Animals Cells Plant Cells
advertisement

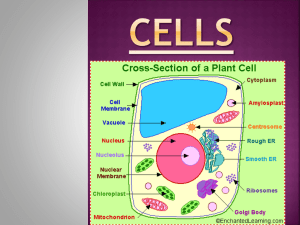
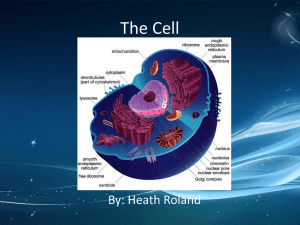
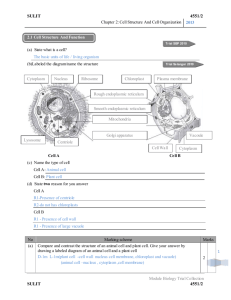
Unit 3 Study Guide Part 1: Cellular Theory and The History of the Cell 1. Look at the Pioneers of Cellular Theory Foldable. Describe how these scientists contributed to the discovery of the cell. A. Robert Hooke: Improved the microscope’s lighting and was the first to name and discover cells using samples of cork B. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek: Shaped the lense in a microscope so the he could study microorganisms that he called animalcules (bacteria and protozoa) C. Matthias Schleiden: Botanist who discovered different types of plants cells. D. Theodore Schwann: Zoologist who researched different types of animal cells E. Rudolf Virchow: Microbiologist who studied how bacteria reproduces. 2. What did Robert Hooke need in order to discover cells? The microscope 3. Are viruses considered living things? Explain your answer. No, they have to have a host cell in order to reproduce I found this on page ________ in my notebook. Part 2 Cell Parts and Their Functions 1. Look at the chart of cell parts and their functions. Name the organelles pictured and list their functions: 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome 4. Peroxisome 5. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 6. Golgi Body 7. Cytoskeleton 8. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 9. Mitochondria 10. Vacuole 11. Cytosol 12. Lyosome 13. Centrioles 14. What type of cell is this? _Animal___ 15. What organelle that is in your notes is not labeled in this diagram? _Cell Membrane_ 2. How is the endoplasmic reticulum like a highway? ____It delivers materials into the nucleus________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How is the cell like a galaxy? ______Contains several parts that are working and interconnected to each other___________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Use the notes on the differences of animal and plant cells to complete the Venn Diagram: Animals Cells 1. Has smaller vacuoles 2. Is flexible due to no cell wall 3. No chloroplasts Plant Cells 1. Has a nucleus 2. Has a membrane 3. Mitochondria 1. Have chloroplasts 2. Has a cell wall 3. Has a large central vacuole Part 3: Levels of Cellular Organization Fill out the triangle using your notes on Organization of life, give an example for each level: Organism, Example: whale, daisy Organ System, Example: Digestive System, Skeletal System Organ, Example: Stem, skin Tissue, blood Cell Example: Amoeba I found this on page ________ in my notebook. Part 4: Vocabulary Scavenger Hunt: Using all the materials for Unit 3 in your notebook look up the following vocabulary words and complete the chart. Vocabulary Word Definition Unicellular Organism made of one cell Multi-cellular Organism made of more than one cell Prokaryotic Organism lacking a nucleus Eukaryotic Organism with a nucleus Microorganism Organism that can only be seen with a microscope Cell Organelle Membrane covered structure with everything necessary for living Part of the cell that undergoes specific functions Semi- Permeable Selective; allows only certain materials to pass ATP Energy the mitochondria produces Analogy Page found in notebook