Powerpoint
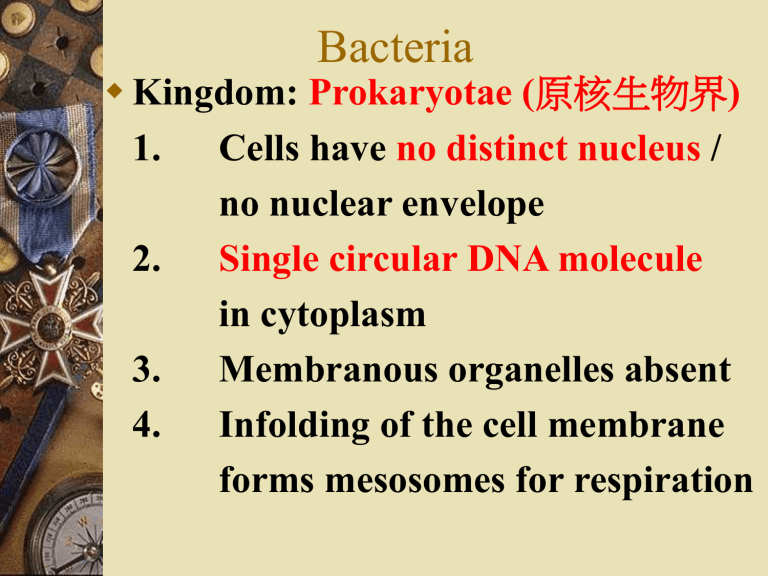
Bacteria
Kingdom: Prokaryotae ( 原核生物界 )
1.
Cells have no distinct nucleus / no nuclear envelope
2.
Single circular DNA molecule in cytoplasm
3.
Membranous organelles absent
4.
Infolding of the cell membrane forms mesosomes for respiration
Basic structure of bacteria
Binary fission
Mode of nutrition
Photosynthetic – cyanobacteria
Chemosynthetic – nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Saprophytic – putrefying bacteria
Parasitic – pathogenic bacteria
Oxygen demand
Aerobes – bacteria require oxygen for respiration
Anaerobic – bacteria unable to tolerate oxygen
Facultative anaerobes – can grow with or without
Gram stain reaction oxygen)
Bacteria can be categorized based on the cell wall
structures which in turn influences the Gram stain
reaction.
Gram –ve : appears pink after staining
Gram +ve : appears purple after staining
Bacterial diseases
1.Anthrax
炭疽病
2.Tuberculosis (TB) 肺結核 / 肺癆
3.Cholera 霍亂
4.Diphtheria 白喉
5.Syphilis 梅毒 (STD)
6. Gonorrhea 淋病 (STD)
7. Leprosy 痲瘋
8.Plague 瘟疫 / 黑死病 / 鼠疫
9.Tetanus 破傷風
10.Typhoid 傷寒
11.Typhus 斑疹傷寒
Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- - in gastrointestinal (GI) tract and colon
S synthesis of vitamin K
In immunosuppressed host, even nonpathogenic strains can cause infection
Diarrhoea
Anthrax 炭疽病 – caused by spore-forming
Bacillus anthracis
- occur in humans when they are exposed to infected animals or to tissue from infected animals or when anthrax spores are used as a bioterrorist weapon.
- will not transmit from person to person
- the spores can be used as a bioterroist weapon,
as was the case in 2001, when the spores had been intentionally distributed through the postal system, causing 22 cases of anthrax, including 5 deaths
Bacillus anthracis ,
Gram stain
Anthrax skin lesion
Tuberculosis (TB) 肺結核 / 肺癆 - caused by rod-shaped Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuberculosis creates cavities visible in x-rays like this one in the patient's right upper lobe.
- chronic or acute bacterial infection that primarily attacks the lungs
- transmitted by inhaling bacteria-carrying droplets drug resistant strains developed
Tetanus
破傷風
- caused by bacillus Clostridium tetani,
- bacteria on rusty nails
- release exotoxin
- serious infections disease to the nervous system
- lockjaw, stiffness of abdominal and back muscles , facial muscle spasms, fast pulse, slight fever, severe sweating ,headache
Fungi
真菌界
- eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that have rigid cellulose- or chitin-based cell walls
- unicellular e.g. yeast or multicellular
- saprophytic fungi – decomposer parasitic fungi – pathogenic
- may be opportunistic
Yeast invade internal tissues :
Fungi that are external parasites of humans:
Ringworm, athlete’s foot
Ringworm
Athlete’s foot
Protozoa 原生動物
Kingdom – protoctista 原生生物界
M alaria 瘧疾 - by Plasmodium
- transmitted by bite of female mosquitoes
Trypanosomiasis 昏睡病 by Trypanosoma
Life cycle of Plasmodium
Other pathogens
(not microorganisms)
Parasitic worms
Wuchereria bancrofti
絲蟲 -> Elephantiasis 象皮腫
Mad cow disease – caused by prion
Prion – protein
Transmission of infectious diseases
1. Through air or air-borne particles
2. Through contaminated food and water
3. Direct contact (including sexual)
4. Blood transfusion
5. Through body fluid
6. Though sharing infected tools
(needles)
7. Through sexual contact
8. Through vector