sch4u- final exam review
advertisement

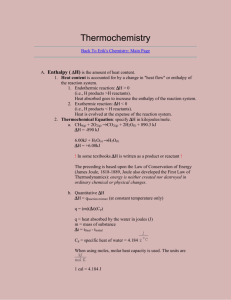
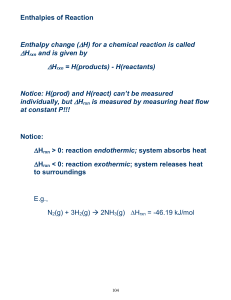
Name: SCH4U FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 Chemistry Final Exam Review 2014 Unit: Structure and Properties of Matter Things to Remember: 1. Bohr’s Atomic Model – Basic understanding of emission spectra, how is it different in different elements and successes and failures of Bohr’s Model 2. Line Spectra- Hydrogen Line Spectrum 3. What is Quantum Mechanics? 4. Four Quantum Numbers – ONLY Basic Concept, NO CALCULATIONS ON THE TEST, please review the presentation notes to know what they. 5. Difference between Orbit and Orbital – Check the presentation notes and review why we use the term orbital instead of orbit. 6. Aufbau Principle –You should know how to use it and also the definition. 7. Hund’s Rule- Definition and what it states. 8. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle - Definition and what it states. 9. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle - Definition and what it states. 10. Shapes of “s” “p” “d” and “f” orbital- names and shapes especially of s, p and d orbitals. 11. Electronic Configuration – Symbolic representation using arrows, unabbreviated configuration i.e. IS2 2S2………….. , Abbreviate electronic Configuration by using noble gas configuration [Ar] 4s2. of first 40 elements of the periodic table Practice Questions 1. Among the following pairs of compounds, which is made up of only polar molecules? a. CCl4, BF3 b. NH3, CBr4 2. For each of the following predict the shape and bond angles; a. AlCl3 ………………………………………….……………………………………………………………………………… b. H2S …………………………………….……………………………………………………………………………………… c. PH3 ...………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… d. CS2 .…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… e. SO2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… f. 3. Calculate the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN) for the bonds that would form between the groups of atoms listed below. State whether the bond would be ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent. a) N and H -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------b) B and Cl -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Name: c) SCH4U ------------------------------------------------ --------------------------------------------- d) Al and O ------------------------------------------------ --------------------------------------------- e) N and O ------------------------------------------------ --------------------------------------------- f) C and H -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4. Define the following: a. Pauli Exclusion Principle b. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle c. Hund’s Rule d. Quantum Mechanics e. Orbit f. Orbital g. Quantum Numbers and four types Write the complete ground state electron configurations for the following: 1) lithium 2) oxygen 3) calcium 4) titanium 5) lead 6. Give the n and L values for the following orbitals 5. B and F FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 a. 2s b. 4s c. 3p d. 4d e. 5f 7.Draw the orbital notation diagrams for the following elements. 1. Cl ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 4s 3d1 3d2 3d3 3d4 3d5 2. S ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 4s 3d1 3d2 3d3 3d4 3d5 3. Ca ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 4s 3d1 3d2 3d3 3d4 3d5 4. Kr ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 4s 3d1 3d2 3d3 3d4 3d5 5. Ti ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 4s 3d1 3d2 3d3 3d4 3d5 6. a) Draw Lewis Structure for the following molecules or polyatomic ions. SO42- b) BCl3 c) CH4 d) BF3 e) CO2 ) CO32- g) HCN 2 Name: 7. SCH4U FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 Draw the Lewis Structure, geometrical structure of the following Molecules. Please determine the shapes and bond angles by referring to VSEPR chart, write if the bonds in these molecules are polar/non polar/ionic. Predict if the molecules are polar or non polar. Also predict the hybridization. BF3 ZnCl2 BeF3 HCN CCl4 PCl5 XeF4 C2H2 BeI2 BCl3 CF4 CO2 HCl NH41+ BeCl2 SiF4 H2O CCl4 BCl3 SiF4 C2H2 Short Answers: a) Why HBr is a polar molecule, but H2 and Br2 are not. b) Discuss the successes and failures of Bohr’s Model c) What happens to ionization energy when you move across the period or down a group in the periodic table? Compare the ionization energy of metals and non-metals? d) State the four quantum numbers and the possible values they may have. e) What type of bond occurs in the chlorine molecule? f) What is VSEPR Theory? UNIT: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. Name the following compounds: a) CH 3 CH 3CH 2CH2CH 2CH 2CH 2CHOH b) O CH3CH2C–NH2 ___________________________ ___________________________ O c) H2 C H3C C C H2 O _____________________________ d) ______________________________ CH2CH2OH e) f) _________________________________ _________________________________ 3 Name: SCH4U g) FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 ----------------------------------------------------- h) -----------------------------------------------------2. Draw the structure of the following organic compounds: a) cis-2-butene b) 2, 3 dimethyl hex-1-ene c) 3 pentanol d) 2 butanone e) pentan-1,4-diol 2-ethoxybutane g) 3-methyloctanal h) penta-1,4-dione f) 3. Define the following with examples: a) Alkanes b) Alkenes c) Alkynes d) Cycloalkanes e) Isomers f) Cis and Trans 4. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) 5. a) b) c) Explain the following organic reactions and predict the products with proper equations. Dehydration reaction of a propanol Dehydration reaction of a butanol Condensation reaction of ethanol and a methanol Oxidation reaction of a butanol Oxidation reaction of 2 propanol Hydrogenation reaction of a propanal Hydrogenation reaction of propanone Oxidation of hexanal Oxidation of a ketone Esterification Reaction with examples Synthesizing Amines from Alkyl Halides Physical and Chemical Properties of: Alcohols Aldehydes Ketones 4 Name: d) e) f) g) 6. SCH4U FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 Ether Esters Carboxylic Acid Amines Short Answers: a) How are Alkyl Halides synthesized from Amines? Explain using equations. b) What are Polyalcohol’s? Write any three properties of alcohol group. c) What is Esterification Reaction? Explain the importance of this reaction with examples. d) Draw and name the five structural isomers of hexane (C 6H14) UNIT: THERMODYNAMICS 1. Define the following: 2. Enthalpy b) Specific heat e) Standard enthalpy of reaction i) Thermal Energy j) endothermic 3. 4. 5. c) open system d) closed system f) Hess’s Law g) Bond Energies h) Bond Length k) exothermic l) kinetic energy m) potential energy Describe the relationship between bond length and bond energy? What is a calorimeter? What are the TWO rules for Enthalpy changes? 6. Describe the difference between heat, thermal energy and temperature using examples from your experience. 7. Liquid water at 0°C turns to ice. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain what is occurring using the terms “system,” “surroundings,” “thermal energy,” “potential energy,” and “kinetic energy.” 8. For each of the following, describe which is greater – the potential energy or the kinetic energy. a. A stick of dynamite prior to exploding. b. A space shuttle before launch. c. The soot rising above a campfire. d. The chemicals inside a new battery. 9. For each of the following, identify whether the reaction process is exothermic or endothermic. a. Water evaporating into steam. b. A candle burning. c. The melting of ice. d. The splitting of a nitrogen molecule, N2, into individual atoms. e. Dissolving barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2, in water and observing a temperature decrease in the surroundings. 10. In what ways can a closed system exchange energy with its surroundings? Practice Problems 11. How many J would it take to raise the temperature of 200 grams of water from 5 degree Celsius C to 85 degree Celsius? 12. How many J would problem number 1 be if it was aluminum instead of water? 13. How many grams of copper could be heated from 20 oC to 75 oC if 1200J are applied to it? 14. What is the specific heat capacity of a substance if 750 J caused 100 grams of it to go from 90 oC to 135 oC? 15. For the equation: Na + H2O =NaOH + ½ H2 If 5 grams of sodium is placed into 100 grams of water at 20 oC and the final temperature of the system reaches 5 Name: SCH4U FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 27 oC, calculate the ∆Hrxn 16. For the equation: NaNO3 (s) = NaNO3 (aq) If 20 grams of NaNO3 were placed into 200 grams of water at 22 oC, and the temperature dropped to 12 oC, what is the ∆Hrxn? 17. Given the following equations: 2 H2 + O2 = 2 H2O N2O5 + H2O = 2 HNO3 ½ N2 + 3/2 O2 + ½ H2 = HNO3 ∆Hrxn= -572 kJ ∆Hrxn = -74 kJ ∆Hrxn= -174 kJ Calculate ∆Hrxn for: N2 + 5/2 O2 = N2O5 18. Given the following equations: Sr + ½ O2 = SrO ∆Hrxn= -592 kJ SrO + CO2 = SrCO3 ∆Hrxn= -234 kJ C + O2 = CO2 ∆Hrxn= -394 Calculate the ∆Hrxn for: Sr + C + 3/2 O2 = SrCO3 19. Given the following equations: C + 2 H2 = CH4 ∆Hrxn= -75 kJ C + 2 Cl2 = CCl4 ∆Hrxn= -96 kJ H2 + Cl2 =2 HCl ∆Hrxn= -92 kJ Calculate the∆Hrxn for: CH4 + 4 Cl2 = CCl4 + 4 HCl UNIT: RATE OF REACTION & CHEMICAL EQUILLIBRIUM 1. Define the following: a) Catalyst b) homogeneous catalyst f) activation energy k) rate law g) dynamic Equilibrium d) heterogeneous catalyst h) Rate Constant e) collision theory i) Forward reaction j) Chemical Kinetics l) Colllision model 2. List the five basic factors that control the rate of a chemical reaction, and give an example of each. 3. Two reactant molecules collide with the correct orientation, but their kinetic energy is less than the activation energy of the reaction. Why does an effective collision occur only when reactant entities possess activation energy> 4. Why do so many reactions occur more quickly in solution than when the entities are in other states of matter? 5. What is the relationship between reaction rates and stoichiometry? 6. What are the two important conditions to be met for a reaction to occur? 6 Name: SCH4U FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 7