Neutralization - HomeConnection
advertisement
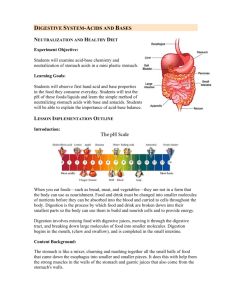
Chemistry Mr. Ross If acids and bases are mixed together in the proper amounts, they neutralize each other to produce water and a new compound, called salt. Acid Ex: + Base Water + Salt HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl titration= a base is added one drop at a time until the acid is neutralized. A color change in the indicator indicates when neutralization has occurred. The more drops required to neutralize the acid the strong the original acid An ion is an atom that loses or gains an electron so the number does not equal the number of protons An acid has a high concentration of positive hydrogen ions A base has a high concentration of negative hydroxide ions How do you think titration can be accomplished? What is the difference between titration and neutralization? • Your stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, the pH of your stomach varies, from 1-2 up to 4-5. When you eat, the stomach releases proteases and hydrochloric acid to aid in digestion. After the meal has been digested, your stomach pH returns to a resting level of about 4 or 5. Your stomach secretes acid in response highprotein meal, your stomach pH may drop to as low as 1 to food, so first thing in the morning you can expect a slightly acidic stomach pH, but not an acidic level representative of pure hydrochloric acid. Antacids are medicines that help correct the pH balance in your stomach. Your stomach has its own natural acids and sometimes these acids become too much for your stomach to handle. This is caused when you don’t eat on time and you have an empty stomach. What the antacid does is to neutralize this affect. They buffer the stomach’s gastric acid since they are basic in nature. Human blood normally has a pH of 7.35 and this pH is maintained even when small amounts of acid or base are added. A solution that resists changes in pH when an acid or base is added is called a buffer. Aspirin often contains a buffer. The point at which there are stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base. [H+] = [OH-] Buret Valve Acid with Phenolpthalein End-Point Indicators are chosen, such that they change colors at the range of the pH of interest. The solution itself at the end-point may be: • Basic, if the reaction involves a strong base and a weak acid. • Neutral, if the reaction involves a strong acid and a strong base. • Acidic, if the reaction involves a strong acid and a weak base.