Fig. S1 Relative expression levels of VaPAT1 in transgenic
advertisement
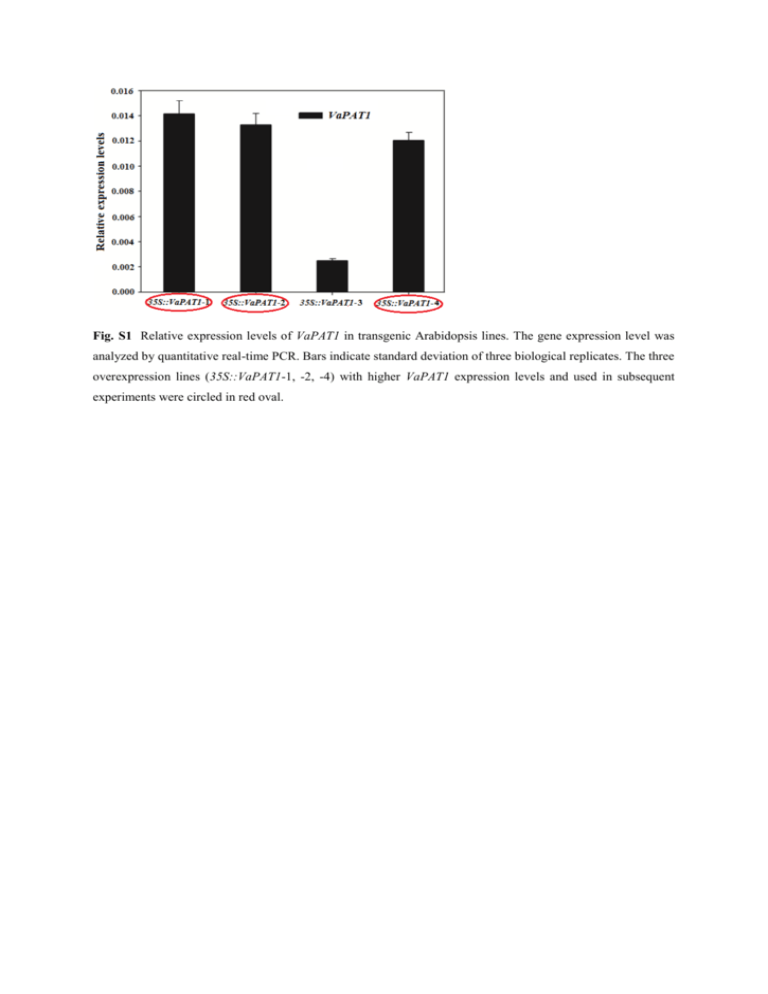
Fig. S1 Relative expression levels of VaPAT1 in transgenic Arabidopsis lines. The gene expression level was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. Bars indicate standard deviation of three biological replicates. The three overexpression lines (35S::VaPAT1-1, -2, -4) with higher VaPAT1 expression levels and used in subsequent experiments were circled in red oval. Fig. S2 MDA concentration, activity of SOD, POD and CAT of WT and VaPAT1 trangenic seedlings in normal growth conditions or exposed to cold (4 °C for 3 d), drought (withholding water for 8 d) and salt (200 mM NaCl for 7 d) stress. Values were the means of three replicates and bars represent the standard errors (n = 3). Table S1. Stress-related genes and their main functions Gene Functions in stress AtSIZ1 (small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) E3 ligase) AtCBF1 Modulate expression, Reference stress-responsive increase genes drought and freezing tolerance (C-repeat/DRE binding Induce COR (cold-regulated) genes factor 1) expression , increase stresses tolerance AtATR1/MYB34 (altered tryptophan response to various phytohormones and regulation 1) salt stress AtMYC2 ( bHLH transcription factor) (responsive dessication 29A) Nakata et al. 2013) to various expression stresses, increases Response to various abiotic stresses via ABA-dependent and -independent pathway AtRD29B (responsive to dessication Response to various abiotic stresses via 29B) ABA-dependent pathway AtProDH1 1) (proline-dehydrogenase (Chen et al. 2006) various biotic and abiotic stresses constitutive to (Novillo et al. 2007) (Abe et al. 2003; freezing tolerance AtRD29A/COR78 Catala et al. 2007) Response to ABA, JA (jasmonate) and Response AtCOR15A (cold-regulated 15A) ( Miura et al. 2007; (Thalhammer et al. 2014) (Miyazaki et al. 2015) (Kim et al. 2014) Catalyze proline metabolism, oxidative (Miguel Cecchini et and drought stress responsive genes al. 2011)