Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421
advertisement

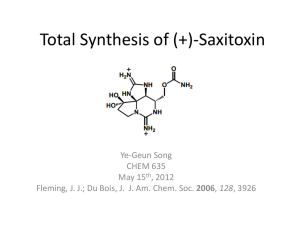
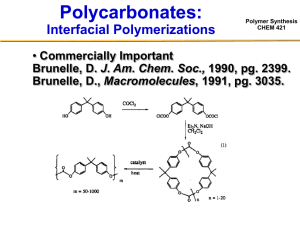
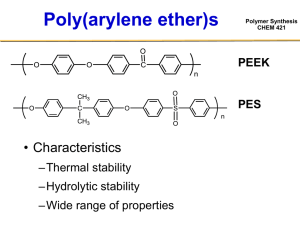
Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Reading (Odian Book): Chapter 2-1, 2-2, 2-4 Step Growth Polymerizations • Bifunctional monomers Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • AB monomers Example Polymers via Step Growth Reactions DacronTM, MylarTM Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Importance of Equal Reactivity Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B A—ba—B + A—B + A—ba—B + A—ba—B + A—ba—B + FA° = # of A groups at the beginning FA = # of A groups at any given time p = conversion = 1 – FA / FA° = 1 – (6 / 10) Xn = average degree of polymerization total # of molecules present initially Xn = ———————————————— total # of molecules present at time t A—B Importance of Equal Reactivity Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B + A—B p = 0.0 A—ba—B + A—B + A—ba—B + A—ba—B + A—ba—B + p = 0.4 A—ba—ba—ba—B A—ba—ba—ba—B A—ba—ba—ba—B + + + A—ba—B + A—ba—ba—B A—ba—ba—ba—ba—B + + Xn = 1 A—B Xn = 1.67 A—B p = 0.6 Xn = 2.5 p = 0.7 Xn = 3.33 p = 0.8 Xn = 5 A—B A—ba—ba—ba—ba—ba—B MW and Conversion Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Given that: [M] = [M]0 - [M]0 p Rewriting: [M] = [M]0 (1 – p) Rewriting: 1 (1 – p) = Knowing: [M]0 Xn = [M] Xn = 1 (1 – p) [M]0 [M] Implications of Carothers Equation • Conversion Xn – 50% 2 – 80% 5 – 90% 10 – 95% 20 – 99% 100 – 99.5% 200 Xn = Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 1 (1 – p) Weight Average and Number AveragePolymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Molar Masses Factors Involved in the Synthesis of High MW Linear Polymers via Step-Growth Reactions Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • High purity monomers • Di-functionality • Proper stoichiometry • Very high conversions • No side reactions • Accessibility of mutually reacting groups • In general: – Suitable for bulk reactions – Moderate viscosity during much of the reaction – Incredible effort ($$) goes to pushing the reaction forward in last stages Methods for Polyester Synthesis • Direct reaction • Acid halide / hydroxyl • Transesterification • Melt acidolysis Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Direct Reaction • “Le Chatelier’s Principle” Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Mechanism Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Overall Reaction Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Self-catalyzed Rp [OH] [COOH] [COOH] • Catalyzed by added acid ( [H+] = constant) Equilibrium Considerations: Closed System Keq Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 [ester] [H2O] = ———————— [RCOOH] [ROH] • Initial hydroxyl and carboxyl concentrations are [M]0 • Concentration of ester groups @ equilibrium is p [M]0 where p = extent of reaction @ equilibrium • The concentrations of hydroxyl and carboxyl groups @ equilibrium must therefore be: ( [M]0 – p [M]0) • Therefore Keq ( p [M]0)2 p2 [M]02 p2 = ———————— = ———————— = ———— ( [M]0 – p [M]0)2 [M]02 ( 1– p )2 ( 1– p )2 Equilibrium Considerations: Closed System Keq Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 [ester] [H2O] = ———————— [RCOOH] [ROH] • Solve for p yields: K½ p = ———— 1+ K½ Xn = 1 + K½ • Knowing that: Xn = 1 (1 – p) Effect of Equilibrium Constant on “p” Synthesis and Degree of Polymerization: Polymer CHEM 421 Closed System Effect of Equilibrium Constant on “p” Synthesis and Degree of Polymerization: Polymer CHEM 421 Closed System • Indicates the limitation imposed by equilibrium on the synthesis of high MW polymer – @ Xn = 100 (corresponding to Mn ≈ 10k) can be obtained in a closed system only if K is 104!!! – Can not be done in a closed system for most polymers… Polymer Polyesters Polycarbonates Transesterifications K 1 - 10 15 0.1 – 1.0 Polyamidation 102 - 103 • Therefore must drive the equilibrium Open System Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Extent to which one must drive the system in the forward reaction – can be seen by calculating the lowering of the small molecule condensate concentration that is necessary to achieve a particular MW – Knowing that [H2O] = p [M]0 Keq Xn = 1 (1 – p) ( p [M]0)2 p [H2O] p [H2O] (Xn)2 = ———————— = —————— = —————— ( [M]0 – p [M]0)2 [M]0 ( 1– p )2 [M]0 – Solve for [H2O] K [M]0 [H2O] = ————— Xn ( Xn – 1) [H2O] 1 —— Xn2 Drive the Equilibrium Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Need to remove the small molecule condensate –H2O –HCl • Small molecule condensate needs to diffuse through and eventually out of the reaction mixture –Not easy because of high viscosity –Can lead to reactions becoming diffusion controlled Effect of Water Concentration on Degree of Polymerization: Open, Driven System Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 How best to drive the Equilibrium? Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Mixing is energy and capital intensive –Wiped film reactors to increase surface area • Increase diffusivity of the condensate –Raise the temperature to lower the viscosity of the melt » Potential for side reactions –Swell the melt with solvents » Supercritical CO2