Test Study Guide: Cell Theory, Types, and Structures
advertisement

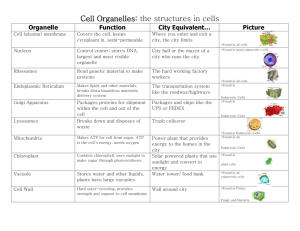
Unit 3: Cell Theory, Types, Structures & Functions Test Study Guide Cell Theory and Scientists There were many different scientists that had an influence in the discovery of cells. The invention and improvement of the microscope played a key role in the development of our understanding of cells. Below, you will find a list of scientists involved and their contributions to the scientific community. 1. Robert Hooke- British scientist, who in 1665, built a microscope and looked at cork from a plant. He described the cork as looking like hundreds of boxes, and named these boxes “cells” which means “little boxes”. 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek- Dutch merchant, in 1673, built a microscope to look at pond scum. He saw many small creatures swimming around and named them “animalcules” which means “little animals”. He also was the first person to see bacteria. 3. Matthias Schleiden- German scientist, in 1838, made the observation and conclusion that all plant parts are made of cells. He came to this conclusion after looking at thousands of plant slides and reading about other scientists’ research. 4. Theodor Schwann- German scientist, in 1839, stated that all animal tissues are made of cells. He concluded this after studying numerous animals under the microscope. He also wrote the first two parts of the cell theory: a. ALL ORGANISMS ARE COMPOSED OF ONE OR MORE CELLS. b. THE CELL IS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE IN ALL LIVING THINGS. 5. Rudolf Virchow- German scientist, in 1858, saw that cells could not develop from anything except other cells. He then wrote the third part of the cell theory: a. ALL CELLS COME FROM EXISTING CELLS. CELL THEORY 1. ALL ORGANISMS ARE COMPOSED OF ONE OR MORE CELLS. (Schwann) 2. THE CELL IS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE IN ALL LIVING THINGS. (Schwann) 3. ALL CELLS COME FROM CELLS. (Virchow) Cell Organelles: the structures in cells Organelle Cell (plasma) membrane Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Function Covers the cell, keeps cytoplasm Where you enter and exit a city, in, semi-permeable the city limits Control center; stores DNA, largest City hall or the mayor of a city Picture *Found in all cells *Found in most eukaryotic c ells and most visible organelle who runs the city Read genetic material to make The hard working factory proteins workers *Found in all cells Makes lipids and other materials, breaks The transportation system like *Found in down hazardous materials, delivery the roadway/highways system Golgi Apparatus City Equivalent… Packages proteins for shipment Packages and ships like the within the cell and out of the cell UPS or FEDEX Eukaryotic Cells *Found in Eukaryotic Cells Lysosomes Breaks down and disposes of Trash collector waste Mitochondria Chloroplast Vacuole *Found in Eukaryotic Cells Power plant that provides cell’s energy, needs oxygen energy to the homes in the city Contains chlorophyll, uses sunlight to Solar powered plants that use *Found in make sugar through photosynthesis sunlight and convert to energy plant cells Stores water and other liquids, Water tower/ food bank *Found in all Wall around city *Found in Plants, algae plants have large vacuoles Cell Wall *Found in all Makes ATP for cell from sugar, ATP is the Hard outer-covering, provides strength and support to cell membrane Eukaryotic Cells eukaryotic cells Fungi, and Bacteria *Things ALL cells have in common: -DNA -cell membrane -cytoplasm -ribosomes Eukaryotic Cells (all organisms except bacteria) have nuclei, have membrane covered organelles, have linear DNA, and can reproduce sexually and/or asexually Animal Cell: Has Centrioles Small Vacuoles No Cell Wall Plant Cell: Has chloroplasts Has large vacuole Has Cell Wall Prokaryotic Cells (bacteria) have no membrane-covered organelles, Circular DNA, usually reproduce asexually, and are unicellular