PYCO worksheet answers
advertisement

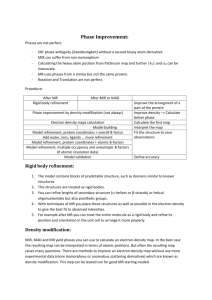
CHEM 3030 EXPT # 5 A WORKSHEET PYCO NAME ________________________ Please fill in answers to the following and hand it in with your lab. See EQ1 and Eq2 of X-ray handout. Step 1. Record the intensity and standard deviation for a few strong reflections, data given in the hkl file OR. From the Hg powder pattern (Mo radiation) identify the two strongest reflections and there relative intensity and Bragg angle. 110 at θ = 2.25 o 111 at θ = 2.65o 002 at θ = 2.87o Hg pwd is vs. 2θ change λ to Mo What do you understand by an intensity like 1.35 +/- 5.4 ? within expt error of 0 Recall Bragg’s Law : λ = 2d sin(θ) AND λ = 0.71073 Å for Mo The unit cell dimensions for an orthorhombic PYCO crystal are 12.436 13.246 14.158 What is the d spacing for the 100 planes and the Bragg angle using Mo radiation. 12.436 What is the d spacing for the 800 planes and the Bragg angle using Mo radiation? 12.436/8 Ditto for the 001 and 0,0, 23 reflections? 14.158 1.4o 14.148/23 35.3o 1.6o 13.20 sin (theta) = 0.71073 / 2 d Step 2. From the unit cell parameters, 12.436 13.246 14.158 90 90 90 which crystal system does PYCO belong to? orthorhombic On what basis does the software decide the lattice type is P and space group P212121 ? systematic absences Give one reflection which is absent as a result of the 21 parallel to a 300 b 050 and c 007 . any odd # is OK If the computer recommended a value of Z = 5 why would you change it to 4 ? There are only 4 general positions in this space group. SHELX INS FILE: Do the SYMM lines generate the other three general positions? yes How does the software come up with the number of each type of atom in the UNIT LINE? 4 times the molecular formula since Z =4 Step 3. While you will not understand much of the direct methods information shown on the screen, what exactly does direct methods seek to obtain? phases for each reflection Where subsequently is it used? in eq2 to obtain electron density map Once tentative locations of most of the atoms are obtained from the E-map, the phases are tossed out and new ones computed using EQ2 in what is called a Fourier synthesis. What information is used to do this? atom locations found so far (Fcalc) and the intensity data in the HKL file (Fobs) the signs (phase) for Fobs are taken to be those for Fcalc. Which structure factor would be used to obtain the coefficient of a term cos(4πz), one of some 2000 terms in the expression for the electron density RHO = 1/V Σ Σ Σ Fhkl cos(2π(hx + ky +lz – αhkl ) sum over h, k and l where αhkl is a phase angle between 0 and 2π. 002 Assume α is zero here. cos((2π(hx + ky +lz) h= 0, k =0 and l =2 For F(000) (the zero angle reflection) all atoms scatter in phase and the value = total number of electrons in the cell. What is F(000) in this case? 1160 electrons If F001 = 0 and F 002 = 280 what fraction of the electrons are scattering in phase at the angles corresponding to these reflections? 0 % and 280/1160 x 100 = 24% (note change for pyco data – value was 280 in fcf file) Step 4. Graphical editor SXGRAPH How does the computer determine which atoms are connected to each other? What are the Q’s displayed on the screen and where did they come from ? within 0.5 Å of sum of covalent radii Q’s are peaks in the e-density map Record the coordinates for the Iron atom recorded in the INS file before running XLS and then record them in the RES file after running XLS. _ if you can find this data you may note a slight change before and after refinement In your own words what happens in a least squares refinement? the positional and thermal parameters are varied to minimize the R factor Step 5 Least Squares Refinement. Examine the new INS file generated by FILE PYCO in the previous step. Record and explain the entries for the Iron in the atom list. code is based on order in SFAC line, then x/a, y/b and z/c followed by site occupancy and thermal parameter The number of parameters (np) are used for the isotropic least squares refinement is 4N + 1 where N is the number of non-hydrogen atoms? What exactly are these parameters? x,y,z and U for each of the non-H atoms Which most accurately describes what the R factor measures? a)Agreement between bond lengths and correct values b) Agreement between magnitudes of Fobs and F calc c) How good the structure is. Step 6. What is a difference electron density map? Explain how the coefficients for the 2000 cosine terms in the Fourier series are obtained. Explain. RHO 1 uses the intensity data in the HKL file for Fobs RHO 2 uses the Fcalcs obtained from the atom locations Diff map : subtract RHO 2 from RHO 1. to find possible missing atoms Explain how missing atoms in the structure appear in the difference map? they are picked off the difference map Step 7. Why do the number of parameters increase to 9N + 1 for an anisotropic refinement? there are 6 U’s for anis and only 1 U for isotropic Step 8. Comment on the Flack parameter and whether you have the correct absolute structure. (see SHELXL.LST) from LST file something like : Flack x parameter = 0.0185 with esd 0.0353 Expected values are 0 (within 3 esd's) for correct and +1 for inverted absolute structure. SUMMARY : The software contains quite a bit of data which otherwise you could look up. List below what was needed : a) in order obtain the space group absences for each possible space group b) to compute Fc (see eq 2 of handouts) you need scattering factors fi for each atom type (element) vs. sin(theta)/λ) and all atom coordinates c) to connect atoms for graphic displays of the structure. you need tables of covalent radii for the elements