Network polymers
advertisement
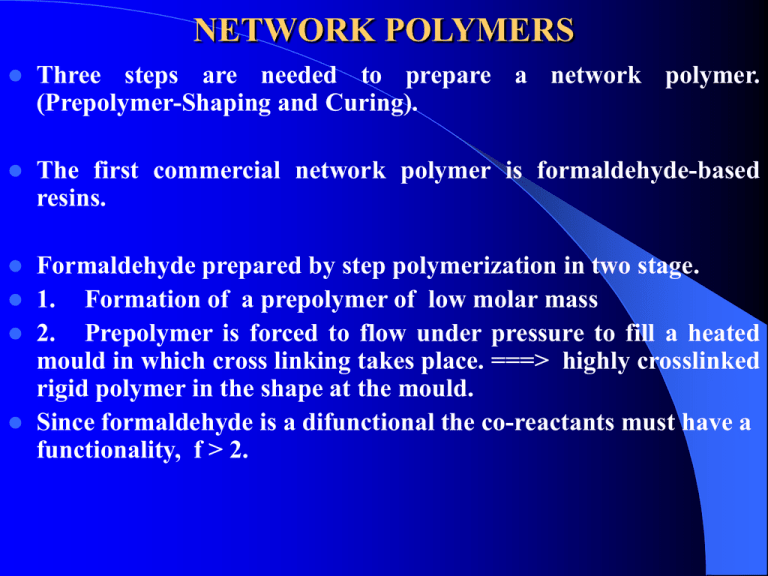
NETWORK POLYMERS Three steps are needed to prepare a network polymer. (Prepolymer-Shaping and Curing). The first commercial network polymer is formaldehyde-based resins. Formaldehyde prepared by step polymerization in two stage. 1. Formation of a prepolymer of low molar mass 2. Prepolymer is forced to flow under pressure to fill a heated mould in which cross linking takes place. ===> highly crosslinked rigid polymer in the shape at the mould. Since formaldehyde is a difunctional the co-reactants must have a functionality, f > 2. The most commonly employed are OH Phenol (f = 3) Urea (f = 4) Melamine (f NH2-C-NH2 O = 6) H2 N N NH2 C C N N C NH2 PHENOL FORMALDEHYDE RESIN The OH of the phenol activates the O & P position of the ring. OH OH + H2C-H-O CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH Further reaction leads to the formation of methylene bridge and dimethylene ether link OH CH2 OH CH2 acid OH Novolak CH2 OH + H2C-HO Phenol + formaldehyde base OH OH CH2OH HOH2C CH2OH + CH2OH Resoles CH2OH There are two types of phenol-formaldehyde resin. 1. Resoles prepared with excess formaldehyde with base catalysis. The product contain many unreacted methylol groups which upon heating react to produce the net work structure. 2. Novolaks prepared with excess phenol and acid catalysis which promotes condensation reaction of the methylol groups. The prepolymers contain no methylol groups and are unable to crosslink. Curing OH OH CH2 achieved by the addition of hardeners (curing agent). UREA AND MELAMINE FORMALDEHYDE RESIN The reaction of urea and melamine formaldehyde resin involves the formation and condensation reaction of Nmethylol groups. H2C = O + H2N-C-NH2 O CH2OH NH + HOCH2 C =O NH2 Same H2N-C-NH-CH2-OH O CH2OH N-CH2OH +H2O C =O NH2 Urea formaldehyde reaction is used to prepare the melamineformaldehyde. EPOXY RESINS They are formed from prepolymer containing the epoxide end group CH2 CH O The most important are the diglycidyl ether prepolymer. O CH3 (n+2)Cl-CH2 - CH-CH2 + (n+1) HO -C-O CH3 Epichlorohydrin bisphenol -A aqueous O CH2 - CH-CH2 [ O NaOH CH3 -CCH3 -O CH2 CH-CH2 ]n These resin are either viscous liquid or solid depending on n. Curing usually achieve by using of a multifunctional amines. CH CH CH CH 2 2 H O H O N–R–N O H CH2 CH CH OH CH2 O H OH CH – CH2 CH2 – CH N–R–N CH – CH2 OH CH2 – CH OH Epoxy resin are shrinkage on curing, electrical insulators, matrix materials composites. characterized as low and used as adhesives, surface coatings and for fiber reinforced POLYURETHANE NETWORKS Uses Elastomers, flexible foams and rigid foams) Preparation By the reaction of diisocyanates with branched polyester or Polyethers which have hydroxyl end groups. O = C = N - CH2 -N=C =O CH3 CH2 [ O-CH2 - CH]n OH CH2 [ O-CH2 - CH]n OH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 [ O - CH2 - CH]n OH CH3 Cross linking density and molar mass control the flexibility of the network formed. Thank You See You Next Lecture