Fig. S1 Inheritance of salt-resistant phenotype of AT1362 in T3
advertisement

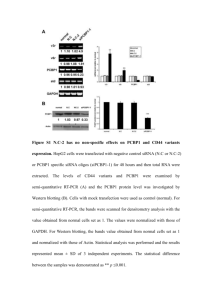
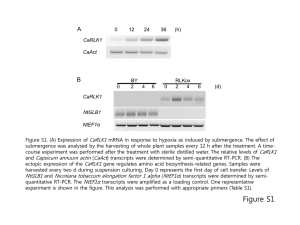
Fig. S1 Inheritance of salt-resistant phenotype of AT1362 in T3 generation. a Germination of WT plants and three independent T2 lines of AT1362 on 140 mM NaCl-containing medium. b Germination ratio of WT plants and three independent T2 lines of AT1362 on 140 mM NaCl-containing medium up to 6 DAG. Fig. S2 Comparison of amino acid sequences between AtSFT12 and other Qc-SNAREs in Arabidopsis. a Phylogenetic tree of Qc-SNAREs in Arabidopsis. Phylogenetic tree was made by ClastalW2 Phylogeny using default parameters. b Multiple alignment of SNARE motif of AtSFT12 with those of 11 other Qc-SNAREs in Arabidopsis. Alignment was made using ClustalW2 with default parameters. Box indicates the 0-layer residue in the center of SNARE motif. Fig. S3 Oxidative stress responses of AtSFT12 OXs and atsft12-2 mutants. a and b Responses of WT and AtSFT12 OX seedlings to 0, 1.5, 2, or 2.5 μM MV. c and d Responses of WT and atsft12-2 seedlings to 0, 1, or 1.5 μM MV. In b and d, error bars represent standard deviation (n = 24 plants). Fig. S4 Salt stress response of atsft12-1. a Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of AtSFT12 transcription levels in 4-week-old WT plants and atsft12-1 mutants. GAPc was used as an internal control. b and c Responses of WT and atsft12-1 seedlings to 0, 130, or 140 mM NaCl. In c, error bars represent standard deviation (n = 24 plants) and * indicate t-test P < 0.05. Fig. S5 Expression patterns of AtSFT12 under abiotic stress conditions. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis in response to 300 mM NaCl (a), cold (b), 100 μM ABA (c), 300 mM mannitol (d), or 10 μM MV (e) treatment for the indicated times. GAPc was used as an internal control. Similar results were obtained from at least two biological replicates, with one shown here. Table S1 List of primers used in this study Gene Forward Reverse Purpose AtSFT12 5′-GTGGTTCTTCTCGTTACCTG-3′ 5′-AGGCCAGATTTGAACTGGTC-3′ Quantitative RT-PCR GAPc 5′-GTGTCCCAACCGTTGATGTC-3′ 5′-TCCCTTGAGTTTGCCTTCGG-3′ Quantitative RT-PCR AtSFT12 5'-AGAGAAGGGCTAAGCACTAG-3' 5'-ATGTTGTTCTTCACCCCTGC-3' Semi-quantitative RT-PCR AtSFT12 mutant 5'-GTCTCACAGGGACTTCTTAG-3' 5′-AGGCCAGATTTGAACTGGTC-3′ Semi-quantitative RT-PCR GAPc 5'-CACTTGAAGGGTGGTGCCAAG-3' 5'-CCTGTTGTCGCCAACGAAGTC-3' Semi-quantitative RT-PCR RD29A 5'-GAAACAGAGTCTGCCGTGAC-3' 5'-TGCTGCCTTCTCGGTAGAGA-3' Semi-quantitative RT-PCR RAB18 5'-AATGCTTCACCGCTCCGGAT-3' 5'-TTCTTCTCGTGGTGCTCACC-3' Semi-quantitative RT-PCR WRKY33 5'-AGATTGTGGGAGTGAACCTG-3' 5'-GACTGAAGACGAATCCTGTG-3' Semi-quantitative RT-PCR AtSFT12 5'-ATAGGATCCATGGCGTCCAATCGCGGTGC-3' 5'-CGCGGTACCCTATCTTTTGAACATCTTGG-3' Cloning LB1 5′-ATGGTCATAGCTGTTTCCTGTGTGAAATTG-3′ TAIL-PCR LB2 5′-AACCTGTCGTGCCAGCTGCATTAATGAATC-3′ TAIL-PCR AD1 5′-NGTCGASWGANAWGAA-3′ TAIL-PCR AD2 5′-TGWGNAGSANCASAGA-3′ TAIL-PCR AD3 5′-AGWGNAGWANCAWAGG-3′ TAIL-PCR AD4 5′-WGTGNAGWANCANAGA-3′ TAIL-PCR LB-seq 5′-CATTAATGAATCGGCCAACG-3′ Sequencing