Igneous Rocks

21.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
Rocks are classified into three major groups based on how they formed
Igneous Rocks
• Can be divided into two categories based on where they form
A. Intrusive Rocks
– igneous rocks that form underground from magma
– Cool slowly allowing crystals to grow large giving it a coarse-grain texture
B. Extrusive Rocks – igneous rocks that form at the surface from lava
– Cool quickly resulting in the crystals to be small giving it a fine grain texture
Igneous Rock Textures
II. Sedimentary Rock – rock that forms over time as sediment is squeezed and cemented together
– Sediment
– small, solid pieces of material that comes from rocks or living organisms
• Sediment is deposited in layers by running water or wind
• Sediment is cemented together by pressure from overlying layers
Three Main Groups of Sedimentary Rocks:
1. Clastic
2. Chemical
3. Organic
1.
Clastic Rock
– sedimentary rocks that form from the broken fragments of other rocks
–
–
Clastic Rocks are classified based on the size of their fragments
Example: Conglomerate
– rock fragments that consist of gravel and pebbles
Some clastic rocks are made of smaller particles ( sandstone)
2. Chemical Rocks
– rocks that form when minerals precipitate out of solution
– Example: when ocean water evaporates
(halite)
3.
Organic Rocks
– rocks that form as a result of organic processes
Shells of marine animals like corals, clams, mussels sink to the ocean floor when they die.
– Example: Limestone and calcite (chalk)
III. Metamorphic Rocks
– rock that have been changed by temperature, pressure, or chemical reactions.
– Most metamorphic rocks form under high temperatures and pressures deep underground.
(slate and schist– shown below)
Metamorphic Rocks
Foliation: a layering of minerals in a rock due to intense pressure squeezing the crystals together.
Metamorphic Rock pictures
Metamorphic Rocks like gneiss show banding of light and dark minerals.
Metamorphic Rocks and their
Parent Rocks
Examples:
– Slate: parent is shale
– Gneiss: parent is granite/schist
– Quartzite: parent is sandstone
– Marble: parent is limestone
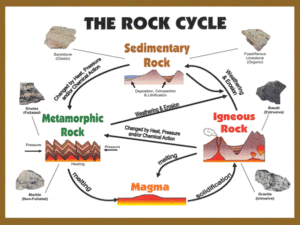
IV. Rock Cycle
Rock Cycle – series of processes in which rocks continuously change from one type to another.