rabbit, deer) Scavenger – gets food from dead and decaying animals (vulture) Producer – Plants that make their own food from sun, water, and CO2 Consumers – Animals that have to find food by eating other organisms (humans) Decomposers – get food from dead and decaying matter (bacteria and fungi) Food Chains Food Chain – the movement of energy (food) throughout an ecosystem when one organism eats another (arrow points to the animals that is taking the energy). Food chains always start with plants. Food Web - many food chains combined; arrows show how the energy moves from one organism to another. It shows how some animals compete for food. Plants All food chains start with plants (the sun gives energy to the plants). All organisms depend on plants. A plant starts as a seed, grows roots, sprouts, produces fruit, reproduces, and then dies. Part of Plant Roots Stems Leaves Animals Purpose Absorb water and nitrogen from soil, anchors plant in the ground Supports plants and allows nutrients to travel to rest of plant (grows with time – tree rings) Take in sunlight and carbon dioxide to make food (sugar), contain chlorophyll, gives off oxygen Animals take in oxygen given off by plants and use oxygen and sugar to make carbon dioxide that plants need. Some animals (frogs, butterflies, and other insects) change shape from baby to adult Metamorphosis Egg-Larva-Pupa-Adult Other animals give birth to babies that look similar to the adult (people, dogs) Metamorphosis Complete Stages Egg, Larva, Pupa, Adult (ELPA) Egg, Nymph, Adult Incomplete None Type of Animal Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Food Plants Meat (other animals) Plants and animals Example Butterfly, Frog, Most insects Grasshopper Humans, Dogs Example Rabbit, cow, Lion, snake, owl Bear, people Matter and Energy Matter – anything that has mass and takes up space; can be classified (grouped) based on properties (characteristics) Property Description Tool / Example Physical state Solid, Liquid or gas (changes when heat is added or removed) Magnetism Conduction Mass Weight Volume Density Attracted to a magnet Carries heat, electricity, sound How much matter is in an object (grams) Determined by the pull of gravity How much space an object takes up (liters) More dense – sinks in water / Less dense – floats in water (salt changes the density of water) Iron, nickel, cobalt, steel Metal – conducts / Plastic, paper, rubber - insulates Balance Scale Graduated Cylinder, Beaker Substances like water boil and freeze at different temperatures Boiling Point Change from liquid 100˚ C to gas Freezing Point 0˚ C Change from a liquid to a solid States of Matter State Example Solid Ice Liquid Water Gas Steam( water vapor) Energy (Molecule Movement) Very little- molecules packed tightly - vibrate Medium – molecules slip and slide - flow High – molecules move freely and rarely touch Shape Keeps its shape Takes shape of container Spreads out to fill entire space When an object gains energy (heat) the molecules begin to move faster. Mixtures and Solutions Mixture – two or more substances mixed together, but can be separated. Solution – when one substance gets dissolved into another substance. It looks the same throughout (salt in water or chocolate in milk) FORCE MOTION AND ENERGY Form Potential Kinetic Chemical Mechanical Description Stored energy – no motion taking place Energy in motion Energy created from chemical combinations Energy that moves objects Electrical Sound Energy that passes through a circuit Sound created from molecules vibrating. The more molecules, the better sound travels. Sound moves best through solids because the molecules are densely packed Example Book on a shelf, on top of a rollercoaster Falling book, rollercoaster moving Battery, food Bicycle, simple machines (lever, wedge, screw, wheel and axel, pulley, inclined plane, gears) Radio, hairdryer, TV Drum, wind chime, Light Bounces off objects so we can see them. Thermal Solar Energy from heat Energy from the sun (can be converted to electricity) Sun (heat and light), flashlight (chemical and light), campfire (heat and light) Toaster (electrical and thermal) Photovoltaic Cell (solar cell) Electricity Electricity – energy that travels through a circuit, and can be converted into other types of energy (heat - blow dryer, light - lamp or sound - radio) Circuit – a closed system that allows electricity to flow through it. Make up of a source (batter), path (wires), load/resistor (light bulb), and switch (turns on and off) Conductor – will allow heat and electricity to travel through it (metal) Insulator – will not allow heat or electricity pass through it (plastic, rubber, wood) Series circuit – there is only one path for the electrons to travel through, so if you remove one bulb, the others will go out. Parallel circuit – there is more than one path for the electrons to travel through, so if you remove one bulb, the others will still work – they will even get brighter. Battery – uses chemical energy to produce electricity Circuit Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Light In order to see an object, you must have light. Objects can either be transparent, translucent or opaque. Transparent All light passes through – light is refracted Glass, water, lenses Translucent Some light passes through – some light refracted, some reflected Tinted windows, sunglasses Opaque No light passes through – all light reflected Mirror, table, book, Light can either be reflected or refracted. Reflected Light bounces off the object (mirror) Refracted Light passes through the object, but is bent causing the image to look different (lens) Lens - a transparent object used to refract light (hand lens, microscope, telescope, and camera) Convex Causes an image to Hand lens, microscope, drop of appear larger water, eyeglasses Concave Forces Causes an image to appear smaller Some eyeglasses Force – a push or a pull on an object. A force is needed to start a motion, stop a motion, or change the direction of a motion. • Objects at rest, stay at rest until moved by a force. • Objects in motion, stay in motion until stopped by a force. Mass - affects how much force is needed to move an object. A bowling ball takes more force to move than a baseball. Gravity – a force that pulls objects towards one another Friction – when two objects rub together it causes motion to slow down or stop and will produce heat. EARTH AND SPACE Solar System Our solar system is made up of the sun and all the objects moving around (orbiting) it. Sun, Rocky inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, (asteroid belt); Gas Giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune; Dwarf planet: Pluto Sun – the largest object in our solar system. It is a big ball of burning gas (star).Its gravity is strong enough to keep all the planets in orbit (revolving) around it.It provides heat and light to Earth. Darker spots (sun spots) are cooler regions on the surface of the sun. Moon Characteristics Earth Characteristics No atmosphere or water Has an atmosphere and water Inner core, mantle, crust Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust Craters Has some craters, but not as many as the moon because of the protective atmosphere Moon’s gravity causes two tides a day on Earth Earth’s gravity keeps the moon orbiting around it Takes a month (29.5 days) to orbit the Earth Orbits the sun once a year (365 days) Goes through phases as it orbits Earth (takes about 1 month to go from Is tilted (seasons) and spins (rotates) on its axis once every 24 hrs (day / full moon to next full moon) night) Has 1/6 the gravity of Earth Is tilted and spins on its axis very slowly Reflects sunlight off its surface 4 times the size of the moon Only planet with life Third planet from the sun Rotation: spinning on its axis. It takes the earth 24 hrs to rotate once on its axis. It takes the moon about 1 month to rotate once on its axis. Revolution: orbiting around another object. It takes the earth 365 days to revolve around the sun. It takes the moon about 1 month to revolve around the earth. Properties of Sediment Particle size Properties of Particles Clay (finest) Individual particles only visible with a microscope Silt Very fine particles. Has to be separated from sand by settling out with water. Feels smooth and powdery when dry. Sand Visible particles Gravel(largest) Soils How Water Passes Through Particles Not at all medium medium easily *Soil is a mixture of many materials including sand, clay, rocks, water, fungi, bacteria, and decayed plants and animal material (humus). There are different types of soil based on the mix of materials found in each type. Humus Loam Decaying organic matter Equal parts: sand, silt, clay humus *Soils with a large amount of clay and decayed material will hold more water than sandy soils. Best for planting Earth’s Surface Changes - The earth’s surface is constantly changing. Some changes occur quickly as a result of earthquakes and volcanoes. Some occur slowly as a result of weathering and erosion. Weathering The breaking down of rock into smaller sediment (biological – plant roots, chemical or physical) Erosion Water, wind or gravity moves loose sediment to another place. Deposition Moving eroded rock and soil to a new place. The sediment will form layers. Oldest layer is onthe bottom and the youngest on the top (will sometimes have fossils) Landforms – caused as a result of weathering, erosion and deposition Mountains, beaches, glacial valleys (created by moving glaciers), volcanoes, canyon (created by water erosion from a flowing river), island, sand dune (created by wind erosion), delta (created at the mouth of a river by deposition of sediment) Natural Resources Renewable – these can be replaced over time (plants, animals, water, air) Nonrenewable – once these are gone, they cannot be replaced. (coal, oil, natural gas, minerals) Fossil fuels - made from dead plants and animals millions of years ago. (coal, oil, natural gas) Foramtion of fossil fuels- dead plants and animals begin to decay and are covered by many layers of sediment. The layers of sediment add a great deal of heat and pressure. After millions of years the dead plant and animal material is transformed into fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. Alternative Energy Resources Wind energy: energy that comes from harnessing the movement of air (wind turbines) Solar energy: energy that comes from the sun (use of solar panels) Hydroelectric energy: energy that comes from harnessing the movement of water ( dams) Geothermal energy: heat energy from deep inside the earth Biofuel: fuel made from burning of organic material like plant and animal waste Weather and Climate Term Description Weather The day to day conditions of a particular area. (changes, short time period) Climate The average weather for an area over a long period of time Precipitation Rain, sleet, snow or hail Vapor Gas form of water Evaporation Caused by the sun heating up water and turning it to vapor Condensation The cooling off of water vapor and turning it back to a liquid (clouds) Water Cycle Movement of water between Earth’s surface and air. It is powered by the sun.