Handout D
advertisement
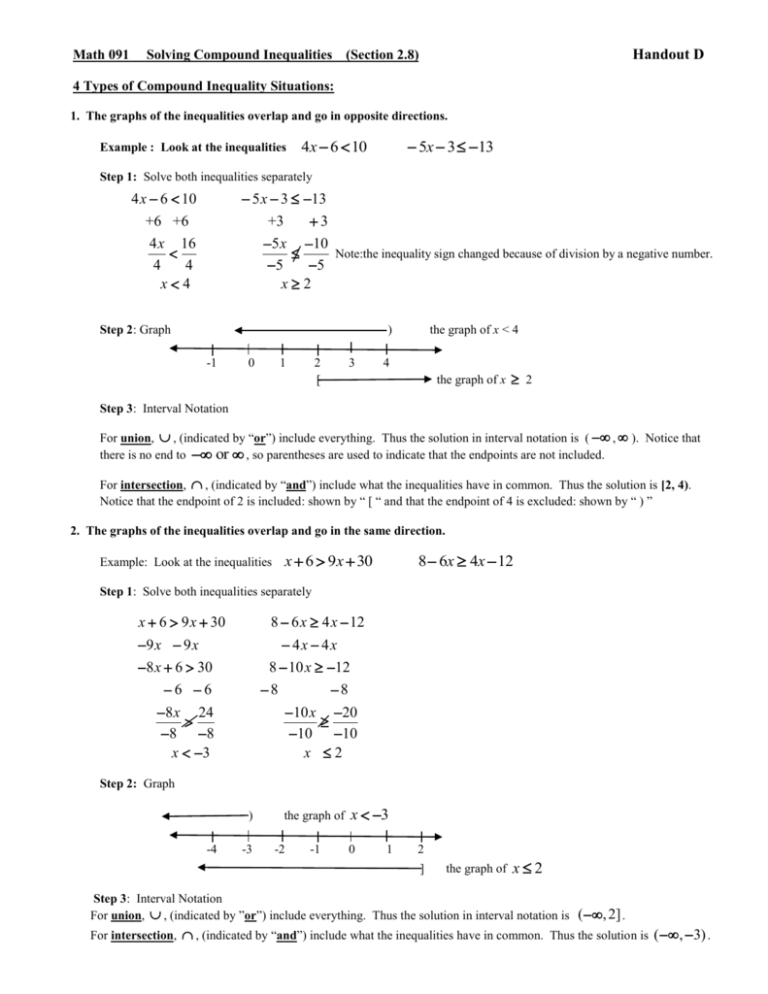
Math 091 Handout D Solving Compound Inequalities (Section 2.8) 4 Types of Compound Inequality Situations: 1. The graphs of the inequalities overlap and go in opposite directions. Example : Look at the inequalities 4x 6 10 5x 3 13 Step 1: Solve both inequalities separately 4 x 6 10 5 x 3 13 +6 +6 3 +3 5 x 10 Note:the inequality sign changed because of division by a negative number. 5 5 x2 4 x 16 4 4 x4 Step 2: Graph ) -1 0 1 2 [ 3 the graph of x < 4 4 the graph of x 2 Step 3: Interval Notation For union, , (indicated by “or”) include everything. Thus the solution in interval notation is ( , ). Notice that there is no end to or , so parentheses are used to indicate that the endpoints are not included. For intersection, , (indicated by “and”) include what the inequalities have in common. Thus the solution is [2, 4). Notice that the endpoint of 2 is included: shown by “ [ “ and that the endpoint of 4 is excluded: shown by “ ) ” 2. The graphs of the inequalities overlap and go in the same direction. Example: Look at the inequalities x 6 9x 30 8 6x 4x 12 Step 1: Solve both inequalities separately x 6 9 x 30 9 x 9 x 8 x 6 30 6 6 8 6 x 4 x 12 4x 4x 8 10 x 12 8 8 8 x 24 8 8 x 3 10 x 20 10 10 x 2 Step 2: Graph ) -4 -3 the graph of -2 -1 x 3 0 1 2 ] the graph of x2 Step 3: Interval Notation For union, , (indicated by ”or”) include everything. Thus the solution in interval notation is (, 2] . For intersection, , (indicated by “and”) include what the inequalities have in common. Thus the solution is ( , 3) . 3. The graphs of the inequalities don’t overlap. 3x 4 10 Example: Look at the inequalities 2x 5 x 9 Step 1: Solve both inequalities separately 3x 4 10 4 4 3x 6 3 3 x 2 2x 5 x 9 x x x 5 9 +5 +5 x 4 Step 2: Graph [ -4 ] -3 -2 the graph of -1 0 1 the graph of x2 2 x 4 Step 3: Interval Notation For union, , (indicated by “or”) include everything. Thus the solution in interval notation is (, 4] [2, ) . For intersection, , (indicated by “and”) include what the inequalities have in common. Thus the solution is . 4. You start with the union or intersection of two intervals already in interval notation. Example: Look at the intervals [2,5) [ 1 ,4) Step 1: There is nothing to solve, so go to step 2, graph. Step 2: Graph [ -1 [ 0 1 2 ) the graph of [2,5) 3 4 ) 5 the graph of [ 1 ,4) Step 3: Interval Notation For union, , (indicated by “or”) include everything. Thus the solution in interval notation is [1, 5) . For intersection, , (indicated by “and”) include what the inequalities have in common. Thus the solution is [ 2, 4) . EXERCISES A. Solve each inequality, graph, and write the solution in interval notation. 1. x 3 and x 7 2. x 2 and x 1 3. x 4 and x 0 4. x 2 or x 6 5. x 8 or x 12 6. x 3 and x 5 7. x 3 and x 5 8. x 3 or x 5 9. x 3 or x 5 10. x 3 or x 5 11. x 3 5 and 13. 3x 3 and x 2 0 14. 3x 3 and x 2 2 15. 2x 1 3 and 2x 8 4 16. 5x 2 2 and 5x 2 7 17. 6x 8 16 and 4x 1 15 2 18. x 4 and 2x 6 3 3 x 2 6 or x 3 4 20. x 3 2 or x 4 3 21. 2x 3 7 or 4x 1 3 22. 3x x 12 or x 1 5 23. 2x 5 10 or 4x 4 24. 3x 6 15 or 2x >15 25. 5x 2 17 or 2x 1 9 26. 3x 4 9 or 4x 5 13 19. 1 x2 2 B. Graph each interval and write the solution in interval notation. 27. , 1 4, 28. 1, ,9 30. , 6 9, 31. 33. 5,11 6, 34. 9,1 , 3 36. 3,6 4,9 37. ,3 , 2 1, 2 0,5 12. x 5 9 and x 3 2 29. 4, ,12 32. ,5 0, 35. 1, 4 2,7 38. 3,8 5,11 Answers To Selected Exercises. 1. (3,7) <---l----l----l----(----l----l----l----)-----> 0 3 7 5. , 8 <----l----]-----l-----l-----l-----l----> 8 6 4 2 9. 13. ( 2, 0 1 0 11. [4,8] <---l----l----l----l----[----l----l----l----]---> 15. 27. [ 4, 0 <----l-----(-----l------l----> 1] ,3 17. 8 , 4 <----l------l------l------l-------]----> 21. 4 ,1 2, <-----l----l----)----(----l----> 4 1 25. 2 , <----l------l------l------l------l----> 2 1 1 0 1 2 <----[------l------l------]------l----> 4 1 29. [4, 12] <----[------l------l------l------]-----> 4 6 8 10 12 <----l-----l-----l-----)----> 33. [6, 11] <----[----l----l----l----l----]-----> 3 35. (2, 4) 4 0 , 4 4, <--l--)--l--l--l--l--l--l--l--(--l--> 1, 5 0 1) <----l-----(-----)-----l-----> 2 1 0 0 31. 0 2 4 23. 5, <----l----l----l----l----l----[----l---- > 7. , <----l------l------l------l------l----> 2 1 19. 3. (0,4) <----l----(----l----l----l----)-----> 0 4 <----l----(----l----)----l-----> 2 4 6 37. [ 1, 5) 11 <----[----l----l----l----l----l----)-----> 5 1