4.04 Identifying Rocks Worksheet
advertisement

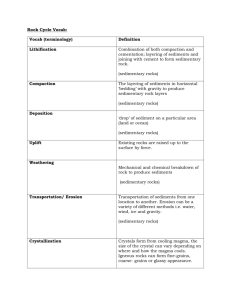
Janai Otero Gregory Mathis 4.04 Identifying Rocks Worksheet Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks are formed when lava cools underground. They are also formed when volcanoes erupts causing the magma to rise to the top of the earth’s surface. The specific name for the rock formed when lava cool and hardens below the earth’s surface is an extrusive and intrusive igneous rock. The crystal size compare in extrusive vs. intrusive rock have different process. For intrusive rock are characterized by large crystal size, well their appearance shows individual crystals interlocked together to form the mass. Extrusive rocks are formed from magma at or above the surface of the earth, and normally display smaller minerals crystals or no crystals at all, because of cooling environment in which they form. The obvious difference between the two are the crystal size, intrusive rocks have a large crystal/grain texture due to slow cooling of magma below the earth surface which boots the growth of large crystals, while extrusive rocks, because of the fast cooling at/ above the earth’s surface does the opposite. Intrusive rocks are formed inside the earth. Extrusive rocks cool from lava and are formed outside of the earth. Sedimentary Rocks: Sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments is stashed out of air, ice, wind, gravity, or water flow carrying the particles in termination. The name of an impression formed when tiny plans or animals become trapped between sediment layers become a cast. Three examples or sedimentary rocks: Some sedimentary rocks are formed from bits of other rocks. Some are formed from bits that were once part of living things. Another way that sedimentary rocks are formed is from minerals that dissolve in water. Over time, after the water evaporates, just the mineral crystals are left behind as sediment. Metamorphic Rocks: Metamorphic rocks are formed when sedimentary, igneous, or another metamorphic rock are physically deformed and chemically changed due to different temperatures and pressure. Igneous and sedimentary rocks become metamorphic rock as a result of intense heat from magma and pressure from tectonic shifting. Although the rock becomes extremely hot and under a great deal of pressure it does not melt. Limestone: Over time, after the water evaporates, just the mineral crystals are left behind as sediment. Sandstone: Sandstone is a very soft sedimentary rock that breaks easily. When you break a piece off, you can feel the grains of sand that make up sandstone. Shale: Shale is actually composed of mud and clay that has collected underwater. Granite: It is an intrusive rock, meaning that it crystallized from magma that cooled far below the earth's surface. Sample Foliation Intrusive/ Extrusive Fossils Texture Metamorphic/ Sedimentary/ Igneous Name of Rock Example No Extrusive No Coarse Igneous Diorite 1 No Intrusive No Coarse Granite Diorite 2 No Extrusive No Fine Basalt 3 Yes Intrusive No Coarse Gneiss 4 No N/A Yes Nongrained Limestone