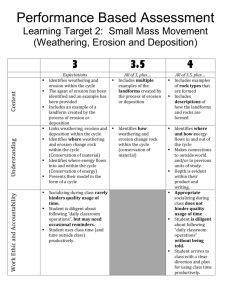
File 3. kud weathering, erosion, and deposition1
advertisement
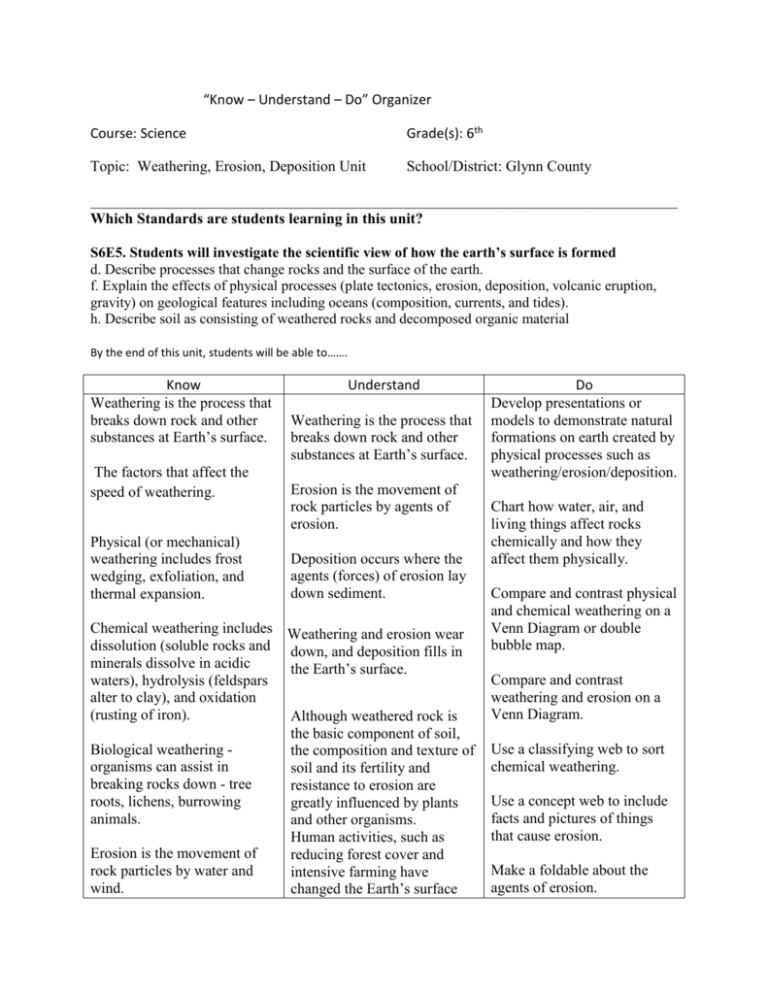
“Know – Understand – Do” Organizer Course: Science Grade(s): 6th Topic: Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Unit School/District: Glynn County ______________________________________________________________________________ Which Standards are students learning in this unit? S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). h. Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material By the end of this unit, students will be able to……. Know Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth’s surface. The factors that affect the speed of weathering. Physical (or mechanical) weathering includes frost wedging, exfoliation, and thermal expansion. Understand Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth’s surface. Erosion is the movement of rock particles by agents of erosion. Deposition occurs where the agents (forces) of erosion lay down sediment. Chemical weathering includes • Weathering and erosion wear dissolution (soluble rocks and down, and deposition fills in minerals dissolve in acidic the Earth’s surface. waters), hydrolysis (feldspars alter to clay), and oxidation (rusting of iron). Although weathered rock is the basic component of soil, Biological weathering the composition and texture of organisms can assist in soil and its fertility and breaking rocks down - tree resistance to erosion are roots, lichens, burrowing greatly influenced by plants animals. and other organisms. Human activities, such as Erosion is the movement of reducing forest cover and rock particles by water and intensive farming have wind. changed the Earth’s surface Do Develop presentations or models to demonstrate natural formations on earth created by physical processes such as weathering/erosion/deposition. Chart how water, air, and living things affect rocks chemically and how they affect them physically. Compare and contrast physical and chemical weathering on a Venn Diagram or double bubble map. Compare and contrast weathering and erosion on a Venn Diagram. Use a classifying web to sort chemical weathering. Use a concept web to include facts and pictures of things that cause erosion. Make a foldable about the agents of erosion. Water, wind, gravity, and ice are agents of erosion. Make a KWL chart about Weathering; Erosion; and Deposition. Waves erode the shoreline. Describe how running water moves sediment. Explain how rivers shape the land. Humans can increase erosion through poor farming practices or disturbing the land through development. There are practices which can be implemented to control erosion, such as contour plowing, terracing, planting ground cover, or windbreaks. Man-made structures are sometimes built to help control erosion. Unfortunately, man-made structures along the coastline often have the unwanted side effect of enhancing coastal erosion. Construction on steep slopes can lead to mass wasting or erosion by gravity, including slumps and landslides. Soil is comprised of a mixture of rock particles, decomposed organic materials, minerals, and water. Deposition occurs where the agents (forces) of erosion lay down sediment. Create a sequence chart to show the formation of a sand dune. Use a stream table to demonstrate how rivers shape the land, and the theories of erosion and deposition. Examine soil samples to determine the presence of both organic and nonorganic materials. Make a pie chart to show the percentage or portion of the components found in an average sample of soil. Identify the horizons of soil.