Acute Respiratory Failure Chapter 66
advertisement

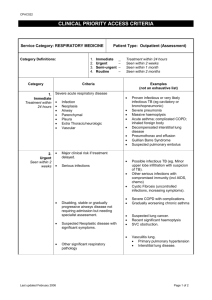
CSUB Department of Nursing Bpulskamp’s Study Helps for Mechanical Ventilation Chapter 64 p. 1776+ Acute Respiratory Failure Chapter 66 1.Review respiratory failure, the terms, lab normals, pathophysiology and risk factors. 2. What can you do to help educate for prevention and early detection especially pre-op patients? Review chapter 28 as needed (COPD). 3.Respiratory failure of Type 1 (hypoxemia) has several causes (give examples). What are they, the causes and /or associated diseases and which are most common? How are they treated? 4. . Type II respiratory failure with Hypercapnic. What are causes? ( give examples). What are they, the causes and /or associated diseases and which are most common? How are they treated? What are some of the symptoms of hypercapnia? What are the risks for the patient? What are nursing interventions? 5. What are clinical manifestations of respiratory failure? How does it differ with PaCO2 and O2 values? What impact does respiratory failure have on ribs and chest muscles? 6. What are the medications used for respiratory failure? What are the main side effects of aminophylline, isuprel, brethaire, Alupent etc? 7. What positions are preferable for the patient to maximize his ventilation? 8. What are some of the most common diagnostic studies? Which are most effective? 9. Evaluation of ventilation is administered through a physical assessment of all systems. See table 66-4 for each system and how it is impacted. 10. Acute respiratory distress syndrome is what? Caused by what or is precipitated by what factors? What are initial symptoms? How do they change with progression of the disease? What is the pathology? 11. What are some of the potential complications? What are the nursing measures to evaluate for the onset of the complication? 12. What impact does hypoxemia have systemically? 13. How will you maintain cardiac outputs, oxygenation, and perfusion? 14. Medications used for treatments of respiratory failure and ARDS. 15. ET tube placement, What do you assess first for correct placement? What do you do next? How is it verified? 16.Nursing Diagnosis of Aspiration. What are particulars? 17.Prevention of ventilator malfunction . Key terms/ideas: ET tube placement, complications and how to evaluate placement? Criteria for inflation of cuff on endotracheal tube? What 1st nursing action for displaced ET tube? Cardiac arrhythmias occur when suctioning. What nursing action and what priority? What is PEEP? Why used? What complications in neuro patients? Hypoxemic and hypercapnia differences in labs and causes. Compare patient diagnoses. Which dx would be candidates for which? What would you expect the treatment to be? ABG values, what is measured? Compare to pulse oximetry values. Acute respiratory failure labs /Symptoms of loss of respiratory function. Patient behavior? Labs?? Who is high risk for Acute respiratory failure? Hypoxemic respiratory failure: Mismatch, shunt, Diffusion alveolar hypoventilation. What do these mean? What is the mechanism involved with examples of each. Pulmonary Emboli impacts respiratory function by? What are the nursing interventions?? Barbiturates impact respirations by…? COPD symptoms and Nursing interventions for a COPD patient with hypoxemia. Hypercapnic respiratory failure symptoms and expected treatments. Pulmonary emboli treatment ARDS Pathology, onset, symptoms, and etiology. How does it impact the overall system? If PEEP is used for ARDS? Why? Treatment options for ARDS Bpulskamp 9-03 Bpulskamp 9-03