Real Time PCR
advertisement

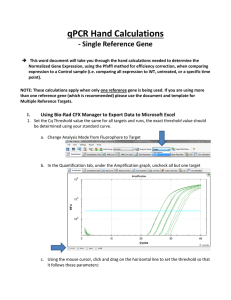
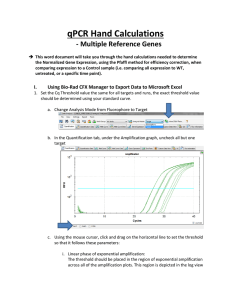
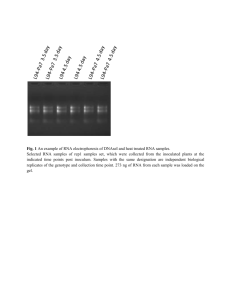
Real Time PCR Principles and Important Considerations Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry Primer/Probe design is really important • Use PrimerExpress • No mismatches are allowed (make sure you have the correct sequence) • MGB labeled with VIC or FAM (never ROX) • Primers/Probe need to be validated • For gene expression experiments it is ideal that one of the primers or probe sits in an exon junction (prevents amplification from genomic DNA). Endogenous control gene: • Present in all experimental samples • Expression does not vary between treatments, tissues, age, etc. i.e. constant expression levels • By using an endogenous control as an active reference you can normalize quantification of mRNA target for differences in the amount of total RNA added to each sample. i.e. loading control • Commonly used: 18S or 25S rRNA, actin, GAPDH, ubiquitin, etc Reference sample • Used in Comparative CT and relative standard curve experiments • Sample used as the basis for relative quantitation results. i.e. Everything gets expressed and compared relative to this sample. • Also called calibrator • It doesn’t matter which sample is used, however normally the negative control is used. Amplification curve: log view Linear Exponential Always use during analysis Plateau Amplification curve: linear view It's all about Ct Threshold Ct Threshold set too high Threshold set too low Threshold is important • Threshold determines Ct values • Ct values are used to calculate relative expression, presence/absence, etc. It's all about Ct values • Threshold should be set in the linear portion (parallel lines) in log view. Always check! • Do not use Ct values of 35 or higher. Repeat using more cDNA/DNA Good Comparative Ct example (for gene expression) Endogenous control Gene of interest • Small variation in endogenous control Ct values • Shape of curve, including linear phase (log view) 1 Bad Comparative Ct example 1 2 2 3 1) Too much variation in endogenous control Ct values 2) Sigmoidal curves. Check baseline levels 3) No amplification Other important considerations • Really sensitive technique: 1 DNA molecule can be detected • Contamination and cross-contamination IS a problem • Always include no template (water) controls for each gene in each plate • Include no RT control (RNA) some of the time. Specially when you are starting using this technique • RNA/cDNA/DNA quality is critical. OD values (260/280≥ 1.8 260/230 ≥2.0) • At least 3 biological replicates Good Practices • Mortars and pestles should be treated with bleach and autoclaved • Pipettes and centrifuge should be decontaminated (RNAase Away) • Cover your working area and replace mats after each round of extractions • Change gloves frequently • If extracting RNA don't talk to your samples! RNases are present in your saliva. Use RNase-free water • Keep your working area clean! Reaction setup ALWAYS set your plates/tubes on a rack NEVER set your plates/tubes directly on the bench or ice Keep the machine clean and free of dust! Plates go directly on the heating block. Tubes go on a black rack. Online help • Real-Time PCR Systems. Chemistry Guide: http://www3.appliedbiosystems.com/cms/groups/mcb_marketing/documents/generaldocu ments/cms_041440.pdf • Guide to Performing Relative Quantitation of Gene Expression Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR: http://www3.appliedbiosystems.com/cms/groups/mcb_support/documents/generaldocume nts/cms_042380.pdf • Troubleshooting guide: http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/absite/us/en/home/support/tutorials/realtime-pcrtrouble-shooting-guide.html