GE Area: C: Department: Term/Year: GEO Area Outcomes GEO 1
advertisement

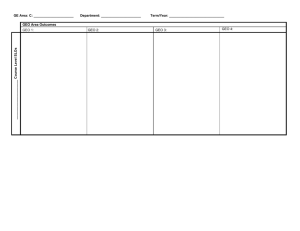
GE Area: C: _____________________ Department: _____________________ Term/Year: _____________________________ GEO Area Outcomes _____________________ Course Level SLOs GEO 1: GEO 2: GEO 3: GEO 4: EXAMPLE: (NOTE: There are a large number of course outcomes associated with each GE outcome in this example. That’s likely not going to be true for most courses. Also note that the mapping might not be great and will facilitate discussion and updates at both the GE and course outcome levels.) GE Area: C: Natural Sciences Department: Earth Sciences Term/Year: Fall 2012 GEO Area C Outcomes GEO 1: communicate scientific ideas and theories effectively GEO 2: demonstrate an understanding of the GEO 3: apply models to explain the behavior of commonly occurring phenomena scientific method Geology 10 Course Level SLOs Diagram and explain features and processes associated with each type of plate boundary. Compare and contrast minerals and the three main rock types and their relationship to the rock cycle and natural geologic processes. Identify, classify, and interpret the formation history of common rock-forming minerals, and igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Compare and contrast the various types of volcanoes ~ their geologic settings, eruptive style, and associated landforms and hazards. Experience and be able to demonstrate the magnitude of geologic time. Synthesize various data points and natural phenomena to understand the origin of the Earth. Diagram and evaluate the structure of the Earth's interior, including physical and chemical layers, heat, magnetic fields, and gravity and the data that support this understanding. Synthesize various data points and natural phenomena to understand the origin of the Earth. Evaluate and interpret the model of Plate Tectonics based on global geologic phenomena and features. GEO 4: evaluate how measurement errors impact the application of scientific models Use the principles of relative and radiometric dating to interpret the geologic history of a sequence of rocks and structures. Diagram, define, and analyze the environments that produce stress and the resulting deformation (elastic rebound, folds, and faults). Compare and contrast the origins, hazards, and consequences of earthquakes that occur in different geologic settings globally. Diagram and evaluate the structure of the Earth's interior, including physical and chemical layers, heat, magnetic fields, and gravity and the data that support this understanding. Diagram and evaluate the formation of continents through accretion of terranes and use this understanding to interpret the variations in continental materials worldwide. Relate rock weathering, mass wasting, streams, glaciers, and waves to the development of major geologic features and phenomena. Evaluate the effects of how humans interact with and try to control a variety of geologic processes such as rivers flooding and sand movement on beaches. 2|Page