skin resection
advertisement

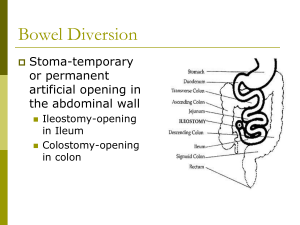
Stomas – surgically created opening between bowel & skin Total colectomy Panproctocelectomy & ileostomy Colectomy & ileo-anal anastomosis (restorative proctocolectomy) Ileostomy Right lower quadrant = ileostomy Spout – contents irritant to skin (corrosive) Liquid faeces Permanent end ileostomy = total colectomy — Ulcerative colitis or familial polyposis Temporary ileostomy = emergency sub-total colectomy with over-sewing of rectum — Toxic megacolon Loop ileostomy – bowel temporarily defunctioned – gives anastomosis time to heal — Reversed after 6/52 — Anterior resection — Rod under to stop downstream bowel — Diverticular disease, UC Urostomy/Ileal Conduit – R. iliac fossa Performed after cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer (T2-T3 – penetrating muscle) Ureters too fine to be brought directly to surface length of ileum isolated but left on vascular pedicle Ureters implanted into ileal reservoir (after bladder removed) Distal end brought our as ileostomy (with spouteverted end) Catheter left in situ post-op to reduce stricture formation Complications: UTI Stricture of ureter or ileum → obstruction & hydronephrosis Ischaemia of ileum or spout Parastomal hernia Renal stones/failure Colostomy Left iliac fossa Flush to skin Solid faeces AP (abdomino-perineal) resection – permanent Low rectal tumour Hartmann’s procedure – emergency colonic resection, rectal stump oversewn - temporary LIF colostomy → reversed after a few months Perforated diverticulitis, obstructed colon cancer Complications of Stomas Fluid loss Odour Ulceration of skin Leakage Stenosis Hernia (parastomal) or prolapse Ischaemia Terminal ileum loss (failure to absorb bile salts & B12 Sexual & psychological problems Hyperchloraemic acidosis — Bowel mucosa contains ion pump that exchanges chloride for bicarbonate — Urinary chloride absorbed & bicarbonate in exchange → hyperchloraemic acidosis (due to loss of bicarb) — More common with ureters transplanted into large bowel than ileal conduit Complications of Stomas Immediate: Haemorrhage Ischaemia Infection Early: Electrolyte abnormality Retraction Obstruction Late: Prolapse Fistula Parastomal hernia Dermatitis Psychological problems