Supplemental document - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement
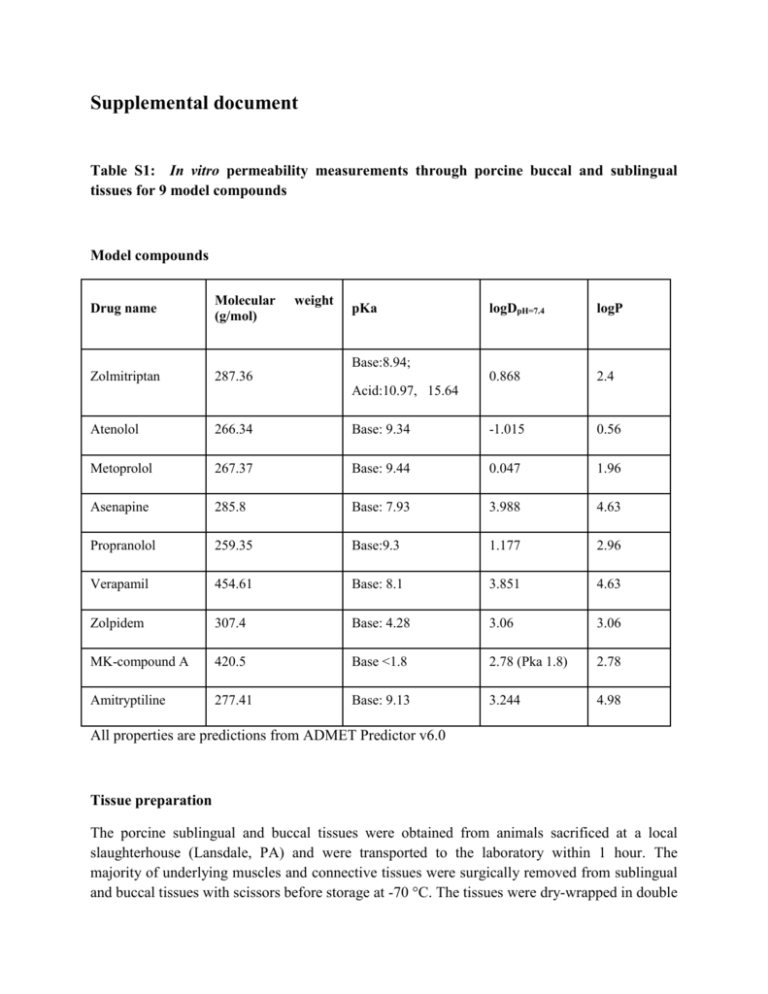
Supplemental document Table S1: In vitro permeability measurements through porcine buccal and sublingual tissues for 9 model compounds Model compounds Drug name Molecular (g/mol) Zolmitriptan 287.36 weight pKa logDpH=7.4 logP 0.868 2.4 Base:8.94; Acid:10.97, 15.64 Atenolol 266.34 Base: 9.34 -1.015 0.56 Metoprolol 267.37 Base: 9.44 0.047 1.96 Asenapine 285.8 Base: 7.93 3.988 4.63 Propranolol 259.35 Base:9.3 1.177 2.96 Verapamil 454.61 Base: 8.1 3.851 4.63 Zolpidem 307.4 Base: 4.28 3.06 3.06 MK-compound A 420.5 Base <1.8 2.78 (Pka 1.8) 2.78 Amitryptiline 277.41 Base: 9.13 3.244 4.98 All properties are predictions from ADMET Predictor v6.0 Tissue preparation The porcine sublingual and buccal tissues were obtained from animals sacrificed at a local slaughterhouse (Lansdale, PA) and were transported to the laboratory within 1 hour. The majority of underlying muscles and connective tissues were surgically removed from sublingual and buccal tissues with scissors before storage at -70 °C. The tissues were dry-wrapped in double aluminum foil to avoid dehydrating during storage. Tissues were thawed in incubator at 37 °C for 30 min prior to the permeation study on the date of the experiment. Any underlying muscles and connective tissues were carefully removed until only epithelium remained. Tissue thickness and integrity Tissue thickness and electrical resistance were measured as quality control for tissue trimming and integrity. The peripheral parts of sublingual and buccal tissues which were mounted on Ussing chambers were measured by caliper. Electrical resistance was measured – ideal values should be within 100-1000 Ω/cm2. Permeation studies In vitro transport was studied using the Multichannel Ussing Chambers System (Navicyte, Warner Instruments) at 37 °C. 3H or 14C radiolabelled compound were used in donor chamber. The Ussing cells have the diffusion area=1.78 cm2. Sublingual and buccal mucosal were thawed in PBS solution for 10 minutes at room temperature. Each tissue was spread over an Ussing chamber and clamped with the epithelial side facing the donor compartment. Donor and receiver chambers were filled with 5 ml of drug solution and PBS buffer, respectively (pH 7.4). Compound donor solutions were prepared in PBS buffer and the concentration in the donor chamber was 3 micro curie (the real mole concentration in donor solution depends on the concentration of radiolabelled stock solution). Oxygen was bubbled through the diffusion system at both donor and receiver sides to minimize the aqueous diffusion layers and facilitate mixing. Diffusion experiments (n≥6) were conducted for 7 or 8 h. Samples (500 µl) were collected from the receiver chamber and replaced with the same volume of fresh PBS buffer. 20 µl of donor side solution was collected at 0 and 6 h. Sample Analysis 500 µl samples collected from receiver chamber (20 µl from donor side) were mixed with 5 ml biodegradable counting cocktail and vortexed for 15 seconds. The mixture was analyzed by liquid scintillation counting. The cumulative amount (Q, μmol) of model compounds permeated across sublingual/buccal epithelium was calculated by the following equation. Q = C𝑛 × V + 0.5 × ∑𝑛−1 𝑖=1 C𝑖 (1) Where V is the volume of the receptor cell, Cn is the drug concentration at time point ‘n’, and Ci is the model compound concentration at time point ‘i’. The radioactivity was converted to molarity based on the conversion factor. The cumulative amount (μmol) of compound permeated across sublingual/buccal epithelium was plotted versus time (h). Each data presents as mean ± SD of six determinations. Figure S1: Permeation results of 9 model compounds through porcine buccal and sublingual tissues Zolmitriptan in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 2.5E-03 2.0E-03 1.5E-03 1.0E-03 5.0E-04 0.0E+00 0 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Zolmitriptan in sublingual tissue 5.0E-02 Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 2 4.0E-02 3.0E-02 2.0E-02 1.0E-02 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Atenolol in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.2E-07 1.0E-07 8.0E-08 6.0E-08 4.0E-08 2.0E-08 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Atenolol in sublingual tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.2E-07 8.0E-08 4.0E-08 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Metoprolol in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.0E-07 8.0E-08 6.0E-08 4.0E-08 2.0E-08 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Amitryptiline in sublingual tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.0E-06 8.0E-07 6.0E-07 4.0E-07 2.0E-07 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 MK compound A in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.0E-06 8.0E-07 6.0E-07 4.0E-07 2.0E-07 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) MK compound A in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 3.0E-06 2.5E-06 2.0E-06 1.5E-06 1.0E-06 5.0E-07 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Propranolol in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.0E-06 8.0E-07 6.0E-07 4.0E-07 2.0E-07 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Propranolol in sublingual tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 1.5E-06 1.2E-06 9.0E-07 6.0E-07 3.0E-07 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Asenapine in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 4.0E-04 3.0E-04 2.0E-04 1.0E-04 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Asenapine in sublingual tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 8.0E-04 6.0E-04 4.0E-04 2.0E-04 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Verapamil in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 8.0E-08 6.0E-08 4.0E-08 2.0E-08 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Verapamil in sublingual tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 3.6E-07 3.0E-07 2.4E-07 1.8E-07 1.2E-07 6.0E-08 0.0E+00 0 2 4 Time (hr) 6 8 Zolpidem in buccal tissue Accumulated Amounts (µmol) 2.0E+00 1.6E+00 1.2E+00 8.0E-01 4.0E-01 0.0E+00 0 2 4 6 8 Time (hr) Table S2: Key model input parameters for prediction of Fa_IO in asenapine, verapamil, propranolol, and nicotine. Values of fut and diffusivity were calculated using Equation 6 and 7 Dose Compounds (mg) Dosage forms logDpH=7.4 pKa (base) Reference Solubility (mg/ml) fut Diffusivity (cm2/s) Asenapine 5 Sublingual Tablet 3.99 7.93 3.7 pH = 4.6 0.059 1.12 × 10-6 Verapamil 40 Sublingual Solution 3.85 8.10 0.0162 (pH = 8.8) 0.063 1.12 × 10-6 Propranolol 40 Sublingual Tablet 1.18 9.30 1.66 (pH=10.5) 0.26 5.54 × 10-7 Nicotine 2 Sublingual Tablet -2.48 8.51 125 (pH=11.2) 0.52 1.52 × 10-7







