6 - Acusis
advertisement

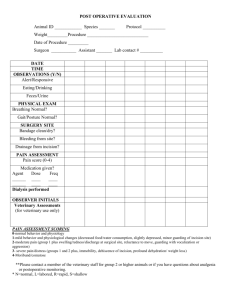
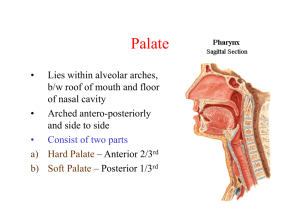
ASSISTANT: ANESTHESIOLOGIST: MARK KENTER, M.D. PROCEDURE: 1. Microscopic bilateral myringotomy and PE tubes. 2. Tonsillectomy. 3. Adenoidectomy. PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Chronic bilateral serous otitis media, enlarged tonsils and adenoids blocking the eustachian tubes. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Chronic bilateral serous otitis media, enlarged tonsils and adenoids blocking the eustachian tubes. ANESTHESIA: General. OPERATIVE FINDINGS: Patient with chronic bilateral serous otitis media, enlarged tonsils and adenoids. OPERATIVE PROCEDURE: After adequate endotracheal anesthesia was accomplished, the left ear was visualized using an aural speculum and operating microscope. With microscopic visualization the canal was cleaned of cerumen. With microscopic visualization an anterior inferior myringotomy incision was performed. Thick serous fluid was aspirated from the middle ear and PE tube was placed for ventilation purposes. The head was turned and the right ear was visualized, again with aural speculum and operating microscope the tympanic membrane was visualized. An anterior inferior myringotomy incision was performed. Thick serous fluid was aspirated from the middle ear and PE tube was placed for ventilation purposes. The head was turned to the midline. A McIvor mouth gag was placed to hold the mouth open. A red rubber catheter was placed into the nose and brought out through the mouth to retract the soft palate. The left tonsil was grasped with a tenaculum. Using a Peak Plasma coagulating blade an incision was made in the anterior pillar, superior pole. The tonsil was dissected beneath the capsule extending to tonsillar fossa from superior to inferior, anterior to posterior, across the inferior pole, separating it from the posterior pillar, leaving it intact. Bleeding was controlled with Peak cautery and electrocautery. Marcaine 0.25% with 1:200,000 epinephrine was used for local infiltration of tonsillar fossa. The right tonsil was grasped with a tenaculum. Again, using a Peak, incision was made in the anterior pillar, superior pole. The tonsil was dissected beneath the capsule, extending to the tonsillar fossa from superior to inferior, anterior to posterior, across the inferior pole, separating it from the posterior pillar, leaving it intact. Bleeding was controlled with Peak cautery and electrocautery. Marcaine 0.25% with 1:200,000 epinephrine was used for local infiltration of the tonsillar fossa. The nasopharynx was visualized with laryngeal mirror. Adenoids were removed with Peak adenoid cauterizing curets and bleeding was controlled with electrocautery. The red rubber catheter was removed and the nasopharynx was thoroughly irrigated with saline. The McIvor mouth gag was removed. The patient tolerated the procedure well.