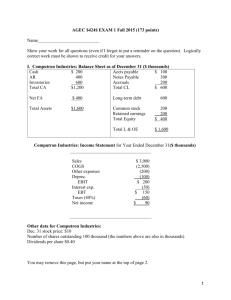
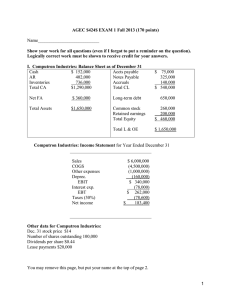
AGEC $424$ EXAM 1 (125 points)
advertisement
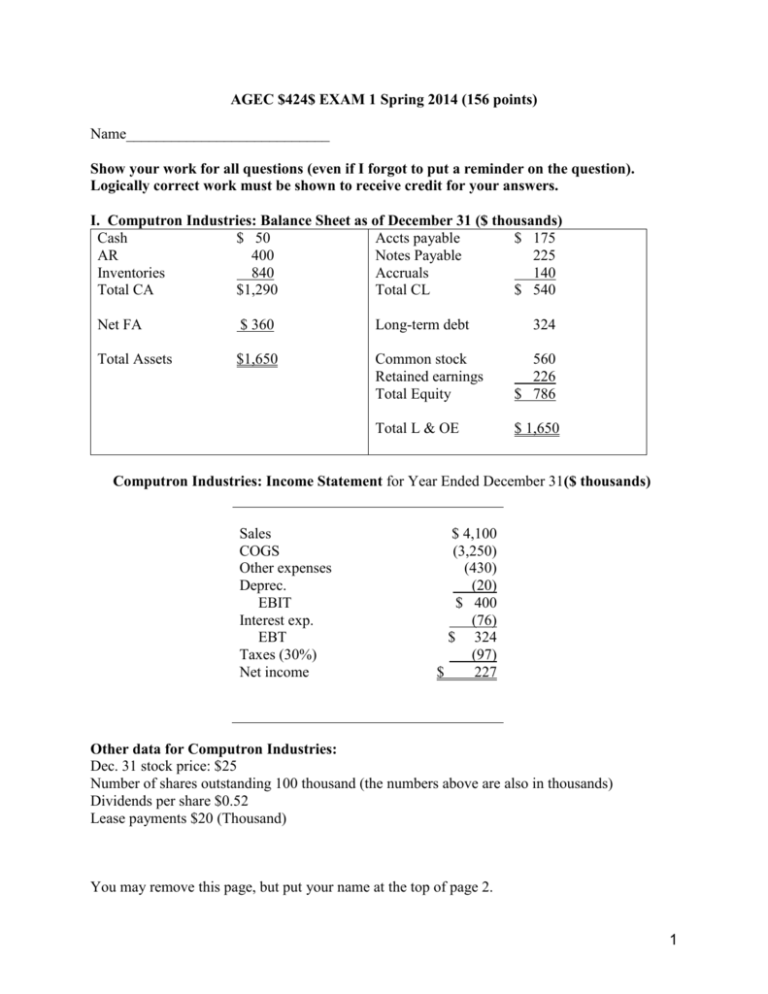
AGEC $424$ EXAM 1 Spring 2014 (156 points) Name___________________________ Show your work for all questions (even if I forgot to put a reminder on the question). Logically correct work must be shown to receive credit for your answers. I. Computron Industries: Balance Sheet as of December 31 ($ thousands) Cash $ 50 Accts payable $ 175 AR 400 Notes Payable 225 Inventories 840 Accruals 140 Total CA $1,290 Total CL $ 540 Net FA $ 360 Long-term debt 324 Total Assets $1,650 Common stock Retained earnings Total Equity 560 226 $ 786 Total L & OE $ 1,650 Computron Industries: Income Statement for Year Ended December 31($ thousands) Sales COGS Other expenses Deprec. EBIT Interest exp. EBT Taxes (30%) Net income $ 4,100 (3,250) (430) (20) $ 400 (76) $ 324 (97) $ 227 Other data for Computron Industries: Dec. 31 stock price: $25 Number of shares outstanding 100 thousand (the numbers above are also in thousands) Dividends per share $0.52 Lease payments $20 (Thousand) You may remove this page, but put your name at the top of page 2. 1 Name_______________________ 1. (51 points) Calculate ratios for Computron Industries for use in comparison to the following industry averages. Show your work in the Computron Industries box. Ratio Industry Computron Industries Evaluate briefly and then support If you don’t show your work in this average your statement by comparing to column you don’t get the points. the industry average. 5 pts each 2 points each Current Ratio 1.6x Evaluate liquidity: Quick Ratio 0.8x Debt ratio (TL/TA) 50% Times Interest Earned 2.5x Inventory turnover 5x Days sales outstanding 40 days Fixed Asset turnover 7.5x Total assets turnover 2.0x Profit margin (ROS) 3.5% Return on total assets (ROA) 7% Return on equity (ROE) 14% Price-Earnings 10x Market to Book 2.2x Acts pay. Def. 20 da. Evaluate debt level: Evaluate asset management Evaluate profitability: Evaluate market ratios: 19 da. Don’t evaluate. Use the above data for questions 2 through 5. 2 2. (10 points) Construct the extended Du Pont equation for both Computron and for the industry. Then analyze the component breakdown of the company's ROE in comparison to the industry (say something about each component). 3. (3 points) Which is more responsible for the deviation of Computron’s ROE from the industry average: cost control, asset management, or debt management? Explain. 4. (6 points) Show a side by side comparison of the cash conversion cycle for Computron with the industry. Use the CCC to analyze working capital management for Computron in comparison to the industry (say something about each component). Say which is best and why? 5. (3 points) Based on the ratios and information in questions 1-4, point out red flags and major successes for Computron. 3 6. (10 points). Jill’s Wigs Inc. had the following balance sheet last year: Last Cash Accounts rec. Inventory Fixed assets Total assets $ 800 450 950 34,000 $36,200 Factor 1stPass Last Fact. 1st Pass Accounts payable $ 350 Accrued wages 150 Notes payable 2,000 Mortgage 26,500 Common stock 3,200 Retained earnings 4,000 Total liabilities and equity $36,200 Jill has just invented a non-slip wig for men which she expects will cause sales to double, increasing after-tax net income to $1,000. She was at 80% of capacity last year. Will Jill need any outside capital if she pays no dividends? If so, how much? Show the forecast balance sheet above and your final answer and supporting calculations below. 7. (12 points) You are given the following selected financial information for The Blatz Corporation. Income Statement Balance Sheet Ratios COGS $750 Cash $250 ROS 10% Net Income $160 Net Fixed Assets $850 Current Ratio 2.3 Inventory Turnover 6.0 ACP 45 days Debt Ratio 49.12% Calculate the following items and show your work in the space provided below. Sales: Total Liab.: Inventory: LT Debt: Accts Rec: Equity: Current Assets: ROA: Total Assets: Current Liabilities: ROE: 4 8. (30 points) You have been given the following information on the Crum Company. Crum expects sales to grow by 50% next year, and variable costs should increase at the same percentage. Fixed assets were being operated at 80% of capacity last year. Fixed costs will increase with fixed assets. Underutilized fixed assets cannot be sold. Current assets and spontaneous liabilities should increase at the same rate as sales. The company plans to finance any external funds needed as 35% notes payable and 65% common stock. After taking financing feedbacks into account, and after the second pass, what is Crum's projected AFN using the projected balance sheet method? Sales factor ____________ Capacity factor____________ Last factor $1,000.00 600.00 ___200.00 Sales variable costs Fixed costs EBIT Interest $ EBT Taxes (40%) $ 200.00 16.00 1st pass 110.40 66.24 _________ 2nd pass _________ _________ ________ _________ 184.00 73.60 _________ Net Income Dividends (60%) feedback ________ _________ $ Add'n to R.E. $ Current Assets Net fixed Assets $ ________ ________ _________ ________ ________ 44.16 700.00 300.00 _________ Total assets $1,000.00 A/P and Accruals N/P 8.00% Common stock Retained earnings $ Total Liab & Equity ________ 150.00 200.00 150.00 500.00 _________ $1,000.00 AFN1: ________ AFN2: ________ Show Interest expense calculation: Financing Breakdown 1st pass 2nd pass Total New N/P needed ________ _________ __________ New C.Stock needed ________ _________ __________ 5 9. (5 points) Inflation is expected to be 5% next year and a steady 7% each year thereafter. Maturity risk premiums are zero for one year debt but have an increasing value for longer debt. One-year government debt yields 9% whereas two-year debt yields 11%. a. What is the real risk-free rate and the maturity risk premium for two-year debt? b. Forecast the nominal yield on one- and two-year government debt issued at the beginning of the second year. Show work here for a and b: 10. (3 points) Adams Inc. recently borrowed money for one year at 9%. The pure rate is 3%, and Adams’ financial condition warrants a default risk premium of 2% and a liquidity risk premium of 1%. There is little or no maturity risk in one-year loans. What inflation rate do lenders expect next year? Show work here: 11. (2 points) Which of the following ratios would probably not be used to assess the profitability of a firm? a. Return on stockholders’ equity b. Return on total assets c. Times interest earned d. A and c only 12. (2 points) Under the DuPont system, the return on assets is equal to: a. the product of the gross profit margin and inventory turnover b. the sum of the debt-equity ratio and the return on sales c. the product of the return on sales and total asset turnover d. the product of the return on sales, total asset turnover, and equity multiplier e. none of the above 13. (2 points) Which of the following is not affected by a change in interest expense? a. Gross margin b. EBIT c. ROE d. A and b e. All of the above 14. (2 points) Management is prone to overstate: a. accounts receivable and inventory b. accounts receivable, but not inventory c. inventory, but not accounts receivable d. neither accounts receivable nor inventory 6 15. (2 points) The tax schedule for married couples filing jointly: a. results in less tax than would be paid by a single person if only one spouse works. b. saves on taxes regardless of whether one or both spouses work c. results in most two income families paying more tax than if they were single d. both a & c 16. (2 points) In order to compare the yields on municipal and corporate bonds, the investor must restate the yield of either the taxable corporate bond to an after-tax basis or the municipal bond to a pretax equivalent because a. corporate bonds are tax free b. municipal bonds are tax free and investors must compare rates on an equal basis c. a municipal bond is typically safer than a taxable corporate bond d. such restatements are not necessary for most taxpayers 17. (2 points) The cash conversion cycle measures the time: a. between the creation of receivables and their collection. b. it takes for inventory to be turned into product and sold. c. between payment for inventory and collection of cash for its subsequent sale as product. d. for a check to clear the banking system. 18. (2 points) J&J Production Inc. has annual sales of $30 million and accounts receivables of $1.5 million. They have an inventory turnover of 4. How long is J &J's operating cycle? (Assume a 360-day year) Show work. a. 18 days b. 90 days c. 108 days d. 72 days 19. (2 points) Marshall Manufacturing has an ACP of 60 days, an inventory turnover of 6, and turns its payables over once a month. How long is Marshall’s cash conversion cycle? (Assume a 360-day year) Show work. a. 30 days b. 60 days c. 90 days d. 120 days 20. (2 points) CVD, Inc. has an equity multiplier of 2. What is CVD’s stockholders’ equity if total liabilities are $100,000? Show work. a. $100,000 b. $150,000 c. $200,000 d. $50,000 21. (3 points) A firm had a piece of machinery that cost $7,000 when new and has accumulated $4,500 in depreciation. If the machine is sold for $4,000, which of the following is true? Show work. a. The firm has a taxable gain of $4,000 on the sale of the machine b. The firm has a taxable gain of $1,500 on the sale of the machine c. The firm has a deductible loss of $3,000 on the sale of the machine d. The firm has a taxable gain of $7,000 on the sale of the machine 7