2008 prelims – litho
advertisement
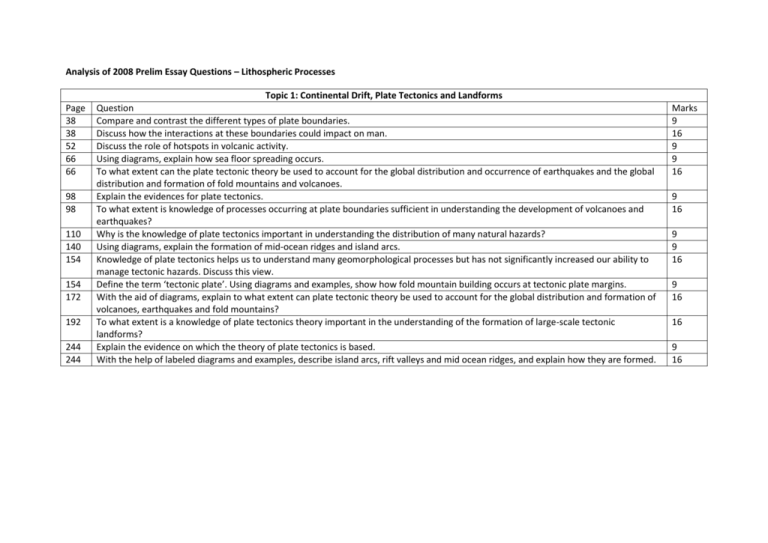
Analysis of 2008 Prelim Essay Questions – Lithospheric Processes Page 38 38 52 66 66 98 98 110 140 154 154 172 192 244 244 Topic 1: Continental Drift, Plate Tectonics and Landforms Question Compare and contrast the different types of plate boundaries. Discuss how the interactions at these boundaries could impact on man. Discuss the role of hotspots in volcanic activity. Using diagrams, explain how sea floor spreading occurs. To what extent can the plate tectonic theory be used to account for the global distribution and occurrence of earthquakes and the global distribution and formation of fold mountains and volcanoes. Explain the evidences for plate tectonics. To what extent is knowledge of processes occurring at plate boundaries sufficient in understanding the development of volcanoes and earthquakes? Why is the knowledge of plate tectonics important in understanding the distribution of many natural hazards? Using diagrams, explain the formation of mid-ocean ridges and island arcs. Knowledge of plate tectonics helps us to understand many geomorphological processes but has not significantly increased our ability to manage tectonic hazards. Discuss this view. Define the term ‘tectonic plate’. Using diagrams and examples, show how fold mountain building occurs at tectonic plate margins. With the aid of diagrams, explain to what extent can plate tectonic theory be used to account for the global distribution and formation of volcanoes, earthquakes and fold mountains? To what extent is a knowledge of plate tectonics theory important in the understanding of the formation of large-scale tectonic landforms? Explain the evidence on which the theory of plate tectonics is based. With the help of labeled diagrams and examples, describe island arcs, rift valleys and mid ocean ridges, and explain how they are formed. Marks 9 16 9 9 16 9 16 9 9 16 9 16 16 9 16 Topic 2: Volcanoes and Earthquakes Page 2 2 18 18 66 84 110 110 172 206 218 218 230 230 258 Page 2 38 84 140 206 Question Describe the nature of the erupted materials from a volcano and explain how they may be hazardous. Using examples, explain why volcanic hazards have more severe effects in some areas than others. Explain how earthquake magnitude and intensity can be measured. With reference to specific examples, assess the extent to which volcanic hazards and its impacts can be mitigated. Discuss, with reference to an example or examples, the problems of managing an environment prone to tectonic hazards and of responding to the effects of the hazards. Assess the strategies used to mitigate and respond to the effects of volcanic eruptions. Describe and account for the differences between the types of volcanoes found at convergent and divergent plate boundaries. To what extent is it possible to predict earthquakes and to limit their hazardous effects? With reference to one specific type of tectonic or geomorphological hazard, evaluate the attempts to predict and limit its effects on the environment. Distinguish between the Richter Scale and the Mercalli Scale. Briefly describe the nature and effects of earthquakes. With reference to relevant examples, assess the effectiveness of various earthquake mitigation strategies. Describe the main characteristics of seismic waves and their immediate effects at or near the ground surface. With reference to examples, discuss the view that the largest earthquakes are not always the most deadly and damaging. To what extent can earthquakes be predicted and its effects reduced? Topic 3: Rock Cycle Question Compare and contrast the characteristics of the three rock types. Compare and contrast igneous and sedimentary rocks and their responses to weathering. Explain the formation of various tock types. What is the rock cycle? Show how the rock cycle explains the formation and characteristics of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Discuss the differences between igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Marks 9 16 9 16 16 16 9 16 16 9 9 16 9 16 16 Marks 9 9 9 9 9 Topic 4: Weathering Page 2 140 180 180 192 192 206 218 230 258 Question Using examples, discuss the extent to which the weathering of a rock is dependent upon climate. With the use of examples, explain the extent to which climate is influential in the development of block and granular disintegration of rocks. Explain the differences between chemical weathering and physical weathering. How true is it that weathering is mainly physical in dry climates and mainly chemical in wet climates? Explain the conditions under which block disintegration, spheroidal weathering and exfoliation may occur. To what extent is the distribution of weathering types across the world’s regions determined by climate? “Rock structure may not be the most significant factor affecting weathering but it plays an important role.” Discuss. Describe the weathering process in Humid Tropical and Low Latitude Desert areas and its impact on rock structure. Compare the characteristics of the following: i) granite and basalt ii) joints and bedding planes iii) block disintegration and granular disintegration Compare the processes of chemical weathering and physical (mechanical) weathering. Marks 16 16 9 16 9 16 16 9 9 9 Topic 5: Limestone and Granite Landscapes Page 18 52 98 98 110 124 124 154 180 230 244 258 Question To what extent can rock composition and structure account of the nature of weathering and landforms in granitic rocks. Assess the extent to which rock characteristics determine the landforms in granite areas. Explain the characteristics of granite and limestone. Evaluate the role of rock jointing in the development of granite landforms. To what extent is geological structure important in the determination of landforms found in limestone areas. Compare and contrast the characteristics of granite and limestone. Using examples, discuss the extent to which rock characteristics may account for the structural differences between granite and limestone landscapes. Identify and suggest reasons for the contrasts between weathering processes in tropical regions. Assess the extent to which these weathering processes contribute to the formation of either granite or limestone landforms in the tropical environments. Describe the landforms commonly found in regions of granite and briefly explain how they have been formed. Describe the characteristics of weathering profile and discuss its role in the development of landforms in granite. Giving examples, explain the extent to which weathering processes have contributed to the formation of either granite or limestone landforms in the humid tropics. To what extent does climate play a role in affecting the weathering of granite and its resultant landforms? Marks 16 16 9 16 16 9 16 16 16 16 16 16 Topic 6: Mass Movement Page 18 38 52 52 66 84 84 124 124 140 180 206 218 244 Question Explain the causes of hazardous mass movements. Discuss the role of man in mass movements. Explain the factors determining the stability of a slope. With reference to examples, assess the strategies used to manage mass movement hazards. Using diagrams, explain the difference between a rock slide, a mud flow and soil creep. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms. i) convergent and divergent boundaries ii) carbonation and oxidation iii) shear strength and shear stress Assess the strategies used to mitigate and respond to the effects of mass movement. Explain the role of climate in the occurrence of mass movements. Using examples, discuss the extent to which man is in control of mass wasting hazards. How do rapid mass movements occur? Assess the strategies used to mitigate the effects of hazards associated with rapid mass movements. Briefly define the term ‘mass movement’ as applied to slopes. Discuss the effects of mass movement and assess to what extent these effects can be mitigated. Illustrate your answer with example or examples. With reference to examples, discuss the effects of mass movement and assess the strategies used to mitigate its impact on the human and physical landscape. Explain the processes that could bring about a landslide and describe the circumstances under which it might become hazardous. Marks 9 16 9 16 9 9 16 9 16 16 9 16 16 9








