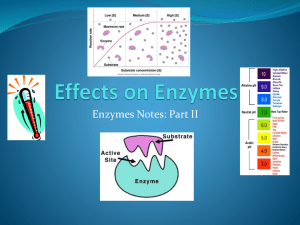
substrates
advertisement

First Five Explain the meaning of the following terms: enzyme substrate product active site denatured What are Enzymes? Globular proteins that act as biological catalysts to increase reactions rates Catalysts: substances that speed up reactions w/o being consumed Biological? Because they are proteins; NOT because they are alive (they aren’t!) Enzymes: How they work speed up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy of reactions that would normally happen anyway. Mode of Action Enzymes bind substrates (enzyme reactant) into active sites (pocket or groove on enzyme). While the enzyme and the substrate are joined, the enzyme catalyzes the reaction and converts the substrate to the product(s). Enzymes A classic example of an enzymatic reaction is the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose. Enzymes Another look… Practice Find the enzyme, substrate(s), and product(s) in the sentences. I) Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine into acetyl and choline. Enzyme: ________________________ Substrates: ______________________ Products: _______________________ II) A disaccharide can be broken down into glucose and fructose by lysozyme Enzyme: ________________________ Substrates: ______________________ Products: _______________________ Practice Find the enzyme, substrate(s), and product(s) in the sentences. I) Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine into acetyl and choline. Enzyme: Acetylcholinesterase Substrates: acetylcholine Products: acetyl & choline II) A disaccharide can be broken down into glucose and fructose by lysozyme Enzyme: lysozyme Substrates: sucrose Products: glucose & fructose Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity: Rate of Reaction vs Enzyme Concentration Describe the activity of the enzyme as Enzyme activity increases as concentration of the enzyme concentration enzyme Eventually increases.enzyme increases. activity plateaus even though enzyme concentration continues to increase. Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity: Rate of Reaction vs. Temperature Describe the activity of the enzyme as temperature increases. Increasing heat energy causes more collisions between enzyme and substrate, until an optimal temperature is reached. Above the optimal temperature, the enzyme denatures so the rate falls rapidly. Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity: Rate of Reaction vs. pH Describe the activity of the enzyme as pH increases. Activity gradually increases up to the optimal pH and gradually decreases after the optimal pH. Effects on Enzyme Activity Rate of Enzyme Activity is influenced by: ◦ Substrate concentration ◦ more substrate = more activity until saturation ◦ Amount of enzyme ◦ more enzyme = more activity until saturation ◦ Temperature ◦ higher temperature = more activity until the enzyme’s protein denatures ◦ pH ◦ usually in range of 6-8 for enzymes in humans ◦ Inhibitors ◦ reduce activity by binding or changing shape of active sites Two types of inhibitors Competitive Inhibitor When something besides the substrate blocks the active site Noncompetitive Inhibitor When a molecule binds to another spot on the enzyme causing it to change shape and become inactive Enzyme Simulation Rules: Only do your action upon your substrate. The starting substrate and ending product must match the picture on your enzyme’s instructions. If you can’t operate upon a particular substrate, move it on to another person or another table. Enzyme E is the last step in the process. Although the description only shows two of the monomers stuck on the pencil, it will continue adding more and more until it is full.