Circulatory and Gas Exchange
advertisement

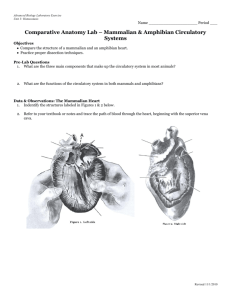
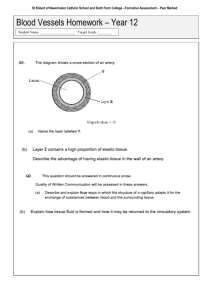
Circulatory and Gas Exchange Figure 42.0 External gills of a salmon Intimate exchange of gases via capillaries Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian Aurelia Invertebrate: Jelly fish Figure 42.1x Aurelia (moon jelly) Figure 42.2 Open and closed circulatory systems Figure 42.3 Generalized circulatory schemes of vertebrates Figure 42.4 The mammalian cardiovascular system: an overview Blood circulation Figure 42.5 The mammalian heart: a closer look Blood Circulation Figure 42.6 The cardiac cycle Figure 42.7 The control of heart rhythm An increase of 1o C increases HR 10 bpm. Had a fever lately? Purkinje Fibers Figure 42.8 The structure of blood vessels Figure 42.9 Blood flow in veins Figure 42.10 The interrelationship of blood flow velocity, cross-sectional area of blood vessels, and blood pressure Figure 42.11 Measurement of blood pressure (Layer 1) Figure 42.11 Measurement of blood pressure (Layer 2) Figure 42.11 Measurement of blood pressure (Layer 3) Figure 42.11 Measurement of blood pressure (Layer 4) Figure 42.12 Blood flow in capillary beds Figure 42.13 The movement of fluid between capillaries and the interstitial fluid Figure 42.14 The composition of mammalian blood Figure 42.15 Differentiation of blood cells Figure 42.16a Blood clotting Injury to blood vessel: Platelets, damaged cells and plasma all contribute clotting factors Prothrombin Fibrinogen Thrombin Fibrin Figure 42.16x Blood clot Figure 42.17 Atherosclerosis: normal artery and artery with plaque Angiogenesis and Cancer • Video: Angiogenesis and Cancer (15-20 minutes) Respiratory System Figure 42.18 The role of gas exchange in bioenergetics Figure 42.19 Diversity in the structure of gills, external body surfaces functioning in gas exchange Figure 42.20 The structure and function of fish gills Figure 42.21 Countercurrent exchange Maximizes oxygen flow from the water to the blood Figure 42.22 Tracheal systems Figure 42.23ab The mammalian respiratory system Figure 42.23c Alveoli Figure 42.23cx2 Alveolar structure of mouse lung Figure 42.24 Negative pressure breathing Figure 42.25 The avian respiratory system Tubes in the lungs are the parabronchi Figure 42.26 Automatic control of breathing Figure 42.27 Loading and unloading of respiratory gases Figure 42.28 Oxygen dissociation curves for hemoglobin Bohr Effect or Shift Hemocyanin: blood pigment in insects; Cu is the oxygen binder giving the blood a bluish tint. Hemoglobin: Heme group Figure 42.29 Carbon dioxide transport in the blood The Tissue Level Tissues O2 Capillary O2 + HHb HHbO2 CO2 CO2 + H2O HbO2- + H+ H2CO3 H+ + HCO3- Plasma At The Lungs Lungs O2 Capillary O2 + HHb HHbO2 CO2 CO2 + H2O HbO2- + H+ H2CO3 H+ + HCO3- Plasma Figure 42.30 The Weddell seal, Leptonychotes weddell, a deep-diving mammal Unnumbered Figure (page 899) Dissociation curves for two hemoglobins Fetal Hb has a different polypeptide that increases it affinity for oxygen.