File - Respiratory Student Insight
advertisement
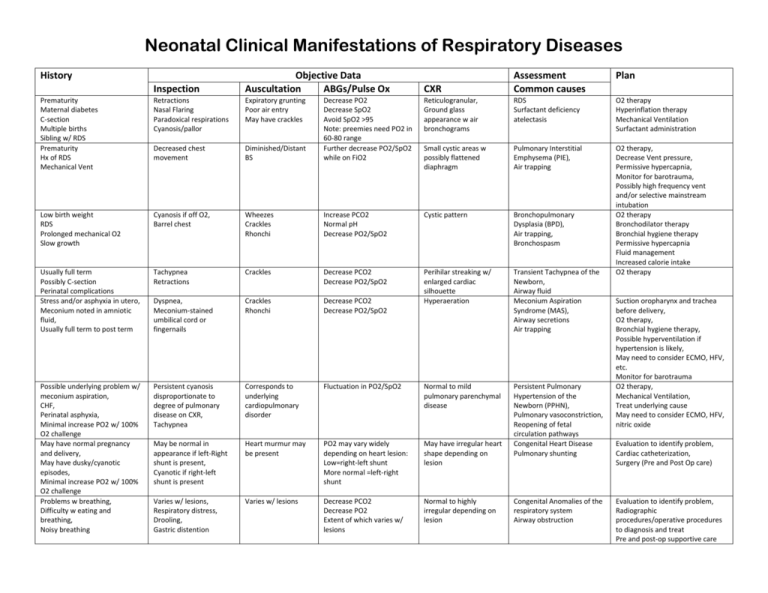
Neonatal Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Diseases History Inspection Objective Data Auscultation ABGs/Pulse Ox Prematurity Maternal diabetes C-section Multiple births Sibling w/ RDS Prematurity Hx of RDS Mechanical Vent Retractions Nasal Flaring Paradoxical respirations Cyanosis/pallor Expiratory grunting Poor air entry May have crackles Decreased chest movement Low birth weight RDS Prolonged mechanical O2 Slow growth CXR Assessment Common causes Plan Reticulogranular, Ground glass appearance w air bronchograms RDS Surfactant deficiency atelectasis O2 therapy Hyperinflation therapy Mechanical Ventilation Surfactant administration Diminished/Distant BS Decrease PO2 Decrease SpO2 Avoid SpO2 >95 Note: preemies need PO2 in 60-80 range Further decrease PO2/SpO2 while on FiO2 Small cystic areas w possibly flattened diaphragm Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema (PIE), Air trapping Cyanosis if off O2, Barrel chest Wheezes Crackles Rhonchi Increase PCO2 Normal pH Decrease PO2/SpO2 Cystic pattern Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD), Air trapping, Bronchospasm Usually full term Possibly C-section Perinatal complications Stress and/or asphyxia in utero, Meconium noted in amniotic fluid, Usually full term to post term Tachypnea Retractions Crackles Decrease PCO2 Decrease PO2/SpO2 Dyspnea, Meconium-stained umbilical cord or fingernails Crackles Rhonchi Decrease PCO2 Decrease PO2/SpO2 Perihilar streaking w/ enlarged cardiac silhouette Hyperaeration Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn, Airway fluid Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS), Airway secretions Air trapping O2 therapy, Decrease Vent pressure, Permissive hypercapnia, Monitor for barotrauma, Possibly high frequency vent and/or selective mainstream intubation O2 therapy Bronchodilator therapy Bronchial hygiene therapy Permissive hypercapnia Fluid management Increased calorie intake O2 therapy Possible underlying problem w/ meconium aspiration, CHF, Perinatal asphyxia, Minimal increase PO2 w/ 100% O2 challenge May have normal pregnancy and delivery, May have dusky/cyanotic episodes, Minimal increase PO2 w/ 100% O2 challenge Problems w breathing, Difficulty w eating and breathing, Noisy breathing Persistent cyanosis disproportionate to degree of pulmonary disease on CXR, Tachypnea Corresponds to underlying cardiopulmonary disorder Fluctuation in PO2/SpO2 Normal to mild pulmonary parenchymal disease May be normal in appearance if left-Right shunt is present, Cyanotic if right-left shunt is present Heart murmur may be present PO2 may vary widely depending on heart lesion: Low=right-left shunt More normal =left-right shunt May have irregular heart shape depending on lesion Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN), Pulmonary vasoconstriction, Reopening of fetal circulation pathways Congenital Heart Disease Pulmonary shunting Varies w/ lesions, Respiratory distress, Drooling, Gastric distention Varies w/ lesions Decrease PCO2 Decrease PO2 Extent of which varies w/ lesions Normal to highly irregular depending on lesion Congenital Anomalies of the respiratory system Airway obstruction Suction oropharynx and trachea before delivery, O2 therapy, Bronchial hygiene therapy, Possible hyperventilation if hypertension is likely, May need to consider ECMO, HFV, etc. Monitor for barotrauma O2 therapy, Mechanical Ventilation, Treat underlying cause May need to consider ECMO, HFV, nitric oxide Evaluation to identify problem, Cardiac catheterization, Surgery (Pre and Post Op care) Evaluation to identify problem, Radiographic procedures/operative procedures to diagnosis and treat Pre and post-op supportive care