Chapter 18 questions key
advertisement

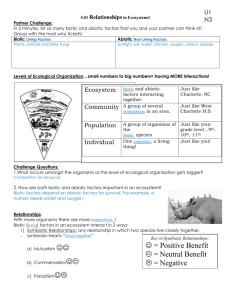
Name_________________________ Chapter 18: The Interactions of Living Things Copy questions or rewrite into sentences on your own paper. Section 1, Everything Is Connected, p. 480-483 1. What does ecology study? The interaction of living things with each other and their environment 2. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic? Biotic is living, abiotic is nonliving 3. Name and explain the 5 levels of environmental organization. a. organism is a single living thing b.population is made up of all the same species of organism in an area c. community is all the biotic things in an area d.ecosystem is the biotic and abiotic things in an area e. biosphere is all the areas on earth where life can exist Section 2, Living Things Need Energy, p. 484-489 and notes 4. What does food provide for living things? energy 5. Draw a picture showing the role of the sun, producers, and consumers in energy flow. Label and explain each part. (You don’t have to copy this question) sun ------producers, which get their energy from the sun -------- consumers, which get their energy from producers and each other 6. What can producers do with sunlight? Make their own food 7. Explain the process of photosynthesis. (notes). Water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight become water, oxygen, and glucose 8. Describe what these consumers eat: a. herbivore plants b. carnivore animals c. omnivore plants or animals 9. Explain in words or pictures the roles of primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers (notes) primary consumers eat producers, secondary consumers eat primary consumers, and tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers 10. Why are food chains usually only a few links? (notes) because each link in the food chain uses up 90% of the energy they get 11. Decomposers break down dead organisms____. Examples of decomposers include fungi and bacteria_. They recycle _water_ and carbon dioxide for use by other living things. 12. What is the difference between food chains and food webs? Food chains explain only one path of energy, but food webs put all possible food chains together to show all the possible paths of energy 13. Why is less energy available as you go up the food pyramid? Because each level uses up 90% of its energy 14. Why are the populations of primary consumers much larger than the populations of tertiary consumers? Tertiary consumers are usually larger and need more energy. Primary consumers can get all the energy they need if enough producers are available 15. Explain how the loss of one predator can affect many other populations. The predator does not eat its prey, so the population of the prey goes up. Then the population which is eaten by the prey goes way down because there are so many of them. This change may affect other populations which share food with the prey. Example: When wolves left Yellowstone Park, the deer population went up. The plant population went down because there were so many deer eating the plants. Other animals which needed the plants were also affected. Section 3, Types of Interactions, p. 490-497 and notes 16. Why are populations limited in their growth? There are not enough resources to support a large population 17. What are some specific factors that can limit the growth of a population? Water, food, air, space 18. The maximum population that an ecosystem can support is its carrying capacity. 19. Explain these types of interactions between organisms. a. competition 2 organisms need the same resource b. predator/prey predator eats the prey c. symbiosis a relationship between 2 organisms d. coevolution two species change in a way that benefits both of them 20. Draw or write examples of these prey adaptations: a. camouflage Walking stick insects look lilke the twigs on which they sit b. defensive chemical tree frogs have poisonous skin c. warning coloration yellow jackets have bright yellow color to warn predators of their sting 21. Draw a graphic organizer to show the differences between mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. (you don’t have to write the question) Mutualism Organism 1 Organism 2 happy happy Commensalism happy doesn’t care Parasitism sad happy 22. In this chapter, we have learned many terms that could describe an organism’s niche in an ecosystem. Write a few of these terms. (don’t write this first part of the question, just say something like, “an organism’s niche could be _____, ______, _______, or _______. “ The definition of niche should be in your notes.) An organism’s could be a predator, secondary consumer, and a food source.