1418326371.
advertisement

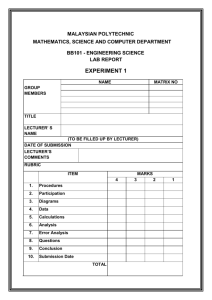
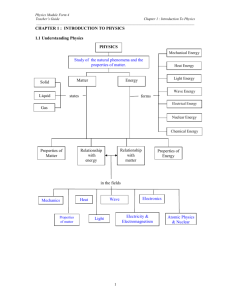
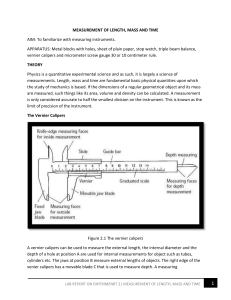
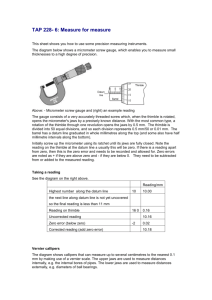
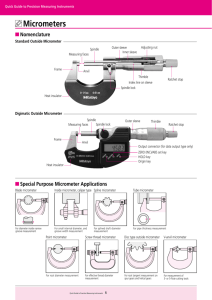
NAME…………………………… STREAM………….... MIDTERM II JUNE 2014 S.1 PHYSICS 1 TIME:1 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS: ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS IN BOTH SECTIONS. IN SECTION A, WRITE YOUR ANSWERS IN THE GRID PROVIDED ON PAGE ONE. WRITE THE ANSWERS FOR SECTION B IN THE SPACES PROVIDED. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 SECTION A 1. What is physics? A. The study of matter in relation to energy. B. The study of the physical quantities and their properties. C. The study of instruments used for measurement of physical quantities. D. The study of living and non-living things. 2. Which of the following is not a derived quantity? A. Density B. Volume C. Speed D. Length 3. The following instruments all measure length except , A. Tape measure B. Micrometer screw gauge. C. Burette D. Metre rule. 4. A cylindrical tank has a diameter of 1400cm and a height of 4.9m.What is the volume of water in the tank when it is half filled? A. 754.6cm3 B. 377.3cm3 C. 1437.3 cm3 D. 718.6cm3 1 5. Which of the following is not a branch of physics? A. Mechanics B. Light C. Heat 6. The SI unit for length is? A. cm B. mm D. C. m 7. Convert 450cm3 to m3. A. 4.5 × 10−4 𝑚3 . C.4.5 × 10−3 𝑚3 Engineering. D. km B.4.5 × 10−6 𝑚3 D.4.5 × 10−2 𝑚3 8. The bowl shown below is hemispherical. If it has a radius of 3.5cm, calculate the volume of liquid in cm3 that fills it up. A. 1 359 3 cm3 5 B.89 6 2 C. 350.0cm3 D. 179 3cm3 9. Why do we use SI units when measuring physical quantities? A. Because they are internationally accepted everywhere in the world. B. Because they are easy to understand. C. Because they are the only units for a given quantity. D. Because they are easy to convert to other units. 10. How can you define matter? A. Physical objects on earth. B. Anything that occupies space and has weight. C. matter refers to liquids such as water which flow. D. matter refers to solids that are heavy. 11. A piece of metal has a mass of 60g. It is lowered into a measuring cylinder containing water. The level of the water rises from 20 cm3 to 50 cm3. What is the density of the metal? A. 2.0 gcm-3 B. 0.2 gcm-3 C. 0.5 gcm-3 D. 1800 gcm-3 12. The width of a meter rule is accurately measured by a A. micrometer screw gauge B. vernier caliper C. tape measure D. meter rule. 13. Convert the length 52400cm to km A. 52km B. 5.24km D. 0.524km D. 5240000000km 14. A Micrometer screw gauge is used to determine the diameter of a circular object. The sleeve reading is noted as 4.5mm while the thimble reading is 35divisions. The diameter of the object is A. 8 . 0 0 m m B. 4.85cm C. 4.535mm D. 4.85mm 2 15. The dimensions of a blackboard are 2.0mx1.5m. The area of this blackboard in centimeters A. 3.0cm2 B. 30000cm2 C. 3000cm2 D. 300cm2 16. Which of the following can be used to measure diameter of a bicycle spoke accurately? A. micrometer screw gauge B. vernier calipers C .metre rule D.tape measure 17. Which of the following is not an S.I unit symbol for a fundamental quantity? A. kg B. m C. s D. ms-1 18. The three fundamental quantities of measurement are: A. Mass, length, time B. mass, frequency, power C. metres, seconds, kilograms D. work, power, energy 19. Find the volume of milk that can be contained in a hemispherical calabash of radius 7cm. 1 4 A. 3 𝜋x7 x7 x7cm 3 B. 3 𝜋 x 7 x 7 x7cm3 2 C. 3 𝜋 x7 x 7 x7cm3 D. 4𝜋 x7x7x7cm3 20. The density of mercury is 13.6gcm-3. Express this density in kgm-3. A. 13.6kgm-3 B. 13600kgm-3 -3 B. 0.0136kgm D. 1360kgm-3 SECTION B 21. Sketch a micrometer screw gauge reading assuming the thimble has 50 divisions. (i) 5.34 mm …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) 3.89 mm ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (b)Find the readings of the following vernier calipers. Write your answer in the boxes provided. (i) 3 (ii) cm cm 22. Convert (show full working). (a) 45 km2 to m2 ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (b) 65cm2 to m2 ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… 23. (a) Define volume of a substance and state its SI unit. ..................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (b) Find the volume of a cylindrical syringe whose diameter is 2.8cm and length is 10cm long. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ………………............................................................................................................ (c) Explain an experiment to determine the volume of an irregular object. 4 ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… 24. Figure the below shows a micrometer screw gauge. (i) Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D, E and F. A B C D E F A…………………….. B……………………… C……………………. D…………………….. E…………………….. (ii) F……………………… Calculate the reading of the micrometer screw gauge shown below. mm ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… mm ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 25. (a) Draw a vernier calliper and label its parts. (c) Calculate the reading shown by the vernier calliper below. cm ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 26. Name three fundamental quantities and state their S.I units Fundamental quantity …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… S.I unit ……………………………. ……………………………. ……………………………. END 6