adult
advertisement
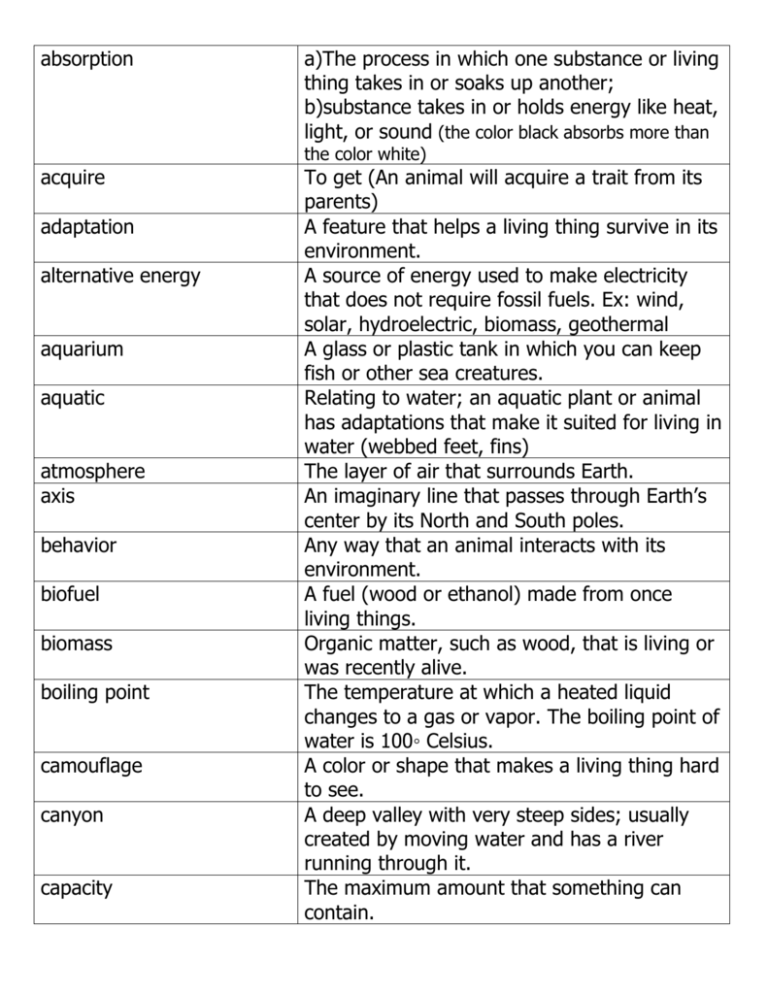
absorption a)The process in which one substance or living thing takes in or soaks up another; b)substance takes in or holds energy like heat, light, or sound (the color black absorbs more than the color white) acquire adaptation alternative energy aquarium aquatic atmosphere axis behavior biofuel biomass boiling point camouflage canyon capacity To get (An animal will acquire a trait from its parents) A feature that helps a living thing survive in its environment. A source of energy used to make electricity that does not require fossil fuels. Ex: wind, solar, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal A glass or plastic tank in which you can keep fish or other sea creatures. Relating to water; an aquatic plant or animal has adaptations that make it suited for living in water (webbed feet, fins) The layer of air that surrounds Earth. An imaginary line that passes through Earth’s center by its North and South poles. Any way that an animal interacts with its environment. A fuel (wood or ethanol) made from once living things. Organic matter, such as wood, that is living or was recently alive. The temperature at which a heated liquid changes to a gas or vapor. The boiling point of water is 100◦ Celsius. A color or shape that makes a living thing hard to see. A deep valley with very steep sides; usually created by moving water and has a river running through it. The maximum amount that something can contain. carbon dioxide Celsius scale cementation chlorophyll circuit climate cloud compaction competition complete metamorphosis a gas that humans and animals produce and release into the air when they breathe out. Plants take this gas in to use during photosynthesis. A scale for measuring temperature where 0◦ is freezing/melting and 100◦ is boiling. When sediment becomes rock because of extreme heat and pressure deep under the ground. The green material in plants that absorbs light energy from the sun, which plants use to make food. The path along which electrons can flow. If the path is broken the flow will stop. The average of all weather conditions through all seasons over a period of time. Ex: Areas close to the equator typically have a tropical climate. Condensed water vapor that rises from bodies of water on Earth Extreme pressure from weight being added to overlying layers The contest among organisms for the limited resources (food, water, mate, territory) of an ecosystem. Changes in the life cycles of certain animals. Has four (4) stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa, and adult. The stage after egg looks completely different than the adult. condensation conduction conductor The process by which a gas changes back into a liquid due to cooler temperatures. Ex: On a cold glass, or clouds in the atmosphere. the direct transfer of heat between objects that touch a material through which energy can flow; a material that conducts electrons easily conserve constructive force consumer current cycle data decomposer decrease delta density (metals) to save or protect resources, or use resources in a careful way A force that creates or builds something (Ex: wind building sand dune, volcano building new land) an organism in a community that must eat to get the energy it needs the flow of electrons from negatively charged objects to positively charged objects Any series of events or actions that happens over and over again (day and night, the seasons, the water cycle) Facts, numbers, or words that provide you with information A consumer that breaks down the tissues of dead organisms To become less, smaller, or have fewer. A flat, triangular area of sediment deposited by a river as it enters the sea The concentration of matter in an object; a more dense material will sink below a less dense one (Ex: vinegar is more dense than oil so it will sink to the bottom in a container. That’s why we shake salad dressing) deposition destructive force The process of dropping, or depositing, sediment in a new location A force that destroys or breaks something down (Ex: flooding causing a mudslide when the land cannot absorb any more water) disposal dissolve dune The action or process of throwing away or getting rid of something. To add a solid or gas to a liquid so that the solid or gas becomes evenly distributed throughout the liquid A mound or ridge of sand or other loose sediment formed by the wind, especially on earth ecosystem electromagnet electrical energy electron energy environment erosion evaporation evidence food chain food web force the sea coast or in a desert. The third planet from the sun in the solar system A community and its physical environment together a temporary magnet made by passing electric current through a wire coiled around an iron bar the energy carried by moving electrons through a conductor a particle with a negative charge the ability to cause changes in matter Everything around a living thing (includes climate, soil, water, food, and living organisms the process of moving sediment from one place to another the process by which a liquid changes into a gas by adding heat (on a stove or the Sun) Facts or information that proves, or disproves, whether something is valid a process by which energy passes from one living thing to another a process that combines many food chains to show how energy moves through an ecosystem a push or pull that causes an object to move, stop, or change direction (Natural forces: magnetism, gravity, friction) formation fossil fossil fuel freezing point The action of forming or the process of being formed. the remains or traces of past life found in sedimentary rock A fuel formed from the remains of once living organisms, found in sedimentary rock (Ex: coal, oil, natural gas) The temperature at which particles in a liquid friction function gas generator geothermal energy germination glacier gravity habitat hazard heat hibernation will slow down and become a solid. The freezing point of water is 0◦ Celsius. A force that opposes, or acts against, motion when two surfaces rub against each other. Produces heat and slows motion How something works in a particular way (Ex: the function of your nose is to breathe and smell). the state of matter that does not have a definite shape or volume A machine that converts one form of energy into another, especially mechanical energy into electrical energy. Energy that comes from hot rocks below Earth’s surface. The rocks make water hot enough to turn to steam, which will turn a generator to produce electricity. The sprouting of a seed A large mass of ice that moves slowly down a mountain or along a valley. As the glacier scrapes Earth’s surface other landforms may be created such as foothills, u-shaped valleys, and lakes. The natural force that attracts one object to another. The greater the mass, the stronger the pull. Earth’s gravity keeps the Moon orbiting around it, and Earth orbits the Sun due to its gravitational pull. A place in an ecosystem where a population lives. Something that may cause unavoidable danger. A form of energy. May come from the Sun, electricity, fire, friction and other sources. An inherited trait of some animals to spend the winter asleep or in an inactive state hydroelectric energy hypothesis inclined plane incomplete metamorphosis Electricity generated from the force of moving water. A possible explanation for something observed. A sloping plank or ramp that makes it easier to raise heavy loads. Changes in the life cycles of certain animals. Has three (3) stages: egg, nymph, and adult. The nymph may molt many times, but it is 3 stages. Nymph looks like the adult but does not have wings and cannot reproduce. increase inherited trait insulate interact instinct investigate kinetic energy landform larva learned behavior lens lever life cycle To become larger, or to have more. A characteristic that is passed down from parents to offspring (physical or instinctive). To use a material to block the flow of (heat, sound, or electric) energy. A kind of action that occurs as two or more objects have an effect upon one another. An inherited behavior that an animal does without ever being taught to do it. To research or study something to get facts or information. Energy that exists because something is moving. A physical feature on Earth’s surface. A young animal with a body form very different from the adult. The second stage of complete metamorphosis. A behavior an animal learns from its parents. A piece of clear glass or plastic with at least one curved surface. A lens bends rays of light that pass through it, making an image look larger, smaller, or different in some way. A bar for lifting loads. The lever rests on a fulcrum. The series of changes in living things. Ex: frog life cycle – egg, tadpole, adult, egg. light energy liquid machine magnetism mass matter mechanical energy medium melting point metamorphosis mixture moon natural resource niche nonrenewable nymph Energy that we can see; passes easily through gases in the air and passes through some other kinds of matter. The state of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape. Something that makes work easier by changing the size or the direction of a force. The force of repulsion (pushing) or attraction (pulling) between poles of magnets. The amount of matter in an object. Anything that has mass and takes up space. Energy that is in motion (Ex: a rolling ball, flowing water). A substance’s physical state like solid, liquid or gas. Light waves travel faster or slower when moving from one medium through another. The temperature at which a solid melts and becomes a liquid. The melting point of ice is 0◦ Celsius. a series of major changes in an animal’s body form during its life cycle A combination of two or more substances. Substances may be easy to separate (like trail mix) or difficult to separate (like lemon in water). Earth’s only natural satellite. The moon has no life, atmosphere, wind, or water. The moon is ¼ the size of Earth and has much less gravity. Any of the useful materials that people take from Earth. The role each population has in its habitat. The way an organism interacts with living and nonliving parts of its ecosystem. A resource that cannot be readily replaced once it is used ( The stage (during incomplete metamorphosis) opaque orbit organism oxygen parallel circuit pattern photosynthesis physical physical properties physical state potential energy precipitation predator pressure prey prism in which the young animal looks like the adult. A material that does not allow any light to pass through. The path an object takes as it revolves around another object. Ex: the path Earth takes as it revolves around the Sun is its orbital path. Any living thing, plant or animal. A gas that is a waste product plants release into the air during photosynthesis. Humans and animals must breathe this gas to stay alive. An electrical circuit split into separate branches. Something that repeats in a predictable way (Ex: day/night, phases of the moon, seasons). The process by which green plants use energy from sunlight make food. Relating to something you can see or touch. Characteristics of a substance that can be observed (using senses) or measured (mass, magnetism, physical state: solid, liquid, gas, density, solubility in water, ability to conduct/insulate thermal or electrical energy. The form matter takes at a given time: solid, liquid, gas Energy that exists because of its position or condition. Any form of water (rain, hail, sleet, snow) that falls from clouds. An animal that hunts other animals for food. The force acting over a given area of a surface. Animals that other animals hunt for food. A transparent solid of glass, plastic or quartz that can bend or reflect light. The prism separates light into the colors of the rainbow. process producer pulley pupa recycle reflect refract reliable renewable resource Retain/retention revolve rotate screw season A series of actions or steps taken in order to accomplish something. An organism that makes its own food (green plants). A wheel with a rope, chain, or belt passed over it. A load is attached to one end and the other end is pulled. the stage (during complete metamorphosis) in which the body form of a young animal changes from the larva to the adult to use something again When light energy bounces off a flat, smooth object. When light rays bend as they pass through different substances at an angle. Accepted as true or correct because the same results were found after several trials or experiments. A resource that can be replaced after it has been used. Materials and energy that make life on Earth possible (air, land, water, minerals, fuels, energy from the sun, living things that provide food. To hold back. To travel in a closed path around an object such as Earth does as it moves around the sun. To move around a central point or axis. Ex: The Earth rotates around an imaginary axis that runs from the North to the South pole. This rotation causes day and night. A kind of simple machine. It is an inclined plane that twists around a central axis. One of the four (4) periods of the year- spring, summer, autumn, and winter. Caused by sediment sedimentary rock series circuit shadow soil solar energy solar system solid solubility soluble solution sound energy species Earth’s tilt as it orbits the sun. Material (sand, clay and rocks) that settles to the bottom of a liquid like a river, lake or ocean. A kind of rock that forms when sediment is under intense heat and pressure (deep in the Earth) for a long period of time. An electric circuit in which the parts are connected one after the other. Electricity follows a single path and all parts share the same current. The dark image or shade cast by an object where it blocks the light. The covering of most of the earth’s land surface. It is made by the breakdown of rocks into small particles, plus material from dead and decaying plants and animals. Energy given off by the sun which can be turned into light, heat, and electricity. The sun and the planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and dust particles that are in orbit around the sun. A substance with a definite shape. The ability of one substance to be dissolved in another substance. Able to be dissolved. Ex: Salt is soluble in water. A mixture where a solid, liquid, or gas is dissolved in another solid, liquid, or gas. Energy produced by vibrations, or a rapid shaking back and forth, and can be heard. Sound energy can travel through the air, as well as some solids and liquids. a group of similar living things that can produce offspring who can also produce offspring structure A body part of an animal (Ex: beak, gills, webbed feet) that is inherited by an animal from its parent. sun A huge ball of gases (star) that provides Earth with most of its heat and light energy. The earth and other planets of our solar system are in orbit around our sun due to the gravitational pull of its great mass. A number of separate parts that work together to perform a function or do a certain job. Ex: your body, a car, a plant. An instrument that magnifies distant objects, or makes them appear larger. (parts: objective lens, eyepiece) A glass or plastic container in which small plants or land animals are kept. When sealed, the water cycle may be observed, but aquatic animals would not live in a terrarium. How something would feel to the sense of touch: rough, smooth, soft Energy from vibrating/moving particles (Fast moving particles will produce more heat, slower particles will produce less heat). The regular rise and fall of ocean water caused by the pull of the moon and sun’s gravity. To lean at an angle or sloping position. Causes the seasons as Earth revolves around the Sun. A characteristic of an organism which is inherited. To move from one place to another. Letting some light pass through. Ex: umbrella, sheer curtains. Letting light through so things on the other side can be clearly seen. Ex: windows. A device in which a flowing liquid or gas turns system telescope terrarium texture thermal energy tide tilt trait transfer translucent transparent turbine U-Shaped Valley valid variable volume water cycle weather weathering wedge wheel and axle wind energy wind turbine a set of blades. A valley formed when a glacier scrapes away the sides of mountains as gravity pulls it down Reasonable or logical A condition in an experiment that can be changed to affect the result. The amount of space that an object takes up. The continuing movement of water from Earth’s surface to the air and back to Earth. The water on Earth evaporates, changing into water vapor (gas), and rises into the atmosphere. The gas cools, and condenses into tiny drops of liquid water and form clouds. The drops get heavy and fall (gravity) as precipitation. The water evaporates and begins again. The changing conditions of temperature, rainfall, pressure, humidity, wind, and clouds in one area at one time. The breaking up of rocks on Earth’s surface by rain, ice, changes in temperature, and growing plants. A simple machine with 2 or more sloping surfaces. A simple machine (Ex: doorknob) An alternative energy source using wind to move turbines A machine used to harness the energy of the wind to generate electricity.