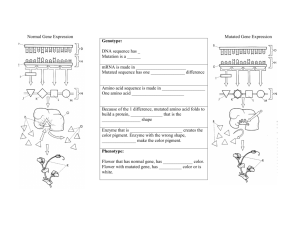
Chapter 10 Reminders
advertisement
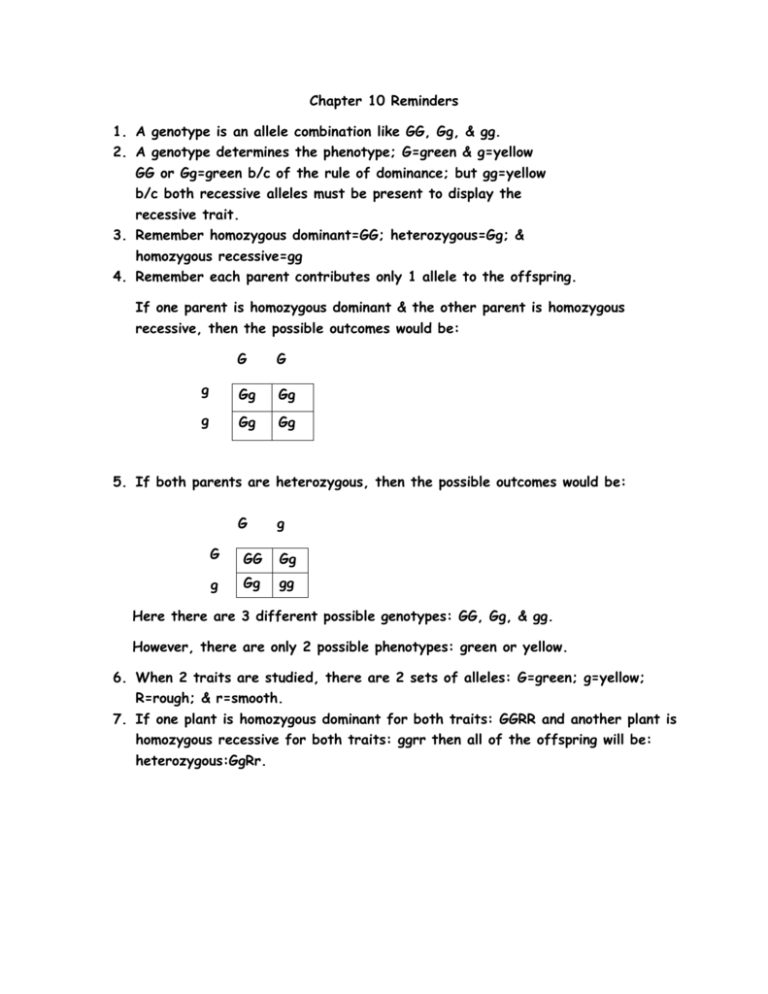
Chapter 10 Reminders 1. A genotype is an allele combination like GG, Gg, & gg. 2. A genotype determines the phenotype; G=green & g=yellow GG or Gg=green b/c of the rule of dominance; but gg=yellow b/c both recessive alleles must be present to display the recessive trait. 3. Remember homozygous dominant=GG; heterozygous=Gg; & homozygous recessive=gg 4. Remember each parent contributes only 1 allele to the offspring. If one parent is homozygous dominant & the other parent is homozygous recessive, then the possible outcomes would be: G G g Gg Gg g Gg Gg 5. If both parents are heterozygous, then the possible outcomes would be: G g G GG Gg g Gg gg Here there are 3 different possible genotypes: GG, Gg, & gg. However, there are only 2 possible phenotypes: green or yellow. 6. When 2 traits are studied, there are 2 sets of alleles: G=green; g=yellow; R=rough; & r=smooth. 7. If one plant is homozygous dominant for both traits: GGRR and another plant is homozygous recessive for both traits: ggrr then all of the offspring will be: heterozygous:GgRr. 8. If 2 heterozygous plants cross pollinate(GgRr x GgRr), then the possible outcomes would be: GR GR Gr gR gr GGRR GGRr GgRR GgRr Gr GGRr GGrr GgRr Ggrr gR GgRR GgRr ggRR ggRr GgRr Ggrr ggRr ggrr gr 9. There are many possible genotypes, but only 4 phenotypes: Green, rough; green, smooth; yellow, rough; & yellow smooth. The red squares (9 out of 16) represent the genotypes that result in the phenotypes: green, rough. The green squares (3 out of 16) represent the genotypes that result in the phenotypes: green, smooth. The yellow squares (3 out of 16) represent the genotypes that result in the phenotypes: yellow, rough. The blue square (1 out of 16) represents the genotype that results in the phenotype: yellow, smooth.