Unpacking Outcomes
advertisement
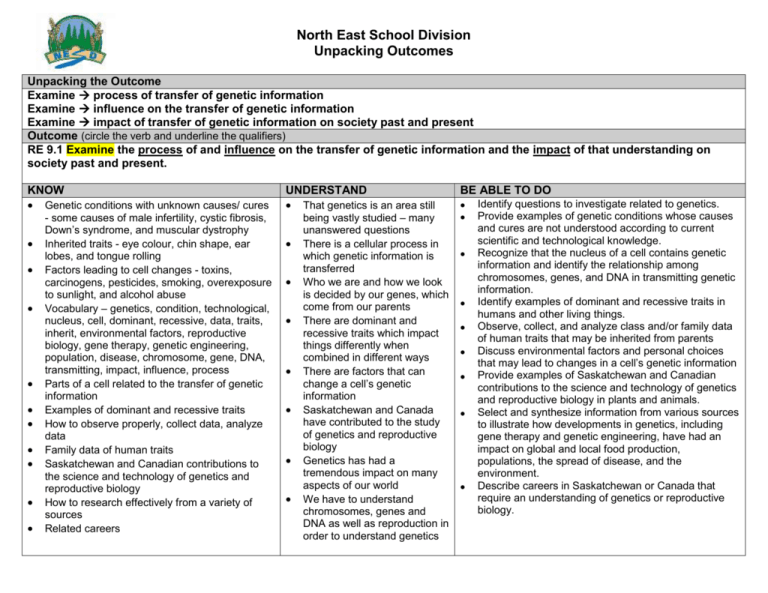
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Examine process of transfer of genetic information Examine influence on the transfer of genetic information Examine impact of transfer of genetic information on society past and present Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) RE 9.1 Examine the process of and influence on the transfer of genetic information and the impact of that understanding on society past and present. KNOW Genetic conditions with unknown causes/ cures - some causes of male infertility, cystic fibrosis, Down’s syndrome, and muscular dystrophy Inherited traits - eye colour, chin shape, ear lobes, and tongue rolling Factors leading to cell changes - toxins, carcinogens, pesticides, smoking, overexposure to sunlight, and alcohol abuse Vocabulary – genetics, condition, technological, nucleus, cell, dominant, recessive, data, traits, inherit, environmental factors, reproductive biology, gene therapy, genetic engineering, population, disease, chromosome, gene, DNA, transmitting, impact, influence, process Parts of a cell related to the transfer of genetic information Examples of dominant and recessive traits How to observe properly, collect data, analyze data Family data of human traits Saskatchewan and Canadian contributions to the science and technology of genetics and reproductive biology How to research effectively from a variety of sources Related careers UNDERSTAND That genetics is an area still being vastly studied – many unanswered questions There is a cellular process in which genetic information is transferred Who we are and how we look is decided by our genes, which come from our parents There are dominant and recessive traits which impact things differently when combined in different ways There are factors that can change a cell’s genetic information Saskatchewan and Canada have contributed to the study of genetics and reproductive biology Genetics has had a tremendous impact on many aspects of our world We have to understand chromosomes, genes and DNA as well as reproduction in order to understand genetics BE ABLE TO DO Identify questions to investigate related to genetics. Provide examples of genetic conditions whose causes and cures are not understood according to current scientific and technological knowledge. Recognize that the nucleus of a cell contains genetic information and identify the relationship among chromosomes, genes, and DNA in transmitting genetic information. Identify examples of dominant and recessive traits in humans and other living things. Observe, collect, and analyze class and/or family data of human traits that may be inherited from parents Discuss environmental factors and personal choices that may lead to changes in a cell’s genetic information Provide examples of Saskatchewan and Canadian contributions to the science and technology of genetics and reproductive biology in plants and animals. Select and synthesize information from various sources to illustrate how developments in genetics, including gene therapy and genetic engineering, have had an impact on global and local food production, populations, the spread of disease, and the environment. Describe careers in Saskatchewan or Canada that require an understanding of genetics or reproductive biology. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why are we still so engaged in genetic research? Why is it so interesting? What questions do we still have? How is genetic information transferred and where does it happen? Why are we the way we are? How is it decided? What do genes have to do with it really? How do dominant and recessive traits work? How can the cell’s genetic information be changed? How has Saskatchewan and Canada contributed to this field? What jobs are available? How can I understand genetics? What do I need to know? North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Observe significance Describe significance Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) RE 9.2 Observe and describe the significance of cellular reproductive processes, including mitosis and meiosis. KNOW Types of cell division – binary fission, mitosis, meiosis Ways to represent cell division How to use a microscope, prepare a slide Vocabulary and concepts – binary fission, mitosis, meiosis, cell cycle, cell membrane, nucleus, cellular process, cell growth, cell theory, diploid cell, haploid cell, theory How to observe and describe effectively UNDERSTAND There are ways to observe and describe cell division Representations help with understanding The nucleus of a cell determines the cellular processes As technology and equipment has changes, so has our understanding of cell growth and division Cell theory is a theory that explains cell division but theories can change as understanding develops Mitosis is different from meiosis in many ways Cancer can be understood through an understanding of cellular processes BE ABLE TO DO Observe and describe cell division (e.g., binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis) using microscopes, prepared slides, and/or videos. Construct a visual, dramatic, or other representation of the basic process of cell division as part of the cell cycle, including what happens to the cell membrane and the contents of the nucleus. Recognize that the nucleus of a cell determines cellular processes. Identify major shifts in scientific understanding of cell growth and division, including the role of microscopes and related technologies. Explain how the cell theory accounts for cell division. Compare binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis, and distinguish between cell division processes during meiosis and mitosis including the creation of diploid and haploid cells. Relate cancer to cellular processes. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can I observe and describe something as small as cell division? Why is cell division important to understand? How is the nucleus related to cellular processes? Why does our understanding change in science? How is a theory important in science? How does the cellular theory describe cell division? How are mitosis and meiosis the same? How are they different? How can understanding cellular processes help me understand cancer? North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Describe processes Describe implications Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) RE 9.3 Describe the processes and implications of sexual and asexual reproduction in plants and animals. KNOW Vocabulary – sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction, population, species, agricultural sector, forestry sector, pollination, hermaphroditic, bud, graft. Binary fission, spore, vegetative reproduction, fragmentation, parthenogenesis Methods of asexual reproduction in plants budding, grafting, binary fission, spore production, fragmentation, and vegetative reproduction Methods of asexual reproduction in animals – budding, parthenogenesis Examples of asexual animal reproducers – hydra, aphid, hammerhead shark Methods of sexual reproduction in plants Hermaphroditic animal examples Clownfish, wrasses, snails, and earthworms UNDERSTAND That plants and animals can reproduce sexually and asexually, depending on the species That each type of reproduction is unique with its own processes, advantages and challenges That there are different ways to reproduce sexually and asexually, too. That asexual reproduction knowledge and techniques are important in the agricultural and forestry sectors That variety truly is the spice of life! BE ABLE TO DO Identify questions to investigate about sexual and asexual reproduction in plants. Compare advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction for individual plants and animals, and for populations. Describe various methods of asexual reproduction in plant species and list specific examples. Describe various methods of asexual reproduction in animal species and list specific examples Investigate and describe applications of asexual reproduction knowledge and techniques in the Saskatchewan agricultural and/or forestry sector. Describe the process of sexual reproduction in seed plant species, including methods of pollination. Describe examples of sexual reproduction in animal species, including hermaphroditic species ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How do plants and animals reproduce? Why does it differ from species to species? How did these differences occur? How are sexual and asexual reproduction similar and different? What are the advantages, disadvantages and processes associated with each type of reproduction? Why is asexual reproduction knowledge important in agriculture and forestry? Why is variety good? North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Analyze process Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) RE 9.4 Analyze the process of human reproduction including the influence of reproductive and contraceptive technologies. KNOW Reproductive technologies - in vitro fertilization, artificial insemination, and embryo transfer Contraceptive technologies - condoms, oral contraceptive pill, diaphragm, intra-uterine devices, sterilization, and the morning after pill Vocabulary – reproduction, structure, function, hormone, conception, birth, chromosome, zygote, embryo, fetus, sacredness, interconnectedness, technology, contraceptive, reproductive, social, cultural, controversial How to ask good questions Structure of male and female reproductive system Role of hormones Major stages of human development from conception to birth Various cultural perspectives – places to look for information How to create a defense of a position on an issue UNDERSTAND That human reproduction has many controversial elements about which people often feel very passionate That scientific understanding does not always cover the spectrum of understanding about an issue That hormones play a role in human growth and development That there are known stages of human development from conception to birth That there are many technologies associated with contraception and reproduction That understanding a topic helps us defend a position more thoroughly (ELA integration) Human reproduction is big business ( Social integration) BE ABLE TO DO Pose questions about the process of human reproduction. Compare the structure and function of the male and female human reproductive systems, including the role of hormones. Describe the major stages of human development from conception to birth, including reference to signs of pregnancy, X and Y chromosomes, zygote, embryo, and fetus. Acknowledge differing cultural perspectives, including First Nations and Métis perspectives, regarding the sacredness, interconnectedness, and beginning of human life. Provide examples of scientific knowledge that has resulted in the development of reproductive technologies and contraceptive technologies Examine social and cultural issues related to the use of reproductive and/or contraceptive technologies in humans and defend a given position on an issue related to the use of reproductive and/or contraceptive technologies in humans. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why is human reproduction controversial? In what ways is there more to understanding something than just science? How do hormones work? How do humans develop from conception to birth? How have humans designed ways to increase and decrease reproduction? Why is this such a big business? How can I successfully defend a position?