Macromolecule Station Introduction
advertisement

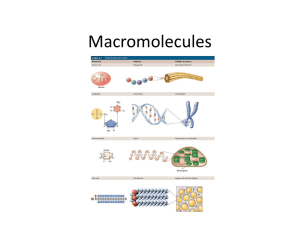
Name: ______________________________ Macromolecule Stations We ALL start here: Block: ____ Do Now: What is the importance of knowing that a large percentage of our body is made of C, H, O, and N? How does this knowledge impact our daily lives? Brainstorming: Explain/conclude what do you think may be happening to the proteins in the frying egg? Use you prior knowledge to answer to the best of your ability. Hint: think about “homeostasis” Carbon Compounds- Close Reading/ Annotate: Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon compounds are also called organic compounds. Many of the molecules in living things are so large that they are known as macromolecules. Macromolecules are formed in a process called polymerization. Smaller units, called monomers, join together to form macromolecules, or polymers. Four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals use carbohydrates in structures. Starches and sugars are examples of carbohydrates. Lipids are made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms. Fats, oils, and waxes are lipids. Lipids are used in living things to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. Lipid molecules are made up of compounds called fatty acids and glycerol. Nucleic acids contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus. Nucleotides are the monomers that make up nucleic acids. Each nucleotide consists of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Proteins contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some are used Important Vocabulary Macromolecule Characteristics and Examples Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids to form bones and muscles. Others transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease. What Macromolecules Are In My Food? Analyze the food label below and answer the following questions: 1. What food is this nutrition label from? 2. What macromolecules are found in this food? 3. What type lipid is found in this food? 4. What macromolecule does cholesterol belong to? 5. What polysaccharide does this food have to help us move things through our digestive system and in what percentage? 6. Based on the percentages, what biological functions would this food mainly help us with? Biochemistry Stations Pick your station…… Directions: Review the information below. Pick the station you are comfortable with and begin your challenge. Complete the worksheets in the station of your choice. Station 1: Organic Molecules Worksheet – Independent Discovery! This station requires the application of your knowledge of macromolecules as well as an introduction to macromolecules not yet discussed in class. You are expected to read the worksheet and apply past biology knowledge to discover new biology concepts at a higher level of understanding of macromolecules. Station 2: Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms – Deeper Understanding using more “visuals” This station allows you to review macromolecules at a deeper level. In addition it helps you to visualize the molecules in a structured format different than what was done in class. This station introduces new macromolecules in the same manner. You are expected to take your prior knowledge as well as the new knowledge learned from the packet to uncover the properties and function of macromolecules not yet discussed in class. Station 3: Organic Molecules Worksheet – Getting Down to the Basics – Independent Research This station requires you to search independently to discover and review macromolecules. You are expected to use any resource you are comfortable with. Independent research will help you to know how to become more resourceful as well as be able to identify important facts. This is an important skill to develop to further your further individual advancement academically. Once you have completed your “station work” submit your packet and ask me “what is next???” Reflection: How well do you understand macromolecules? Explain your answer. CONCLUSION: Complete the following once you have completed your station work. Protein Review Questions: 1, Fertilizers containing radioactive nitrogen compounds are used in growing experimental plants. In which molecules would these compound be detected first? A) sugar B) starch C) proteins D) fats 2. Amino acids are required in the human diet principally for the synthesis of A) proteins B) sugars C) starches D) lipids 3. A sample of small, soluble, organic molecules was analyzed and found to contain the elements carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. It is most likely that the molecules were A) lipids B) fatty acids C) simple sugars D) amino acids 4. The process by which amino acids are chemically joined together is called a. Pinocytosis b. Hydrolysis c. Nitrogen fixation d. Dehydration synthesis 5. Which a. b. c. d. substance is classified as a protein? Sucrose Glycerol Starch Hemoglobin 6. Which type of organic compound has molecules that include both an amino group and a carboxyl group? a. Alcohols b. Proteins c. Carbohydrates d. Lipids 7. Two side groups which are characteristics of all amino acids are a. –OH and –COOH b. –CH3 and –OH c. –NH2 and –COOH d. –NH2 and –CH2OH 8. Which represents a peptide bond? a. –C-Cb. –C-Nc. –N=O d. –O-O9. What occurs when a peptide bond forms between two amino acids? a. Oxygen is released b. Water is released c. Oxygen is added d. Water is added 10. Which a. b. c. d. type of chemical reaction is indicated by this equation? Oxidation Hydrolysis Dehydration synthesis Decomposition Draw and Label dehydration synthesis of a dipeptide. Be sure to label ALL molecules. Draw and Label hydrolysis of a tripeptide. Be sure to label ALL molecules. Summary of Understanding: Create a Pyramid of Knowledge on Macromolecule. To be completed after ALL stations. 1st: 1 thing all macromolecules have in common 2nd: 2 ways that these molecules are made and broken 3rd: 3 biological functions macromolecules have 4th: 4 types of macromolecules 5th: 5 things I learned about macromolecules