Course Title: The Biology of Cancer Course Level: Postgraduate
advertisement

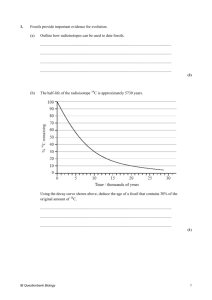
Course Title: The Biology of Cancer Course Level: Postgraduate Lecture Time: 3-6 (St / Wed) Course code: BISC 6358 Academic Staff Specifics : Dr. Saeb Aliwaini. Email: saib.iwini@gmail.com Office hours ( Faculty of science building 307) : Sat, Mon, Wed 10-11 Course module description: The profound impact of cancer on our society has been the driving force behind major research advances in this field. A better understanding of the basic biology of cancer and its impact on the human body has led to more effective treatments, enhanced detection methods, and the development of prevention strategies. This course will provide a comprehensive overview of the biology of cancer. The first part of the course will focus on the genetic and molecular basis of cancer. We will explore the role of mutations in cancer cells and how they lead to the deregulation of essential biological properties such as programmed cell death, cell proliferation, and differentiation. The second part of the course will focus on the interface of cancer and medicine. Classical treatment methods will be compared with newer treatment modalities, such as targeted therapies. We will also explore the challenges associated with diagnosing cancers, as well as ways in which to prevent cancer. Course module objectives: At the end of this module, student will be able to answer principle questions such as: - What are the common cellular and molecular mechanisms that are deregulated in cancerous cells, and how does their deregulation contribute to the development of cancer? - What role does gene mutation play in the development of cancer? In what ways can cancer be considered a “heritable” trait? - In what ways do environmental factors influence cancer susceptibility and how may we use this information to prevent cancer? How does cancer manifest itself in the human body? What features of cancer lead to high mortality rates? What is the biological rationale for both traditional chemotherapies and novel targeted therapeutic approaches? What are the benefits and limitations of each option? In what ways can genomic technologies provide insight into cancer prevention, diagnosis, and treatment? What are the limitations of these technologies? Course/ module components Books - Weinberg, Robert A. The Biology of Cancer, Second edition. New York: Garland Science, 2014 Course/module academic calendar Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Topic The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Nature of Cancer Tumor Viruses and Cellular Oncogenes Growth Factors, Receptors, and Cancer Cytoplasmic Signaling Circuitry Programs Many of the Traits of Tumor Suppressor Genes pRb and Control of the Cell Cycle Clock p53 and Apoptosis and autophagy Eternal Life: Cell Immortalization and Tumorigenesis Multi-Step Tumorigenesis Moving Out: Invasion and Metastasis Crowd Control: Tumor Immunology and Immunotherapy The Rational Treatment of Cancer Attendance policy: Absence from lectures shall not exceed 25%. Students who exceed the 25% limit without a medical or emergency excuse acceptable to and approved by the Dean of the relevant college/faculty shall not be allowed to take the final examination and shall receive a mark of zero for the course. If the excuse is approved by the Dean, the student shall be considered to have withdrawn from the course. Marks: - Mid exam 20 marks Final Exam 40 marks Activities 40 marks : Quizzes and presentations Journals: Any cancer research journal will be of great benefits to the student for their assignment. Examples : Nature reviews cancer (IF 37) http://www.nature.com/nrc/index.html Cancer research (IF 9) http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/ Cancer letter (IF 5) http://www.journals.elsevier.com/cancer-letters/ Breast cancer research (IF 5) http://breast-cancer-research.com/ Molecular cancer research ( IF 4) http://mcr.aacrjournals.org/