Answers - Math Honors 2
advertisement
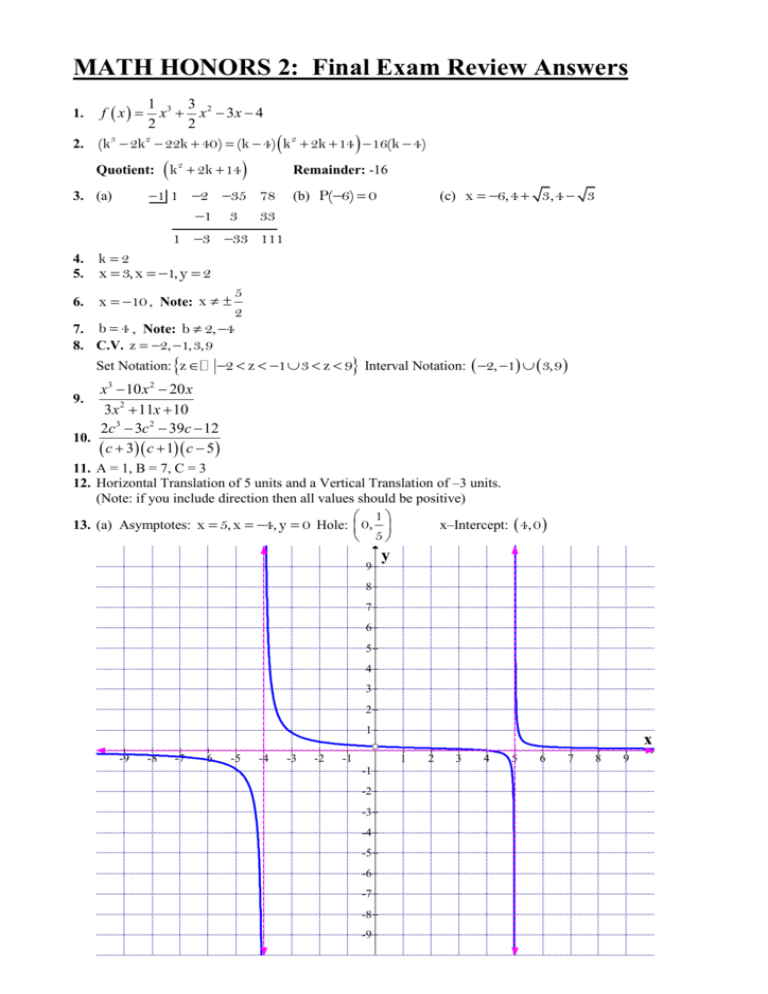
MATH HONORS 2: Final Exam Review Answers 1 3 3 2 x x 3x 4 2 2 3 2 2. (k 2k 22k 40) (k 4) k 2 2k 14 16(k 4) 1. f x Quotient: k 2 2k 14 Remainder: -16 1 1 2 35 78 1 3 33 3. (a) (b) P(6) 0 (c) x 6, 4 3, 4 3 1 3 33 111 4. 5. k2 x 3, x 1, y 2 6. x 10 , Note: x 7. b 4 , Note: b 2, 4 8. C.V. z 2, 1,3,9 Set Notation: z 5 2 2 z 1 3 z 9 Interval Notation: 2, 1 3,9 x3 10 x 2 20 x 3x 2 11x 10 2c 3 3c 2 39c 12 10. c 3 c 1 c 5 9. 11. A = 1, B = 7, C = 3 12. Horizontal Translation of 5 units and a Vertical Translation of –3 units. (Note: if you include direction then all values should be positive) 1 5 x–Intercept: 4, 0 13. (a) Asymptotes: x 5, x 4, y 0 Hole: 0, 9 y 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 x 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 (b) Domain: x (c) Range: y x 4,0,5 y 0, 1 5 Interval Notation: , 4 4, 0 0,5 5, Interval Notation: 1 1 , 0 0, , 5 5 (d) See previous page. 14. Calculator Question y 6 5 4 3 2 1 (-1.21,0) x (1.17,0) -1.8 -1.6 -1.4 -1.2 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 -1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 (-0.0218,-9.32) 15. 2 Real Solutions (2 Real Unequal Roots) because discriminant is greater than zero. 16. (a) x = –1 (b) (–1, –32) (c) f x 2 x 1 32 2 17. (a) or x 1 (b) x 9 or x 1 18. f x 2 x 3 x 5 (d) f x 2 x 3 x 5 19. 8 6a 2 12ai a 3i or in complex form 8 6a 2 a 3 12a i 2 39i 61 1 2 1 2 21. x i 5 or x i 5 3 3 3 3 1 22. Domain: x x Range: 3 23. y 9 x 2 6 x 4 2 24. C.V. x , 4 3 2 Set Notation: x x 4 3 20. y y 3 2 Interval Notation: , 4 3 25. f 1 x 1 x 1 or f 1 x 1 x 1 26. (a) ( g 27. x 4 f )(4) 9 (b) ( f g )( x 2 3) 2 x 2 1 1 (c) f (2) 1 2 28. (a) Function with an inverse that is also a function. (b) Function with an inverse that is not a function. 2 3x 2 30. y 3 x 4 x 1 29. f 1 ( x) 31. a = 1, b = –5, c = 3 32. y 4 3 2 1 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 -3 -4 33. Many Possible solutions. Below is one example. f ( x) x 2 16 and g ( x) 2 x 1 4 x 2 34. f ( x) 1 1 2 x 1 10 35. (a) a 7a 4 c c (b) b2 (c) x y 3 if, x 0 if, x 0 if, x 0 (d) x9a (or x 4 x a ) (e) 3a 36. A shift to the right by 5 units and a shift downwards by 3 units 37. Approximately 7163 (or 7160 ) people would be expected to visit the island in the year 201 38. x 1.7 39. $2818.40 (or $2818 , or $2820 ) 40. 1.96 weeks (or 2 weeks) 2 1 1 A CB 3 5 10 42. 8 10 1 3 43. B 2 3 41. X 44. (a) A 11 4 1 11 11 1 4 1 (b) A1 (or ) 11 3 2 3 2 11 11 (c) A singular matrix means that it has no inverse, occurring when the matrix’s determinant is equal to zero. Since the determinant of matrix A is 11 which is not equal to zero, matrix A is non-singular. 45. m p , n q 3 2 2 4 x 4 46. Use the matrices A 1 2 3 , B 1 ,and X y . Then AX=B and X 29 21 1 1 1 12 z 1 47. (a) x 36 3 (b) x 2 (c) x 10 (d) x 44 48. 43.2 mg 49. x ln 18 5 3 7 5 51. x 4 50. 5 7 , 8 8 2 3 , , (b) x , 4 3 3 4 52. (a) x 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. Use calculator to check your graph. Proof – answer is given Proof – answer is given A = –2, C = 1 A = 0.8, B = 0.5, D = –1.2 3 32 2 3 3 [Hint: use sum identity with 60. 5.16 degrees 61. 52.6 yards 62. (a) about 90.0 degrees (b) 51.7 square kilometers 63. 67 ways [ 7 5 4 8 ] 1 2 4 64. 37.5% [ 6 ] 65. 51.3% [(.75)(.60) + (.25)(.25)] cos( 30) ] sin( 30)