Outcome 1: Health (off-line template)
advertisement
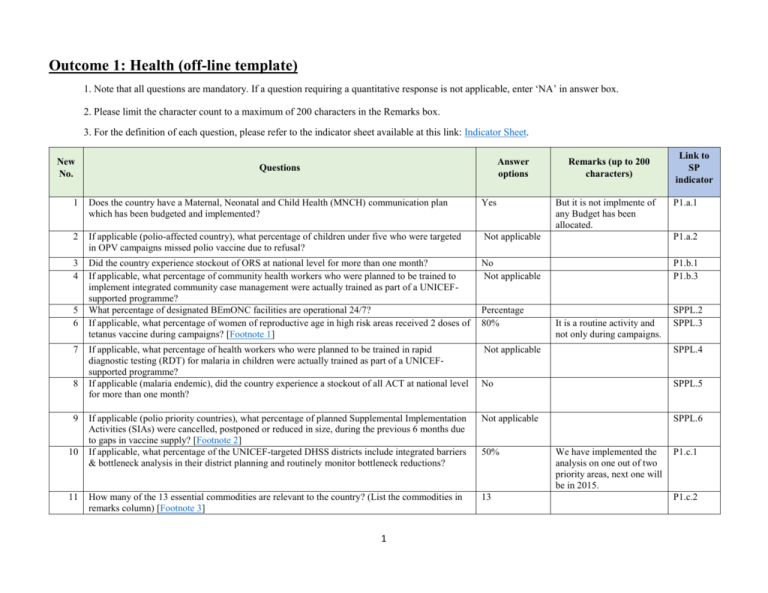
Outcome 1: Health (off-line template) 1. Note that all questions are mandatory. If a question requiring a quantitative response is not applicable, enter ‘NA’ in answer box. 2. Please limit the character count to a maximum of 200 characters in the Remarks box. 3. For the definition of each question, please refer to the indicator sheet available at this link: Indicator Sheet. New No. Answer options Questions Remarks (up to 200 characters) 1 Does the country have a Maternal, Neonatal and Child Health (MNCH) communication plan which has been budgeted and implemented? Yes 2 If applicable (polio-affected country), what percentage of children under five who were targeted in OPV campaigns missed polio vaccine due to refusal? Not applicable P1.a.2 3 4 Did the country experience stockout of ORS at national level for more than one month? If applicable, what percentage of community health workers who were planned to be trained to implement integrated community case management were actually trained as part of a UNICEFsupported programme? What percentage of designated BEmONC facilities are operational 24/7? If applicable, what percentage of women of reproductive age in high risk areas received 2 doses of tetanus vaccine during campaigns? [Footnote 1] No Not applicable P1.b.1 P1.b.3 Percentage 80% SPPL.2 SPPL.3 If applicable, what percentage of health workers who were planned to be trained in rapid diagnostic testing (RDT) for malaria in children were actually trained as part of a UNICEFsupported programme? If applicable (malaria endemic), did the country experience a stockout of all ACT at national level for more than one month? Not applicable SPPL.4 No SPPL.5 If applicable (polio priority countries), what percentage of planned Supplemental Implementation Activities (SIAs) were cancelled, postponed or reduced in size, during the previous 6 months due to gaps in vaccine supply? [Footnote 2] If applicable, what percentage of the UNICEF-targeted DHSS districts include integrated barriers & bottleneck analysis in their district planning and routinely monitor bottleneck reductions? Not applicable SPPL.6 How many of the 13 essential commodities are relevant to the country? (List the commodities in remarks column) [Footnote 3] 13 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 50% But it is not implmente of any Budget has been allocated. Link to SP indicator It is a routine activity and not only during campaigns. We have implemented the analysis on one out of two priority areas, next one will be in 2015. P1.a.1 P1.c.1 P1.c.2 New No. 12 Answer options Questions Out of the essential commodities that are relevant to the country, how many are registered with the relevant regulating authority? (List the commodities in remarks column) 2 13 Remarks (up to 200 characters) Reproductive Health Female Condoms - used for Family Planning & Contraception Contraceptive Implants used for Family Planning & Contraception Emergency Contraception used for Family Planning & Contraception Maternal Health Oxytocin - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage Misoprostol - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage Magnesium Sulfate - used for treatment of Eclampsia & Severe PreEclampsia/Toxemia of Pregnancy Newborn Health Injectable Antibiotics used for treatment of Newborn Sepsis Antenatal Corticosteroids (ANCS) - used for treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome for preterm babies Chlorhexidine - used for Newborn Cord Care Resuscitation Equipment used for treatment of Newborn Asphxia Link to SP indicator P1.c.2 New No. 13 Answer options Questions Out of the essential commodities that are relevant to the country, how many have guidelines on their use in facilities and communities? (List the commodities in remarks column) 3 13 Remarks (up to 200 characters) Child Health Amoxicillin - used for treatment of Pneumonia Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) - used for treatment of Diarrhea Zinc - used for treatment of Diarrhea Reproductive Health Female Condoms - used for Family Planning & Contraception Contraceptive Implants used for Family Planning & Contraception Emergency Contraception used for Family Planning & Contraception Maternal Health Oxytocin - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage Misoprostol - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage Magnesium Sulfate - used for treatment of Eclampsia & Severe PreEclampsia/Toxemia of Pregnancy Newborn Health Injectable Antibiotics used for treatment of Newborn Sepsis Link to SP indicator P1.c.2 New No. Answer options Questions Remarks (up to 200 characters) Link to SP indicator Antenatal Corticosteroids (ANCS) - used for treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome for preterm babies Chlorhexidine - used for Newborn Cord Care Resuscitation Equipment used for treatment of Newborn Asphxia Child Health Amoxicillin - used for treatment of Pneumonia Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) - used for treatment of Diarrhea Zinc - used for treatment of Diarrhea 14 If applicable, is there a national policy supporting community health worker treatment of children with pneumonia with antibiotics? Does the country have a national Maternal, Neonatal and Child Health (MNCH) implementation plan (as a whole plan or as a Maternal Roadmap, Newborn Action Plan, Child Health Strategy) that is costed? Not applicable 16 Has the country implemented a policy for home visits of newborns in line with WHO/UNICEF Joint Statement on Home Visits for the Newborn Child? [Footnote 4] Yes 17 Has the country mainstreamed risk reduction/resilience, inclusive of climate change into national Health or MNCH plans/strategies? No P1.c.6 18 Has the country implemented a policy on Focused Antenatal Care that fulfils all components of the essential elements of a focused approach to antenatal care? [Footnote 5] Yes SPPL.7 19 Did the country produce (or update) and disseminate a national RMNCH management scorecard? [Footnote 6] Yes SPPL.8 15 4 No P1.c.3 Initial plan budget is not updated, once national balance is ready it will be updated. Policy approved, currently guidelines approval is ongoing, and focus will be in pregnant women and newborn. P1.c.4 P1.c.5 New No. 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 27a 27b 27c 27d 27e Answer options Questions If applicable (cholera endemic or at risk for cholera), did the country have in place a national comprehensive multi-sectoral cholera preparedness plan that covers all components listed in the Cholera Toolkit? [Footnote 7] Does the country have national health, family planning and/or other relevant multi-sectoral annual plans/strategies with budget allocated for preventing pregnancy and poor reproductive outcomes among adolescent girls? Did the country produce an analysis of gender gaps in the estimated versus expected infant and child mortality rates? How many papers has UNICEF country office authored or co-authored in peer-reviewed journal on maternal, newborn, child or adolescent health? Did the country conduct a launch of A Promise Renewed followed by annual reviews? Not applicable Did you receive technical assistance from the regional office or HQ in the area of health? If applicable, how would you rate the usefulness of technical guidance and/or support from Regional Office and HQ through all modes on a scale of 1 to 5 (1 being very poor, 2 being poor, 3 Satisfactory, 4 Good and 5 Very good)? Humanitarian Responses [If Q.27 is Yes, Q.27a to 27f will be displayed] Did the country office respond to humanitarian situations (regardless of scale), including new and ongoing situations? Yes 3 What is the number of UNICEF-targeted children 6-59 months for vaccination for measles in humanitarian situations? (Provide disaggregated data for girls in the remarks column, if available.) How many of those children 6-59 months were vaccinated for measles in humanitarian situations? (Provide disaggregated data for girls in the remarks column, if available.) What is the number of UNICEF-targeted children 6 month -15 years for vaccination for measles in humanitarian situations? (Provide disaggregated data for girls in the remarks column, if available.) How many of those children 6 month -15 years were vaccinated for measles in humanitarian situations? (Provide disaggregated data for girls in the remarks column, if available.) What is the number of UNICEF-targeted families to receive 2 ITNs in humanitarian situations? 5 Yes Remarks (up to 200 characters) Link to SP indicator P1.d.1 Budget form supplies is provided by UNFPA Yes P1.e.1 P1.e.2 P1.f.1 Yes No P1.f.2 P1.d.2 Number CSD program responded to Nutrition and WASH emergencies. PAHO takes the lead for health emergencies, this year UNICEF intervention was not needed on health in emergencies. NA Number NA P1.d.2 Number NA P1.d.2 Number NA P1.d.2 Number NA P1.d.3 P1.d.2 New No. 27f Answer options Questions How many of those families received 2 ITNs in humanitarian situations? Number Remarks (up to 200 characters) NA Link to SP indicator P1.d.3 Footnote 1 High Risk Areas for MNT are defined as the geographic areas where analysis of composite indicators such as immunization, reproductive health (ANC, skilled birth attendants), surveillance and socio-economic status provide sufficient evidence that supports likelihood of more than one neonatal tetanus case per 1,000 live births in a district or similar administrative unit in a year. High risk areas nationally defined by country. Footnote 2 Planned as per the Financial Resource Requirements (FRR), or related to rounds not in the FRR, but for which vaccine was ordered on basis of consensus and at least 6 weeks before the campaign. Footnote 3 13 UN Life Saving Commodities are: Female Condoms - used for Family Planning & Contraception; Contraceptive Implants - used for Family Planning & Contraception; Emergency Contraception - used for Family Planning & Contraception; Oxytocin - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage; Misoprostol - used for treatment of Post-partum Hemorrhage; Magnesium Sulfate - used for treatment of Eclampsia & Severe Pre-Eclampsia/Toxemia of Pregnancy; Injectable Antibiotics - used for treatment of Newborn Sepsis; Antenatal Corticosteroids (ANCS) - used for treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome for preterm babies; Chlorhexidine - used for Newborn Cord Care; Resuscitation Equipment - used for treatment of Newborn Asphxia; Amoxicillin - used for treatment of Pneumonia; Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) used for treatment of Diarrhea; Zinc - used for treatment of Diarrhea Footnote 4 For the WHO/UNICEF Joint Statement on Home Visits for the Newborn Child, please see http://www.unicef.org/spanish/health/files/WHO_FCH_CAH_09.02_eng.pdf Footnote 5 • Identification and surveillance of the pregnant woman and her expected child • Recognition and management of pregnancy-related complications, particularly pre-eclampsia • Recognition and treatment of underlying or concurrent illness • Screening for conditions and diseases such as anaemia, STIs (particularly syphilis), HIV infection, mental health problems, and/or symptoms of stress or domestic violence • Preventive measures, including tetanus toxoid immunisation, de-worming, iron and folic acid, intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy (IPTp), insecticide treated bednets (ITN) • Advice and support to the woman and her family for developing healthy home behaviours and a birth and emergency preparedness plan to: Increase awareness of maternal and newborn health needs and self-care during pregnancy and the postnatal period, including the need for social support during and after pregnancy; Promote healthy behaviours in the home, including healthy lifestyles and diet, safety and injury prevention, and support and care in the home, such as advice and adherence support for preventive interventions like iron supplementation, condom use, and use of ITN; Support care seeking behaviour, including recognition of danger signs for the woman and the newborn as well as transport and funding plans in case of emergencies; Help the pregnant woman and her partner prepare emotionally and physically for birth and care 6 of their baby, particularly preparing for early and exclusive breastfeeding and essential newborn care and considering the role of a supportive companion at birth; Promote postnatal family planning/birth spacing Footnote 6 "This is a scorecard tracking indicators for a range of RMNCH interventions at the sub-national level that is updated periodically and disseminated to local officials so they can take action. A dozen countries in Africa have a version of this with TA from ALMA, but similar scorecards exist in other countries. See: http://www.alma2015.org/scorecards-and-reports/map; http://www.unicef.org/india/1._RMNCHAStrategy.pdf Annexure 2; http://www.mchip.net/sites/default/files/RMNCH+A%20Highlight%20-%20Scorecards%20in%20Jharkhand.pdf Footnote 7 Components of a comprehensive multi-sectoral cholera plan are Co-ordination, institutional framework and information management; Cholera preparedness and response plan; Policies, strategies, guidelines, standards and standard operating procedures; Community preparedness; Surveillance & early warning; Supplies/stockpiles; Communication strategy and plan; Human resources; and Resource mobilisation. For details, please see Figure 6 (page 77) in the Cholera Toolkit: http://www.unicef.org/cholera_toolkit/Cholera-Toolkit-2013.pdf 7