1b. Why is the melting of ice not a chemical reaction?
advertisement

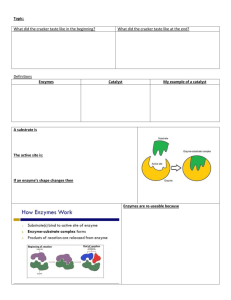
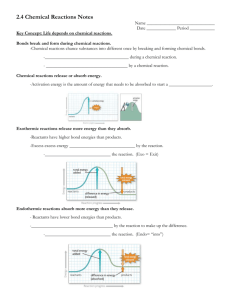
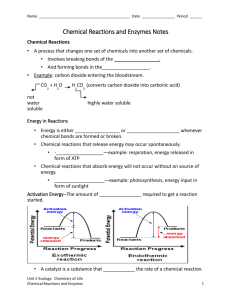
p. 53 A.Q. 1ab, 3abc p. 53 A.Q. 1ab, 3abc 1a. What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? 1a. During chemical reactions, the bonds change—they are formed or broken. 1b. Why is the melting of ice not a chemical reaction? 1b. The melting of ice is not a chemical reaction because new chemicals are not formed. 3a. What are enzymes? 3a. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. p. 53 A.Q. 1ab, 3abc 3b. Explain how enzymes work, including the role of the enzyme-substrate complex. 3b. Enzymes provide a site where reactants, called substrates, can be brought together to react. The substrates bind to a site on the enzyme called the active site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. This reduces the activation energy needed for the reaction. 3c. A change in pH can change the shape of a protein. How might a change in pH affect the function of an enzyme such as carbonic anhydrase? 3c. A change in pH might affect the function of an enzyme such as carbonic anhydrase because the change in pH could change the shape of the enzyme. If the enzyme and substrates no longer fit properly, the enzyme would no longer be able to speed up the chemical reaction.