Revision Ex. Ch2
advertisement

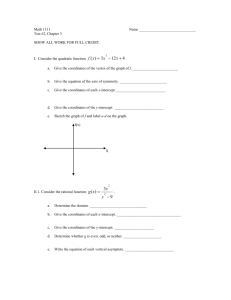
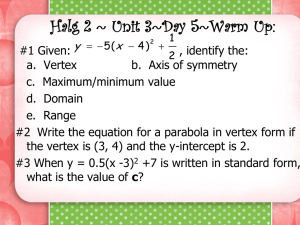
Shatin Pui Ying College F.4 Mathematics Revision Exercise Ch.2 (ANS) 1. Determine the directions of opening and find the y-intercepts of the graphs of the following functions. (a) y = x2 – 4x + 6 (b) y = (1 – 2x)2 – 3 ## (a) For y = x2 – 4x + 6, ∵ Coefficient of x2 = 1 > 0 ∴ Its graph opens upwards. ∴ The y-intercept of its graph is 6. (b) y (1 2 x) 2 3 4x2 4x 2 ∵ Coefficient of x2 = 4 > 0 ∴ ∴ 2. Its graph opens upwards. The y-intercept of its graph is –2. The figure shows the graph of y = 2x2 + 8x + 6. State the following features of the graph: (a) Axis of symmetry (b) Coordinates of the vertex (c) y-intercept (d) Direction of opening From the graph, (a) Axis of symmetry is x = –2. (b) Coordinates of the vertex (2, 2) (c) y-intercept 6 (d) The graph opens upwards. 3. The figure shows the graph of y = x2 – 4x + c. D(d, –16) is the minimum point of the graph. (a) Find the values of c and d. (b) State the following features of the graph: (i) Axis of symmetry (ii) Coordinates of the vertex (iii) y-intercept (iv) Direction of opening (a) From the graph, the parabola y = x2 – 4x + c cuts the y-axis at (0, –12). ∴ c 12 ∵ The parabola passes through D(d, –16). By substituting c = –12 and (d, –16) into y = x2 + 4x + c, we have 1 16 d 2 4d 12 d 2 4d 4 0 (d 2) 2 0 d 2 (b) From the graph, (i) Axis of symmetry is x = 2. (ii) Coordinates of the vertex (2, 16) (iii) y-intercept 12 (iv) The graph opens upwards. 4. ∵ ∴ The figure shows the graph of y = x2 + bx + c which cuts the x-axis at A(–6, 0) and B(1, 0). Find the values of b and c. The graph of y = x2 + bx + c cuts the x-axis at A(–6, 0) and B(1, 0). The roots of the quadratic equation x2 + bx + c = 0 are –6 and 1. x 6 or x 6 0 or ( x 6)( x 1) 0 x 1 x 1 0 x2 5x 6 0 ∴ b 5 and c 6 5. A marble is projected vertically upwards to the ceiling of a house from the floor. After t seconds, its height (h m) above the ground is given by: h = –5t2 + 5t + 1 (a) When will the marble attain its maximum height? (b) If the ceiling is 3 m above the ground, will the marble hit the ceiling? ## (a) h 5t 2 5t 1 5(t 2 t ) 1 2 2 2 1 1 5t t 1 2 2 1 5 5 t 2 t 1 4 4 2 1 9 5 t 2 4 1 , h attains its maximum value. 2 ∴ When t ∴ The marble will attain its maximum height after 1 seconds. 2 2 1 9 (b) From (a), h 5 t 2 4 2 6. 9 m. 4 ∴ The maximum height reached is ∴ The marble will not hit the ceiling. Given that the maximum value of the function y = –3x2 + 6x + p is 11. (a) Find the value of p. (b) State the coordinates of the vertex of its graph. (a) y 3x 2 6 x p 3( x 2 2 x) p 3( x 2 2 x 12 12 ) p 3( x 2 2 x 1) 3 p 3( x 1) 2 (3 p) ∴ The maximum value of y is 3 + p. ∴ 3 p 11 p8 (b) From (a), we have y = –3(x – 1)2 + 11 ∴ Coordinates of the vertex (1, 11) 7. If the sum of two numbers is 12, find the maximum value of the product of these two numbers. Let x be one of the numbers, then the other number is 12 – x, and y be the product of these two numbers. ∴ y x(12 x) x 2 12 x ( x 2 12 x) ( x 2 12 x 62 62 ) ( x 2 12 x 36) 36 ( x 6) 2 36 ∴ ∴ The maximum value of y is 36. The maximum value of the product of these two numbers is 36. 8. (a) Solve (x – 1)2 + 4x < 0 graphically. (b) Find the largest integer x that satisfies x(x + 2) 4. (a) ( x 1) 2 4 x 0 x2 2x 1 4x 0 x2 2x 1 0 x2 2x 1 x2 2x 1 2 Draw the straight line y = 2 on the graph of y = x2 – 2x + 1. From the graphs, there is no solutions for x 2 2 x 1 2 . ∴ There is no solutions for ( x 1) 2 4 x 0 . 3 x( x 2) 4 (b) x 2 2x 4 x 2 2 x 4 x 2 2 x 1 3 Draw the straight line y = 3 on the graph of y = x2 – 2x + 1. From the graphs, the largest integer x that satisfies x 2 2 x 1 3 is 1. ∴ The largest integer x required is 1. 9. In the figure, the graph of y = g(x) is obtained by translating the graph of y = 2x2 8x + 10. (a) Describe the effect of the transformation on the graph of y = 2x2 8x + 10. (b) Find the symbolic representation of g(x). (a) From the graphs, the graph of y = 2x2 – 8x + 10 is translated in the negative direction of the x-axis by 2 units. 2 (b) g ( x) 2( x 2) 8( x 2) 10 2 x 2 8 x 8 8 x 16 10 2x2 2 ∴ The required symbolic representation is g(x) = 2x2 + 2. 10. It is given that f(x) = 2x2 4x 1 is transformed to g(x). If the coordinates of the vertex of the graph of y = g(x) are (1, 3), find the symbolic representation of g(x). f ( x) 2 x 2 4 x 1 2( x 2 2 x) 1 2( x 2 2 x 12 12 ) 1 2( x 2 2 x 1) 2 1 2( x 1) 2 3 ∴ ∵ The coordinates of the vertex of the graph of y = f(x) are (1, –3). The coordinates of the vertex of the graph of y = g(x) are (1, 3). ∴ The graph of y = g(x) is obtained by translating the graph of y = f(x) in the negative direction of the x-axis by 2 units. ∴ g ( x) f ( x 2) 2[( x 2) 1]2 3 2( x 1) 2 3 2x2 4x 1 ∴ The required symbolic representation is g(x) = 2x2 + 4x – 1. 4