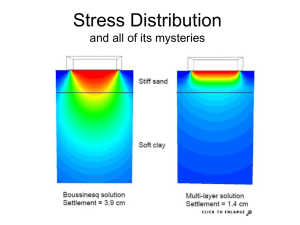
Issues arising from the changing size and distribution of population
advertisement

Issues arising from the changing size and distribution of population including environmental, economic and social impacts… Economic Retro Carrots Befriend Wonderful Drums Resources, Congested, Braindrain, Welfare, Dependants Natural resources become scarcer as more people increase demand. Prices rise which benefits the rich and disadvantages the poor. Quality of life falls as living conditions become congested. This snowballs with effects such as the easy spread of disease and strain on the ecology. Rural populations experience a ‘brain drain’ as skilled workers migrate to cities. Essential services and welfare systems are pushed to the limit. Increased need for additional provisions for the poor. Economic strain on the working population if there is a large dependant population. Social Rude Tingly Sectors Scrape Classy Great Postcards Resource Tension, Shortages, Stresses Crime, Government Planning As resource scarcity and economic inequality increase, social, ethnic and political tensions increase, along with migration and immigration as responses. As resources encounter shortages, transboundary conflict over these resources increases. Instances of antisocial behaviour, crime, social stresses and even suicidal tendencies, increase with population density. Increased pressure on governments to control population size. Makes a dilemma for social planning. Environmental Campbell Will Do Whatever For Senior Prefect Carbon Dioxide, Waste, Desertification, Water, Forests, Soils Increased consumption as more consumers consume… The richest fifth of the population consumes 86% of the world’s goods and services and 53% of greenhouse emissions. Per capita industrial waste grew 30% in industrial nations since 1975 and is now 5 times the level of developing nations Spreading deserts and declining water tables in one-third of the planet are contributing to famine, social unrest and migration. Two thirds of the world’s population lives within 60km of an ocean, inland sea or freshwater lake. The impact includes increasing amounts of sewage, drainage of wetlands, destruction of prime fish nurseries and development of beaches. 300000000 people live in regions that already have water shortages. By 2025, the number could be 3000000000. The world’s forests have shrunk from 11.4 to 7.3 square kilometers per 1000 people since 1970. This is due to the demands of developing nations to meet the demands for wood and paper by the industrial world. Over the last 50 years, 17% of the planets soils have been severely degraded. That is nearly 2000000000 ha, the size of China and India combined. Taken from Macmillan Geography 1