Rock Test Outline
advertisement

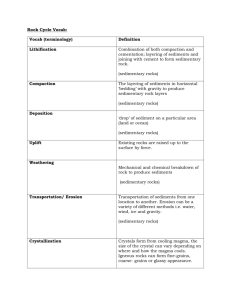
Chapter 3 – “Rocks” Test Outline I. Name: ____________________ Date: _____________________ Period: ___________________ Rocks and the Rock Cycle a. Rocks are mixtures of Minerals i. Example: Granite = Mica, Quartz, and Feldspar minerals ii. Exceptions: 1. Obsidian- volcanic glass 2. Coal – ancient plants and pressed together. b. Rock Cycle i. Rocks change over time through three different classifications of rock – it is a cycle that has no beginning or end; it is continuous. ii. Igneous Rocks 1. Form from cooled magma – called “lava” on the surface of the Earth iii. Sedimentary Rocks 1. Formed when different forms of rock are weathered into sediments which are compacted and cemented to form rock. a. Sand is a good example of sediment iv. Metamorphic Rocks – rocks that have been changed through heat and pressure in the Earth 1. When sedimentary or igneous rocks move deeper into the crust they are exposed to heat and pressure, which causes the rocks to be squeezed and changed in shape. Layers and small crystals can be formed. v. The rocks in the cycle can travel in more than one manner – see the diagram on p.79 in your text. II. Igneous Rocks a. Magma and Lava form different types of rock i. Intrusive Igneous Rocks – when magma cools inside the earth it produces rocks with a rough surface and large crystals 1. The crystal have more time to form because they cool slower inside the Earth 2. Examples: a. Granite b. Diorite ii. Extrusive Igneous Rock- When magma is on the surface of the Earth it is called Lava. 1. Lava cools quickly giving the rocks less time to form crystals, therefore they are smoother with smaller crystals 2. Examples: a. Obsidian – “Lava Glass” - Fractures, glassy b. Pumice – “Lava Foam” cools from bubbling lava – so air gets trapped and creates a rock with a very low density. c. Basalt – no crystals III. Sedimentary Rock i. Form when other forms of rock are “weathered” – effected by precipitation, wind, and heating and cooling of rock – this process breaks the rock into pieces called sediments. ii. These sediments are moved through the process of erosion to the bottom of rivers, streams, lakes, and oceans. iii. In these locations they are deposited and build up in layers. The increasing layers cause them to be pressed together – Compaction – and cemented together – Cementation. iv. This process forms sedimentary rock from the sediments. 1. Examples : a. Sandstone – sand sediments b. Conglomerate – pebble sediments c. Limestone – shell and sand sediments IV. Metamorphic Rocks – When rocks get pressed down into the earth they are exposed to intense heat and pressure, this changes the shape and composition of the rocks. The more heat and pressure the more change will occur. Generally the deeper a rock is in the Earth the more it will change. i. Under these conditions atoms in the rocks undergo a process called recrystallization where their original atomic bonds are broken and new ones are formed. This changes the rock. It can cause the rock to be Foliated. 1. Foliated rocks – Are rocks that have crystals and minerals that are lined up in bands or layers. a. Example: i. Phyllite ii. Gneiss 2. Nonfoliated rocks – have crystals, but not layers. a. Example i. Marble ii. Rocks can go through more than one change. 1. Example: a. Shale SlatePhyliteSchistGneiss