Grade 9 Final Review Answers You should be able to: A) Recognize
advertisement
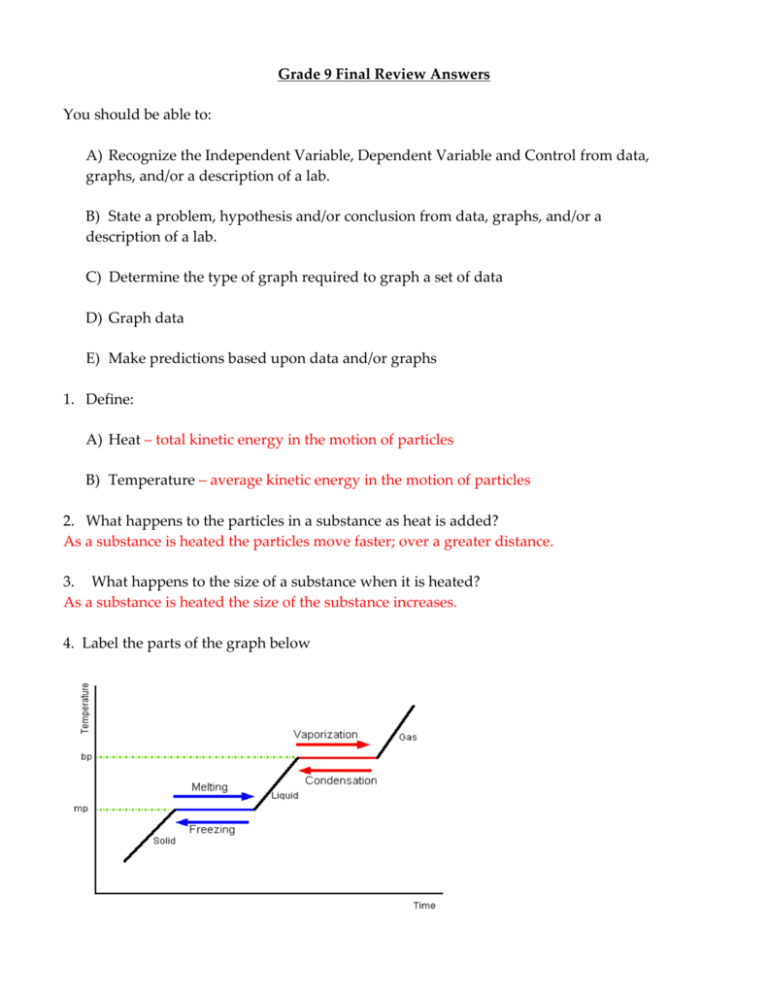
Grade 9 Final Review Answers You should be able to: A) Recognize the Independent Variable, Dependent Variable and Control from data, graphs, and/or a description of a lab. B) State a problem, hypothesis and/or conclusion from data, graphs, and/or a description of a lab. C) Determine the type of graph required to graph a set of data D) Graph data E) Make predictions based upon data and/or graphs 1. Define: A) Heat – total kinetic energy in the motion of particles B) Temperature – average kinetic energy in the motion of particles 2. What happens to the particles in a substance as heat is added? As a substance is heated the particles move faster; over a greater distance. 3. What happens to the size of a substance when it is heated? As a substance is heated the size of the substance increases. 4. Label the parts of the graph below 5. What happens to the temperature as a substance undergoes a phase change? The temperature remains constant 6. What is the energy being used for at a phase change? The energy is being used to change the attractions between particles 7. Define: A) Conduction - transfer of heat energy as a result of collisions between particles B) Convection – transfer of heat energy as a result of current set up in a fluid due to temperature differences C) Radiation – transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves 8. Describe the process that creates convection currents and relate them to Earth cycles. As a fluid is heated its particles move faster, over a greater distance causing the material to expand. This expansion lowers it density allowing the material to rise. New cooler material moves in to take its place and the new material is in turn heated. Meanwhile colder material is sinking to replace the material that was heated. This results in a convection current. Convection currents are one of the driving force behind plate tectonics, weather patterns, breezes, ocean currents, the water cycle and the carbon cycle. 9. What is an electric current? A flow of electrons through a material. 10. What is being measured by: A) Voltage – the difference in potential between 2 points in a wire. This provides the force causing the electrons to move through the wire. B) Current – the rate of the electron flow. C) Resistance – the opposition to the flow of electrons. D) Power – the rate at which energy is used or transferred. 11. What are the units to measure: A) Voltage – volts (v) B) Current – Amperes (A or Amps) C) Resistance – Ohms () D) Power – Watts (W) 12. What happens to the electrons in a wire when the wire is moved in a magnetic field? The electrons move through the wire. 13. What happens to the electrons in a wire when a magnet is moved near the wire? The electrons move through the wire. 14. What is a generator? A device that uses the relative motion of a wire and magnet to produce an electron flow. It usually consists of a coil of wire that rotates with in a magnetic field. 15. How can the current produced by a generator be increased? A) Use a larger coil B) Use a stronger magnet C) Turn the coil faster 16. How can the resistance of a wire be increased? Make it longer, thinner and/or increase its temperature. 17. Describe the sequence of energy changes that take place in a typical power plant starting with a fossil fuel and ending with the electricity. The chemical energy in the fossil fuel is converted to heat energy by the combustion (burning) of the fuel. The heat is used to boil water to create steam. The steam is used to turn a turbine (mechanical energy) which is used to turn the generator (mechanical energy). The generator produces electrical energy. 18. What affect does an increase in voltage have on current? An increase in voltage causes an increase in current. 19. What affect does an increase in resistance have on current? An increase in resistance causes a decrease in current. 20. What effect does the addition of a resistor have on the total resistance of a series circuit – total resistance increases 21. How does adding resistors to a series circuit affect the voltage available to each resistor? As the number of resistors in a series circuit increases the voltage available to each resistor decreases. Solve the following problems. Show all lists, equations, and work. 22. A circuit with a 5.4 A current has a 8 ohm resistor in it. Find the voltage and power for this circuit. I = 5.4A R = 8 V = I x R = (5.4A)(8) = 43.2 V P = V x I = (43.2V)(5.4A) = 233.28 W 23. A 100 W bulb is plugged into a 120 v outlet. Find the current passing through the circuit and the resistance of the bulb. P = 100 W V = 120 V 𝐏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝐖 𝐈= = = 𝟎. 𝟖𝟑 𝐀 𝐕 𝟏𝟐𝟎 𝐕 𝑹= 𝑽 𝟏𝟐𝟎 𝑽 = = 𝟏𝟒𝟒. 𝟔 𝛀 𝑰 𝟎. 𝟖𝟑 𝑨 24. The Symbol for an isotope of carbon is 14 6C based on this information identify: A) Atomic number 6 D) number of neutrons 8 B) Mass Number 14 E) number of electrons 6 C) number of protons 6 25. Give an Isotopic symbol for an isotope of the atom in the previous question. 𝟏𝟐 𝟔𝐂 26. What is an ion? An atom that has become charged by the gain or lose of an electron 27. Describe the difference between a positive ion and a negative ion. A positive ion is formed by the loss of electrons by an atom. A negative ion is formed by the gaining of electrons by an atom 28. Why do atoms form ions? So that they have a complete outer most energy level containing 8 electrons. 29. How does an atom become a: A) Positive Ion – By losing electrons. B) Negative Ion – By gaining electrons 30. Define the term valence. Combining capacity of an atom indicated by the type of ion it forms 31. Define the term valence electron. Electrons found in the outermost energy level 32. What do all of the elements in the same column on the Periodic Table have in common? They have the same number of valence (outer) electrons. 33. What is a chemical bond? Force holding atoms together in a compound 34. What is the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond? Ionic bonds are due to a transfer of electrons Covalent bonds are due to the sharing of electrons 35. What happens to the electrons in the formation of an ionic bond? The electrons in the outer energy level of the metal are transferred to the outer energy level of the nonmetal 36. What happens to the electrons in the formation of a covalent bond? The outermost electrons of two nonmetals are shared. 37. What type(s) of elements are involved in a (an): A) Ionic Bond – metal and nonmetal B) Covalent Bond – 2 nonmetals or a nonmetal and hydrogen 38. For the following list of compounds indicate if they will form Ionic or Covalent bonds. A) Sulfur and Oxygen Covalent E) Carbon and Hydrogen Covalent B) Sodium and Chlorine Ionic F) Aluminum and Sulfur Ionic C) Calcium and Nitrogen Ionic G) Silicon and Oxygen Covalent D) Chlorine and Fluorine Covalent H) Magnesium and Iodine Ionic 39. In a simple chemical compound, the total charge must equal zero. 40. Draw and label the pH scale. 41. Are the following substance acids, bases or neutral. If a chemical is an acid or base indicate if it is strong or weak. A) pH = 1.2 Strong acid D) pH = 8.6 Weak base B) pH = 7.8 Weak base E) pH = 7.0 Neutral C) pH = 13.5 Strong base F) pH = 6.2 Weak acid 42. Indicate if the following common substances are Acid, Base or Neutral. 43. A) Lemon Juice Acid E) Drain Cleaner Base B) Salt Neutral F) Soda Acid C) Soap Base G) Pure Water Neutral D) Rain Water Acid H) Orange Juice Acid What are the products of the reaction between an acid and a base? A salt and water 44. What is the name for the reaction described in question #34? Neutralization 45. What will the pH measure after the reaction in question # 34 has taken place? 7.0 46. What is special about the element carbon? It is a nonmetal with 4 valence electrons allowing it to react by forming up to 4 bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. 47. What makes a compound an Organic compound? It is based on the element Carbon. 48. Give an example of a(n): 49. A) organic compound Any Carbon based compound such as Sugar, Starch, Protein Plastics, etc. B) inorganic compound Any compound that is not based on carbon such as all salts, water, etc. Define: A) Monomer – a small molecule that can be chemically bonded to other small molecules to form a polymer B) Polymer – A large molecule consisting of repeated structural units (monomers) connected by covalent bonds 50. What is a biopolymer? Give an example of one. A polymer made by a living thing such as sugar, starch, protein 51. What is a synthetic polymer? Give an example of one. Polymers made by man in a factor or lab. All plastics. 52. What affects do the following have on a polymer’s properties? A) Linear (straight) Chains – Increases rigidity and density B) Branched Chains – Increases flexibility C) Cross links – Increases strength and gives the polymer memory 53. Name and describe the three types of stress-strain behaviors that polymers are designed to withstand. A) Puncture resistance – ability to stop a moving object without forming a hole B) Abrasion resistance – ability to stand up to scuffing and scraping C) Tensile strength – amount of pulling force the polymer can with stand before tearing 54. Polymers are used because they are strong, durable materials. When we throw these materials away they often end up in landfills. Why is this a concern to environmentalist? Polymers do not breakdown easily in a landfill and so may last a long time without decomposing. 55. State the Law of Conservation of Mass. Matter cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged. 56. According to the Law of Conservation of Mass what will happen to the mass in a: A) chemical reaction Remain the same B) change of state Remain the same C) dissolving of a solute Remain the same Below are the equations for 2 combustion reactions. + 5 O2 A) C5H10O5 5 H2O + B) C5H10O5 + O2 H2O + CO2 + 5 CO2 CO + assorted particulates 57. Which of these equations represents incomplete combustion? B 58. What is meant by “assorted particulates”? The fragments of the original reactant that did not react 59. What is the cause for incomplete combustion? There was not enough oxygen present or the reactant and oxygen separated before the reaction was complete. 60. How can we tell if a reaction is incomplete combustion? The presence of the assorted particulates in the form of smoke and soot. 61. Define: A) endothermic reaction - a reaction that takes in (absorbs) energy from the environment B) exothermic reaction - a reaction that gives off energy to the environment 62. For the following reactions determine if they are endothermic or exothermic. energy A) 2 H2O + B) CH4 + 2 H2 + O2 O2 --> CO2 + 2 H2O + Energy C) Photosynthesis Endothermic D) Respiration Exothermic Endothermic Exothermic 63. Describe what is meant by acid rain, include the gases responsible. Acid rain is rain that has a pH value of less than 5.0. It is produced by the reaction between water in the air and SOx and NOx gases that are given off when fossil fuels are burned. 64. How and where does acid rain gets carried by weather Acid rain is produced in clouds and so the acid rain is carried generally west to east by the clouds. 65. Describe acid rain’s effects on rocks, animals and plants. Rocks containing carbonates and bases react with the acid and breakdown. Animals that live or reproduce in water will have their life processes and reproductive processes damaged by high acid content resulting in a reduction in population. This will put strain on those animals that feed on these animals. Plants are sensitive to acid content and many plants die in acidic soil. 66. What is the pH of acid rain? Less than 5.0 67. Describe the process that creates convection currents and relate them to Earth cycles. When a fluid is heated unevenly, the warmer material will rise and the cooler material will sink resulting in convection currents. Heat from the earth’s core will unevenly heat the mantle creating convection currents. The convection currents in the mantle push on the crust causing it to move resulting in earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains. Convection currents in the atmosphere and oceans are the result of uneven heating by the sun. These currents drive weather patterns. 68. Describe the water cycle, include the energy source. Heat from the sun causes water on the earth’s surface and bodies of water to evaporate. The water vapor rises and condenses as it enters cooler air forming clouds. When the amount of water in the clouds is greater than the clouds can support the water returns to the earth’s surface as precipitation and collects in the various bodies of water. 69. How do human activities affect the following parts of the water cycle: A) infiltration Reduced B) runoff Increased C) groundwater Reduced D) collection in Lakes and Oceans Increased, resulting in more flooding 70. How does Global Warming affect the water cycle? Water will evaporate faster. Clouds will reach their maximum holding capacity faster. The cycle will therefore speed up. 71. Describe the carbon cycle; include the energy source and energy transformations involved. Green plants absorb energy from sunlight and use it in the process of photosynthesis to convert Carbon dioxide and water, from the atmosphere, into sugars, starches and oxygen. Plants use some of the sugars and starches for energy releasing some Carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. The rest of the sugars and starches are storied by the plant. Animals eat the plants and use some of the sugars and starches for energy releasing CO2 and store the excess. Carnivores eat these animals and use some of the stored materials releasing CO2, storing the excess. When a plant or animal dies organisms in the soil break them down, releasing CO2. Under the right conditions some of these decaying organisms will become coal and/or oil (fossil fuels). Burning fossil fuels releases CO2 back into the atmosphere. 72. How long does it take to form coal or oil? Thousands of years 73. What is the basis for rock classification? The way the rock was formed. 74. Name and describe the three types of rocks. Include how they are formed. A) Igneous Rock – made by the cooling of magma and/or Lava B) Sedimentary Rock – made by the compacting and cementing of sediments C) Metamorphic Rock –rock that has been changed by heat and pressure, or by chemical changes 75. Describe the Rock Cycle. Rocks once formed can be altered by a number of different processes. These processes change rocks into other types of rocks producing the wide variety of rocks found on the earth. The ways that a rock can be changed are: A) melting to form magma B) weathering, erosion and deposition to form a sediment C) heat, pressure and/or chemical reactions (metamorphism) 76. Fill in the rock cycle diagram drawn below. Igneous Rock Metamorphic Rock Sedimentary Rock 77. What 2 sources provide the energy needed to run all of the Earth’s cycles? The core of the Earth and the Sun. 78. Describe the Greenhouse Effect. Sunlight enters the atmosphere and is either absorbed by the Earth and atmosphere, or reflected back to space. The absorbed energy is reradiated by the Earth at a different wavelength then it was originally. The new wavelength cannot pass through the atmosphere as easily and some of the energy gets trapped warming the Earth. 79. Why are scientists concerned about an increase in the level of Carbon dioxide in the air? Carbon dioxide is present in the air in large enough quantities to trap solar energy, as the level of carbon dioxide increases so does the amount of energy trapped by it. This has the potential of making the Earth warmer than it should be. 80. A large amount of our energy comes from the burning of fossil fuels. Describe 2 environmental issues associated with the burning of these fuels. This is a very open ended question any of the issues we discussed this year are appropriate. 81. What is a Brownfield site? A site that was used for some commercial purpose in the past, that has been abandoned and may be contaminated. 82. Why are Brownfield sites and landfills areas of concern? They may contain toxic substances that can escape from the site polluting the environment. 83. What are the main types of contaminants found in Brownfields? Heavy Metals Gasoline and its constituents Solvents 84. What is an option available to us that will allow us to reduce our use of fossil fuel? Give an advantage of the option you chose. This is a very open ended question. I would be looking that you gave some thought to what we do and how we could do better. 85. What are some things that we each can do to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels? This is a very open ended question. I would be looking that you gave some thought to what we do and how we could do better. 86. The materials placed in a landfill include the following categories Paper, Glass, Organic (mostly vegetables), Plastic, Metal and some undefined materials. To reduce the amount of material placed in landfills which of these can be: A) burned in a waste to energy plant Paper Products B) used in compost Organic (vegetable matter) C) Recycled Paper, Glass, Plastics, Metals 87. What are the advantages and disadvantages to Landfills? Advantages include: 1) A specific location for disposal that can be monitored. 2) When a landfill is complete, it can be reclaimed, built on or used as parks or farming land. 3) Waste going to a properly designed landfill can be processed to remove all recyclable materials before tipping. 4) Waste going to a properly designed landfill can be processed to remove organic material and use it for compost or natural gas (methane) production. 5) Properly managed landfills can capture the natural gas (methane) produced by the decomposing material underground. 6) Properly managed landfills can minimize and/or capture the leachate produced by the decomposing material underground. Disadvantages include: 1) Materials placed in the dump may include heavy metals like lead, cadmium and mercury, found in paints, electrics, batteries, etc, are water soluble and will become concentrated in any water that percolates through the landfill. 2) Some wastes, like plastics do not breakdown in the landfill. 3) Methane gas production 5) Animals, bacteria, etc can feed off of the wastes and carry diseases. 5) Liners can leak and the wastes that escape can contaminate the groundwater. 88. What are the advantages and disadvantages to Incinerators? Advantages: The ash produced takes up very little space, and can be used for a number of industrial processes including as a cover material for a landfill along with soil, and in road construction. Disadvantages: The gases produced by incineration depend on the waste being burned and may include Carbon dioxide and Carbon monoxide, ash particles, heavy metals, SOx, Hydrochloric Acid, dioxins and furans. 89. What are the advantages and disadvantages to waste to energy plants? Advantages: The waste is used to generate electricity reducing our need for fossil fuels other advantages include those listed in #88 Disadvantages: The gases produced by incineration depend on the waste being burned and may include Carbon dioxide and Carbon monoxide, ash particles, heavy metals, SOx, Hydrochloric Acid, dioxins and furans. 90. What are the affects of using large quantities of fertilizers on nearby rivers and lakes? The fertilizers in the water cause rapid growth of water plants and algae, when these die their decomposition uses up the oxygen in the water causing fish and amphibians to die. 91. How can the problems associated with this be reduced? More direct application of fertilizers to the plants as opposed to general spraying reducing the amount needed. Planting brushes and trees between the fields and streams to absorb and use the excess fertilizers Additional Material, be able to graph energy use data to make a graph like the one given below and answer questions on the trends on the graph. The graph below describes the coal usage in the State of Connecticut from 1961 to 2005. Use this graph to answer the following questions. A) Describe the pattern of Coal usage from 1961 to 1980. Between 1961 and 1980 Coal use showed a steady drop in usage. B) Give a possible reason for the pattern shown for this time period. Awareness of Acid Rain, as well as, the soot and smog associated with the use of coal made it an unpopular fuel choice. C) Describe the pattern of Coal usage since 1980. There was an increase in Coal use from 1980 to 1995, since 1995 the usage has been fairly steady. D) Give a possible reason for the pattern shown for this time period. The Oil Embargo of the 70’s and problems with Nuclear Power made Coal a more attractive option and so use increased.



