Concept 4: Sample
advertisement
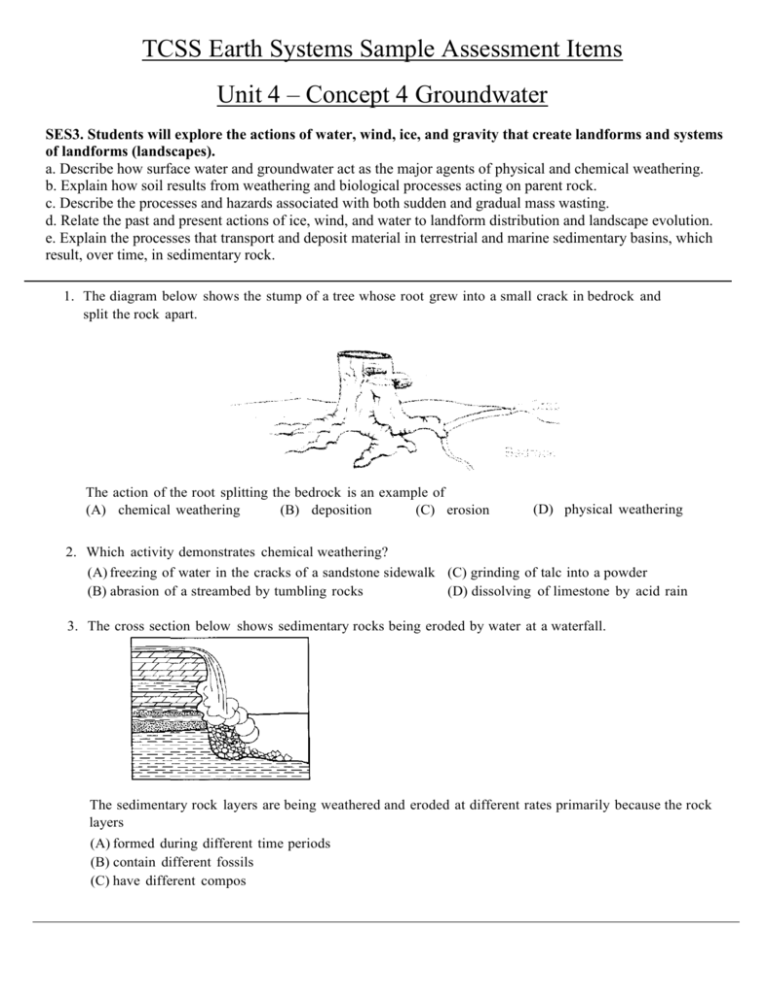
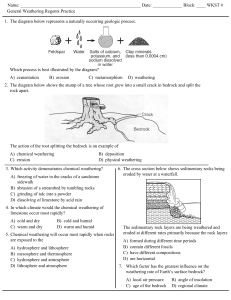
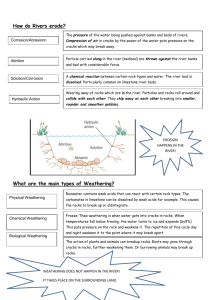
TCSS Earth Systems Sample Assessment Items Unit 4 – Concept 4 Groundwater SES3. Students will explore the actions of water, wind, ice, and gravity that create landforms and systems of landforms (landscapes). a. Describe how surface water and groundwater act as the major agents of physical and chemical weathering. b. Explain how soil results from weathering and biological processes acting on parent rock. c. Describe the processes and hazards associated with both sudden and gradual mass wasting. d. Relate the past and present actions of ice, wind, and water to landform distribution and landscape evolution. e. Explain the processes that transport and deposit material in terrestrial and marine sedimentary basins, which result, over time, in sedimentary rock. 1. The diagram below shows the stump of a tree whose root grew into a small crack in bedrock and split the rock apart. The action of the root splitting the bedrock is an example of (A) chemical weathering (B) deposition (C) erosion (D) physical weathering 2. Which activity demonstrates chemical weathering? (A) freezing of water in the cracks of a sandstone sidewalk (C) grinding of talc into a powder (B) abrasion of a streambed by tumbling rocks (D) dissolving of limestone by acid rain 3. The cross section below shows sedimentary rocks being eroded by water at a waterfall. The sedimentary rock layers are being weathered and eroded at different rates primarily because the rock layers (A) formed during different time periods (B) contain different fossils (C) have different compos 4. The diagram below shows granite bedrock with cracks. Water has seeped into the cracks and frozen. The arrows represent the directions in which the cracks have widened due to weathering. Which statement best describes the physical weathering shown by the diagram? (A) Enlargement of the cracks occurs because water expands when it freezes. (B) This type of weathering occurs only in bedrock composed of granite. (C) The cracks become wider because of chemical reactions between water and the rock. (D) This type of weathering is common in regions of primarily warm and humid climates.