Ch 2 Assignment #3 Proteins and Nucleic Acids
advertisement
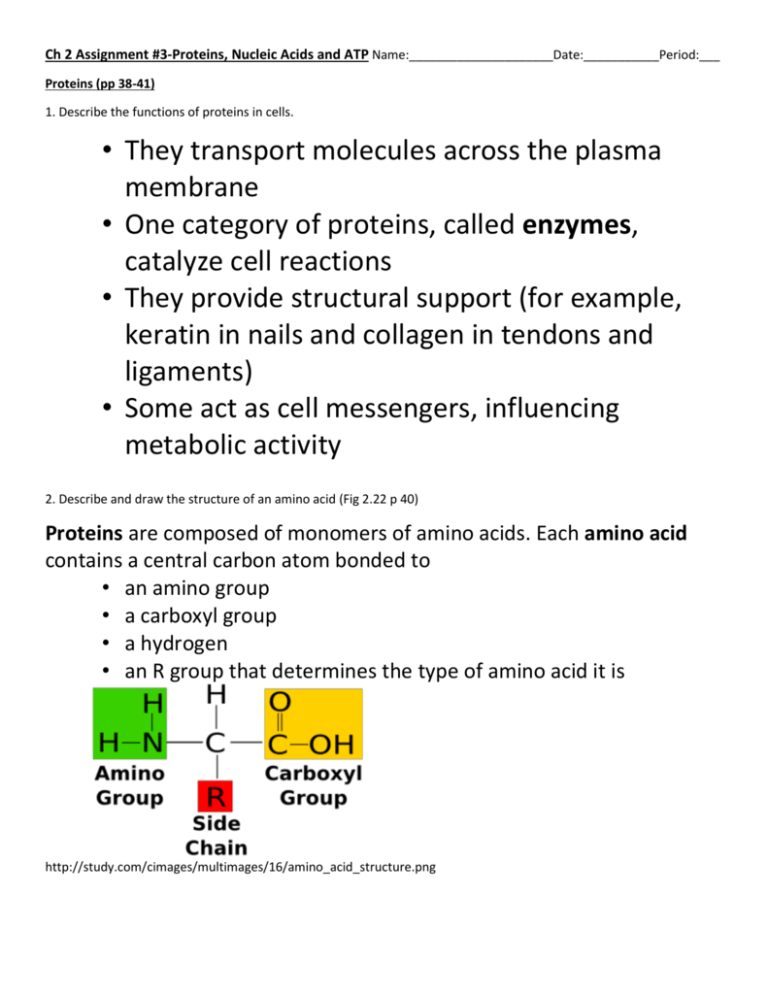
Ch 2 Assignment #3-Proteins, Nucleic Acids and ATP Name:_____________________Date:___________Period:___ Proteins (pp 38-41) 1. Describe the functions of proteins in cells. • They transport molecules across the plasma membrane • One category of proteins, called enzymes, catalyze cell reactions • They provide structural support (for example, keratin in nails and collagen in tendons and ligaments) • Some act as cell messengers, influencing metabolic activity 2. Describe and draw the structure of an amino acid (Fig 2.22 p 40) Proteins are composed of monomers of amino acids. Each amino acid contains a central carbon atom bonded to • an amino group • a carboxyl group • a hydrogen • an R group that determines the type of amino acid it is http://study.com/cimages/multimages/16/amino_acid_structure.png 3. Describe how a polypeptide is constructed from amino acids Polypeptides are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. • Peptide bonds are polar covalent bonds, allowing hydrogen bonding between amino acids. This influences the threedimensional shape of proteins. Fig 2.22 BC Bio 12 4. Draw and compare the four levels of protein structure (organization) Primary structure: amino acid sequence Secondary structure: polypeptide orientation, such as alpha helix or beta pleated sheet Tertiary structure: three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide chain (protein). This shape is held together by covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds between R groups on different amino acids (for example, disulfide linkage S−S between two cysteine amino acids) Quaternary structure: three-dimensional arrangement of polypeptide chains for proteins with two or more chains https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a6/Protein-structure 5. Define denatured. Denaturation (in biology) process of modifying the molecular structure of a protein (so that it has an irreversible change in shape) Denaturation involves the breaking of many of the weak linkages, or bonds (e.g., hydrogen bonds), within a protein molecule that are responsible for the highly ordered structure of the protein in its natural (native) state. Denaturation can be brought about in various ways—e.g., by heating, by treatment with alkali, acid, urea, or detergents. Nucleic Acids (pp 41-42) 1. What are the two types of nucleic acids? *DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which carries the genetic information of an organism *RNA (ribonucleic acid), which consists of different types of molecules such as mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA 2. Describe and draw the nucleotides that make both DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides, which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base. • Nucleotides in DNA contain the sugar deoxyribose and four different types of bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). • Nucleotides in RNA contain the sugar ribose and the same bases as DNA except uracil (U) replaces thymine. 3. How does DNA structure differ from RNA structure? https://cm.jefferson.edu/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/pasted-graphic-11.jpg BC Bio 12 4. How do the functions of DNA and RNA differ? DNA stores and transfers genetic information RNA directly codes for amino acids and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins. ATP (another function of nucleotides) 1. What is ATP? ATP is a nucleotide that also acts as a source of energy 2. Draw and describe what happens to ATP when cells require energy? (Fig 2.26) Energy is stored in the chemical bonds of the phosphates. • Energy is released when the bonds between phosphate groups are broken • Usually, the last phosphate is cleaved to form ADP + Pi, and energy is used for a reaction http://home.comcast.net/~mjmayhew42/Biology%20notes/energy%20notes_files/image005.jpg 3. What are the functions of ATP? • Chemical work: ATP supplies energy for synthesis of macromolecules • Transport work: ATP supplies energy used to pump substances across the plasma membrane • Mechanical work: ATP supplies energy for processes such as muscle contraction and flagella movement












