Shoulder Review and Study Guide
advertisement

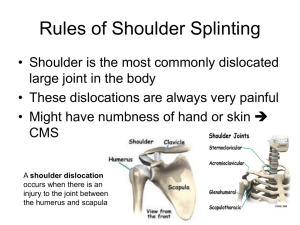
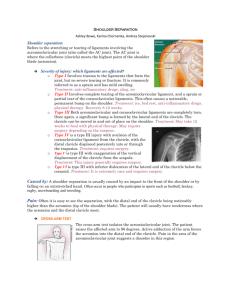
Name ________________________________ Shoulder Review 1. Name the four bones that make up the shoulder joint. ___________________________ _clavicle, sternum, scapula, humerus____________ 2. The joint formed by the sternum and the clavicle is called the ______________________ _sternoclavicular_____________________________________________ 3. A dislocated shoulder is an injury to what joint of the shoulder _____________________ _____glenohumeral___________________________________________ 4. A separated shoulder is a sprain to the _acromioclavicular__________ joint of the shoulder. 5. The most vulnerable position for the shoulder is __abducted______- and ____externally rotated______________________. 6. In most dislocated shoulders, the head of the humerus lies in an __anterior__ and __inferior____________ position. 7. There are no muscles on the ____inferior______ aspect of the shoulder. 8. The __clavicle____ is the most commonly broken bone in the body. 9. The __acromioclavicular_________ joint is formed by the acromion process of the scapula and the clavicle. 10. *The function of the rotator cuff is to__________________________________________ ___hold the head of the humerus into the glenoid fossa_____ _______________________________________________________________________ 11. Unlike the hip, the shoulder sacrifices __stability_ in order to gain __mobility____________________. 12. The __labrum____ is a ring of cartilage similar to the meniscus in the knee and acts to deepen the articular surface of the shoulder. 13. The gliding motion of the __scapula__ (bone) allows for greater that two-thirds the motion of the shoulder. 14. The ____sulcus sign________ tests for multi-directional instability of the shoulder. 15. The __apprehension test____ tests for a subluxing shoulder 16. Evaluates the integrity of the supraspinatus ___empty can test or supraspinatus test___ 17. shrugs the shoulders _ trapezius 18. flexes the arm biceps brachii 19. extends the arm triceps brachii 20. first 10º of abduction supraspinatus 21. All fibers abduct the arm, anterior fibers flex and medially rotate the arm, posterior fibers extend and laterally rotate arm deltoid 22. internal rotation subscapularis 23. external rotation (2) infraspinatus and teres minor Things to remember Joints: Acromion process of the scapula + the clavicle = the acromioclavicular joint (tip of the shoulder) Glenoid fossa of the scapula + humerus = glenohumeral joint (ball and socket joint) Sternum + the clavicle = sternoclavicular joint ( only bony attachment of the upper extremity to the trunk) Injuries Clavicle is the most commonly broken bone in the body Dislocated shoulder is a dislocation of the glenohumeral joint Separated shoulder is a sprain of the acromioclavicular joint/ligament Injuries during acceleration phase of throw are usually to the anterior shoulder Injuries during deceleration phase of throw are usually to the posterior shoulder In a dislocated shoulder the head of the humerus usually lies in an anterior/inferior position Tests Apprehension test= dislocated/subluxing shoulder Drop arm test = rotator cuff Empty can test/ supraspinatus test = supraspinatus Piano key sign = separated sholder Sulcus sign = multidirectional instability Misc Shoulder sacrifices stability to gain mobility There are no muscles on the inferior aspect of the shoulder If someone complains of numbness or tingling you should rule out a neck injury The labrum is a ring of cartilage similar to the meniscus of the knee After taking a history, you may have to palpate for a deformity instead of look for one if the athlete is wearing shoulder pads