Notes: - Ms Williams
advertisement

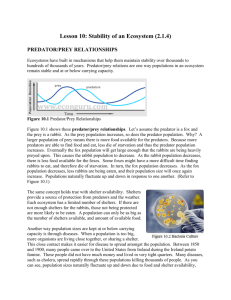
5.01 Relationships in Ecosystems! Partner Challenge: In 3 minutes, list as many biotic and abiotic factors that you and your partner can think of! Group with the most wins tickets! Biotic Living Factors Abiotic Non Living Factors Plants, animals, bacteria, fungi U1 N3 Sunlight, soil, water, climate, oxygen, carbon dioxide Levels of Ecological Organization…small numbers to big numbers= having MORE interactions! Ecosystem Community Population Individual and abiotic factors interacting together. A group of several populations in an area. Just like Charlotte, NC A group of organisms of the Same species One organism, a living thing! Just like your grade level…9th, 10th, 11th Just like you! Biotic Just like West Charlotte H.S. Challenge Questions: 1.What occurs amongst the organisms as the level of ecological organization gets bigger? Competition for resources 2. How are both biotic and abiotic factors important in an ecosystem? Biotic factors depend on abiotic factors for survival. For example, a human needs water and oxygen. Relationships: With more organisms there are more interactions_! Biotic (living) factors in an ecosystem interact in 2 ways: 1) Symbiotic Relationships: any relationship in which two species live closely together. - symbiosis means “living together” Key to Symbiotic Relationships: a) Mutualism b) Commensalism c) Parasitism = Positive Benefit = Neutral Benefit = Negative Station Rotation: Use the following graphic organizer to complete your station rotation on symbiotic relationships! What is mutualism? What is commensalisms? What is parasitism? Two organisms live together, both One benefits, other unaffected. One benefits, the other harmed Benefit Give example: Bee and flower. Bee drinks nectar and flower gets pollinated Give example: Barnacles on a whale. Barnacles attach to A whale and feed when the whale feeds. The whale is not affected. Give example Tapeworm in a human gut. Tapeworm feeds off human digested food, harming the human Draw example: Draw example: Draw example: Predator vs. Competitor: -Predator/Prey, also known as __predation_, is when one organism captures and feeds on another. Ex. A cheetah and an antelope. -Competition is when one organism of the same or _different species uses the same resource as another organism. Organisms compete for food, water, shelter, and mates Independent Practice: Making Predictions. Based on what you learned in the lab….what would happen if… 1) All of the rabbits died off in an ecosystem where they were the primary food for wolves? The wolf population would decrease because they depend on the rabbits for food. 2) The number of predators (wolves) increased in an ecosystem, but the number of prey (rabbits) stayed the same? The population of rabbits would decrease. 3) This graph shows what happens when the number of predator and prey change over time. Interpret this predator prey graph to identify the relationships between population size over time. Be specific! As the prey population increases, the predator population increases as well. As the prey population decreases, so does the predator.