Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass and Radiometric Dating
advertisement

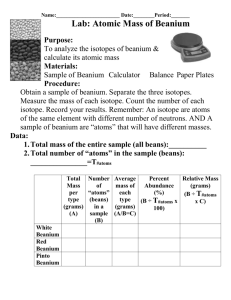
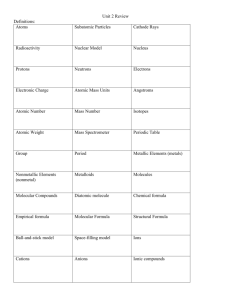
SCH3U Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass and Radiometric Dating 2014 Name: ____________________________________ Knowledge A. B. Inquiry Date: ___________________________ Communication Applications The Development of Atomic Theory. (Refer to pages 14-16 for Mendeleev, Döbereiner, page 27 for Soddy and pages 24-25 for Bohr and Rutherford). A Scientist Mendeleev B Soddy C Bohr D Döbereiner E Rutherford Work The first scientist to see trends in the physical properties of elements and grouped them into triads (ex Li, K & Na) Used the Gold Foil experiment to determine that atoms have very tiny, positively charged nuclei Discovered that atoms could have varying numbers of protons and coined the term “isotope” Used spectroscopy experiments to determine the energy levels and electron arrangement of atoms Created the first periodic table – using physical properties to place elements into groups and ordering elements by atomic mass. Atomic data 1. Complete this table: symbol 1 1H 2 1H 4 2He 7 3Li 18 8O p+1 n0 e-1 symbol 39 19K 88 38Sr 235 92U 239 94Pu 37 17Cl p+1 n0 e-1 2. Give the numbers of neutrons, protons, and electrons in the atoms of each of the following isotopes: a) Carbon-14 b) Radium-222 c) Uranium-238 d) Iodine-131 3. Write the symbols of the isotopes that contain the following. a) An isotope of silver whose atoms have 63 neutrons b) An isotope of cobalt whose atoms have 33 neutrons c) An isotope of strontium whose atoms have 62 neutrons d) An isotope of oxygen whose atoms have 8 neutrons 1 C. Periodic table term A group B C E Noble gases Representative elements Alkali Earth Metals Actinides F Period G H Lanthanides Alkali Metal I Transition elements Halogen D J D. E. Terminology term A Alpha (α) particle B Mass spectrometer C Valence electron D Atomic mass E F G H fission Atomic number Half-life SATP I J radioisotope Beta (β) particle Definition d-block elements that are all metals. They are often multivalent and are found in the “B” columns in the periodic table Very reactive non-metallic elements in column 17 Non-reactive gases found in column 18. These elements have filled valence shells Inner transition elements with atomic numbers between 89 and 102 (if heavier than U, called a trans-uranic element) Elements found in the “A” columns in the periodic table . they have easily determined ionic charges. Elements that are silvery, soft, very reactive, one outer shell electron A row going across the periodic table Inner transition elements with atomic numbers between 57 and 71 (also called rare earth elements) Elements that are silvery, brittle, reactive, two outer shell electrons A column going down the periodic table definition The number of protons in an atom 25°C and 100 kPa An unstable isotope of an element capable of emitting particles or radiation The time it takes for one half of the nuclei in a radioactive sample to decay Electrons that occupy the outer orbital shell of an atom A helium nuclei (42He2+) A high energy electron Splitting of a large nucleus into small nuclei (occurs in the reactor of nuclear power plants) The number of protons and neutrons in an atom A device used to determine the mass of particles (ex. Isotopes) Average Atomic mass 1. Natural lithium comes in only two isotopes of Li-6 (7.42%) and Li-7 (92.58%). Determine the average atomic mass for Lithium. 2. Calculate the relative atomic mass of gallium given that the relative abundance of its two isotopes are: 60.5% of Ga-69 and 39.5% of Ga-71. 2 3. Oxygen occurs as one major isotope and two minor isotopes. O-16 (99.759%), O-17 (0.037%) and O-18 (0.204%). Calculate the average atomic mass of oxygen. 4. Iron has four isotopes; Fe-54 (5.82%); Fe-56 (91.66%); Fe-57 (2.19%) and Fe-58 (0.33%). Determine the average atomic mass for natural iron. 5. Nickel has five naturally occurring isotopes. We will exclude all the special isotopes synthetically made in nuclear reactors. The isotopes are: Ni-58 67.88% Ni-60 26.23% Ni-61 1.19% Ni-62 3.66% Ni-64 1.08% Calculate the average atomic mass of nickel 6. Iridium (a metal rather like platinum) occurs with only two isotopes of mass number 191 and 193. The atomic weight of iridium is 192.2. Deduce the relative abundance of the two isotopes of this element. F. Radioisotope Decay Equations. 1. Write an equation for the β-decay of 8737Rb. 2. Write an equation for the α-decay of Pu-239. 3. Write an equation for the α -decay of 146C. G. Radiometric Dating Questions 1. How do you manage to absorb C-14 into your body? 2. When a rock solidifies from magma, it contains a large amount of the mineral Orthoclase (KAlSi3O8). 0.0117% of all K atoms are the isotope K-40 which is radioactive and undergoes β-decay. Write a β-decay equation for K-40. K-40 has a half-life of 1.277 billion years? A sample of Orthoclase contained 12.48 mg of K-40 when it formed. Today the sample contains 3.12 mg of K-40. What is the age of the sample of Orthocalse? 3. A Woolly Mammath is found frozen in the Siberian Tundra. The normal ratio of 14C to 12 C is 1.046 ppt (parts per trillion). The 14C/12C ratio in the Mammoth is 0.131 ppt. 14C has a half-life of 5730 years. What is the age of the mammoth? H. Nuclear Power 1. Explain in a series of steps how Nuclear Electric Energy is produced. 2. List 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of Nuclear Power. 3