File - Ms. Anderson`sScience and Social Studies Page
advertisement

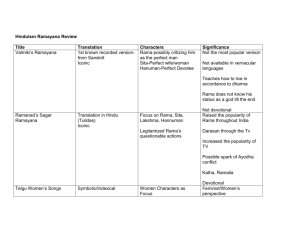
Chapter 5 Empires Ancient India Section 1: Early Times in India Land of the Monsoon Kalidasa: India’s greatest playwright wrote of India’s monsoon seasons April-May: Dry/hot June-Sept: Rainy Winter: Dry/Hot Indian Subcontinent: triangular peninsula of land Contains India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh Half the size of U.S. Separated from Asia by Himalayas and Hindu Kush Mountains Tropical in south Plateau makes up central area (Deccan Plateau) Arabian Sea on West Bay of Bengal on East Indus River—northwest Ganges River—northeast Brahmaputra River—northwest—flows into Bay of Bengal A Lost Civilization Earliest civilization was established 4, 500 years ago Major cities were: Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro Accomplishments: bronze tools, mud bricks, cotton cloth, written language Traded with other nations: jewelry, gold armbands, cooking utensils, statues, and dice games The First City Planners Rectangular Grid Streets Houses the same Indoor wells/plumbing Sewer system Clay toys City Abandoned or Destroyed by natural disaster Newcomers from the NW Aryans: new group to the Indus Valley Used horses to pull chariots Dominated in warfare Domesticated animals and farmed Ist to use sugar cane Religious beliefs influenced Asia Vedas— “knowledge” religious book that contained poems and Hymns 1/3 of book addresses chief god Indras A Priestly Class Priests became powerful rulers 4 mythical classes of Rig-Veda Belief that groups of people came from parts of a body split to create the world Brahmans—priests—mouth Kshatriya—warriors—shoulder Vaishya—trader/landowner—thigh Shudra—peasant—feet Castes: social class a person was born into that affected how he or she was able to relate to others Untouchable castes: low in status and discriminated against Some rejected religious beliefs and searched for “enlightenment” Siddhartha Gautama: became known as Buddha and founded Buddhism Mahavira: founded Jainism Southern India Not invaded by the Aryans Traded with Greece and Rome Known for seaport and powerful women A Mighty Expanision—The Mauryan Empire Maurya, Gupta, and Chola: three great empires of Ancient India Chandragupa Maurya—united India and created Maurya dynasty Reign: period of authority During his son Asoka’s reign the empire was at its greatest After Asoka’s death the empire broke apart due to his son’s fighting 184 BC last Mauryan king assassinated by his own army The Empire’s capital: Multistoried houses, Gold bowls, Gold Clothes Made of 50 million people with different religions, customs, and Languages A High Point—The Gupta Empire Chandra Gupta (AD 320) united empire 200 year reign and the high point of Indian culture Mahabharata and Ramayana writing during this time Pancatantra—wrote animal fables Religious art created Excelled in medicine and science during this time Created math with a decimal point (Arabic #s =India’s #s) A Dynasty of Tigers—The Chola Ruled southern part of India (AD 100) Karikalan Chola—claimed tiger as symbol of his dynasty Rajaraja (AD 985) contolled all of southern India Rajendra (Rajaraja’s son) lands grew to greatest Chola kings were Hindus and built many temples Dynasty wealthy and had leisure activities including games (invented chess) Section 2: Religion of Ancient India The Hindu Religion Hindu: oldest major religion of India “an inhabitant of India” Began with the Aryans Worship god in many forms Brahma—creator Wishna—preserver Shiva—destroyer Parvati—wife of Shiva and mother goddess Rig-Veda (holy book) says there is one god but has many names Believe in reincarnation Reincarnation: soul has lived since the beginning of time and transfers from body of human or animal at death Karma—actions of life that affect the next life (placement of soul) Goal to end cycle of rebirth and to achieve perfection and blend with the universe Each family chooses a god to worship The Teaching of Buddha Siddhartha Gautama (500 BC)—prince who sought “enlightenment” Became Buddha “enlightened one” Teachings include: listening is a path to knowledge, difficult to see own faults The Four Nobel Truths 1. 2. 3. 4. Everyone suffers Cause of suffering is due to desire End suffering by ending the desire End suffering by follow 8-fold path 8-Fold Path Stress good behavior Don’t take life Don’t steal Don’t lie Don’t Cloud Mind Buddhism spread to Tibet, China, Japan, Mongolia, and Korea Jainism—A Religion of Nonviolence Mahavira—founder of Jainism Age of 30 sought enlightenment and self-denied for 12 years Foundation of Jainims: right knowledge, right conduct, right purity Cycle of Rebirth due to misdeeds of previous life Jain “to conquer” --to conquer the chains of reincarnation Non-violence Don’t harm people or animals No farming Carry whisk broom to sweep before step Mohandas Gandhi—was a Hindu inspired by Jainism Section 3: Worship, Work, and Play Your Family Gupta era Many generations inside the same house Lived with father’s parents Money turned over to grandparents Day Begins Work: start early to avoid heat Food: buttermilk, bread, rice, lentils, and vegetables Cow: not eaten—considered sacred Your Village Religion: worship god/ worship statue/bring gifts to temple Work: possible work would be planting in fields Animals: lions and tigers in countryside Seasonal Festivals Describe: include flags, banners, color parasols Epic poem: Ramayona Rama and Sita Rama: hero—exiled by his father the king Sita: Rama’s wife Half brother learns of exile—says he will only rule until Rama’s return Ravana seizes Sita Lakshman and animals help Rama rescue Sita A Happy Ending Ravana : evil king killed Sita: rescued and reunited with Rama Bharata: half-brother of Rama returned the thrown to Rama Section 4: Outstanding Leaders Making a Choice Siddhartha Gautama’s mother dreamt of elephants and said it meant her son would be king or a holy man. Gautama saw beggars and sought meaning of life Became Buddha Ruling with Kindness Asoka was India’s most beloved leader Sought peace in Buddhism Sent teachers to other lands to teach about Buddha Governed with kindness and sent “overseers of the law” to promote the welfare of all Learning Thrives Chandra Gupta II—greatest king of Gupta dynasty Expanded empire and arts flourished Kalidasa—India’s great playwright wrote during this time Extending the Empire Rajendra-greatest ruler of Chola dynasty Expanded Empire Built a powerful navy Established important trade routes Section 5: Tales of Travelers A Visitor From Greece Megasthenes—ambassador to Chandragupta Maurya’s kingdom Quotes from lost book indicate that people ate mostly rice, simple in manners, frugal, eat alone Two Chinese Pilgrims Fa Xian –Chinese Buddhist that travelled to India to study at University of Nalanda Wrote that kings rule without corporal punishment People of India ate no meat Xuan Zang—Chinese Buddhist monk—commented on the cleanliness of India’s people A North African Visitor Ibn Battuta—1330 African visitor to India that served as a judge Wrote of small catapults on backs of elephants Spoke of hundreds of people being killed daily