Affinity chromatography
advertisement
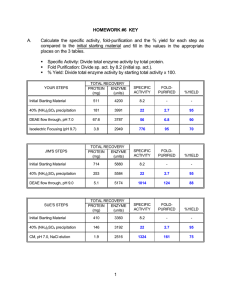
PROTEIN PURIFICATION AND ANALYSIS Basic/initial ste ps 1. Acquire/prepare tissue (1 g = 106 plant cells, 10 9 animal cells, 10 12 bacterial cells) 2. Suspend in buffer (pH stabilizers: phosphate, Tris/TRIZMA, ÒGoodÓ buffe rs, e.g. HEPES), with solubilizers/detergents (e.g. digitonin, Triton X-100), protease inhibitors: cold, PMSF, leupeptin, chymostatin) 3. Lyse cells (Waring blendor, sonicator, French press, mortar and p estle) 4. Centrifuge (e.g. 12 kg x 30 min) lipid supernatant = Òcrude extractÓ pellet 5. (NH 4)2SO4 or pH precipitations: (Òsalting outÓ): Salt competes for water of solvation, precipitating proteins: different proteins precipitate at different concentrations (e.g., 20%, 50%, 80% of saturation); 2-3-fold purification Assays Need measures for the object (enzyme activity, chromophore, etc.) and for total protein concentration: Enzyme: A + B --> C + D: detect C (or A) as func tion of time (ideally, linear with time and amount of enzyme) C or D amount of substrate or product A or B Time Spectrophotometry (for activity, protein concentration, etc.) A = - log10 (I/I o) A = a*c*l a = absorbance (specific for compound); c = concentration; l is cuvette thickness (usually 1 cm) dI/I = -ec dl ºdI/I = -ecl lne(I/Io) = -ecl a = e/2.3 log10(I/Io) = -acl A = -acl = -log10(I/Io) Use spectrophotometry for: 1. 2. 3. 4. Measuring substrate or product concentration if one is “colored” (absorbs UV or visible light). Measuring substrate or product concentration if one reacts with something to form a colored compound. Measuring the concentration of total protein (by UV absorbance: A280 ~ 1 @ 1 mg/ml) or of a specific protein (like hemoglobin) that contains a colored “chromophore.” Measuring the concentration of protein by reacting it with a reagent to form a colored compound. (E.g., cys, tyr, trp reduce Cu2+ to Cu+, which forms an intense blue with BCA; Coomassie reagent turns blue in hydrophobic environment.) Measuring purification Specific activity (SA) = total enzyme activity/total protein or activity concentration/protein concentration 1 IU (international unit) = 1 µmol substrate used (product formed)/min-mg protein “Purification” at step x = SA of step x / SA of crude extract One measure of “purity” is constant SA. Note: if the protein of interest is 0.2% of the total, then you require 500-fold purification for purity; if each step gives 3-fold purification, then you need 5-6 steps; if each step causes some loss of the protein of interest (e.g. 50%), you need to start with 30-60-times more enzyme than you will recover. Purification techniques: size, charge, specific binding Size: exclusion chromatography Size SDS - PAGE (sodium dodecylsulfate - polyacrylamide gel eletrophoresis) SDS: charged detergent that denatures protein and gives uniform surface charge density acryla mide gel: cross-links produce resistance to protein movement negative electrode larger protein smaller pro tein positive electrode Isoelectric electric focusing (IEF): separate by pH at which proteins have zero charge Use ÒampholytesÓ to stabilize pH gradient in an electrophoresis gel. Electrophorese: protein moves to pI (isoelectric point, zero charge) negative electrode high pI (e.g. 10) low pI (e.g. 4) positive electrode 2-D gels combine isoelectric focusing with SDSelectrophoresis Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: IEF followed by SDS-PAGE 3 Isoelectric point 5 7 9 MW (kD) 150 100 50 25 10 Affinity chromatography: separate by biological specificity 1. 2. 3. 4. Attach “ligand” to insoluble column material Combine protein mixture with column: enzyme binds to ligand Wash column to remove unwanted material Elute enzyme with substrate or change in pH (to reduce binding) What do you use for ligand?: su bstrate analog; dyes simulate enzyme cofactors (often planar, aromatic) Summary Enzyme purification involves: breaking cells and stabilizing pH, proteolysis, measuring enzyme activity and protein concentration, a series of separation techniques Spectrophotometry is useful for measuring protein concentration and, often, enzyme activity Exclusion chromatography, electrophoresis, isoelectric focusing, and affinity chromatograph are useful methods for purifying proteins